Tools
工欲善其事,必先利其器
推荐项目
- 学习 mlir 的项目
mlir-tutorial 使用 bazel 构建项目,相比 cmake 构建个人感觉更适合新手。
- 可以抄代码的项目
IREE 架构、风格上很有 Google 的风范。
ByteIR ,字节开源项目。
跳转工具clangd
vscode 专属。
1.首先我们需要生成 compile_commands.json,以编译 llvm 为例:
- 如果是cmake编译
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# mac上编译mlir
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -G Ninja ../llvm \
-DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS=mlir \
-DLLVM_TARGETS_TO_BUILD="host" \
-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=ON \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DLLVM_ENABLE_ASSERTIONS=ON \
-DLLVM_ENABLE_RTTI=ON \
-DLLVM_BUILD_EXAMPLES=ON
cmake --build . -- ${MAKEFLAGS}
cmake --build . --target check-mlir
生成的 compile_commands.json 在 build 目录下
- 如果是bazel编译
在BUILD文件配置一下下面的内容,再bazel run 一下就可以编译出compile_commands.json 详情自学:bazel-compile-commands-extractor
(1) 修改WORKSPACE,添加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
load("@bazel_tools//tools/build_defs/repo:http.bzl", "http_archive")
http_archive(
name = "hedron_compile_commands",
# 记得把下面两处 commit hash 换成 github 上最新的版本
url = "https://github.com/hedronvision/bazel-compile-commands-extractor/archive/ed994039a951b736091776d677f324b3903ef939.tar.gz",
strip_prefix = "bazel-compile-commands-extractor-ed994039a951b736091776d677f324b3903ef939",
)
load("@hedron_compile_commands//:workspace_setup.bzl", "hedron_compile_commands_setup")
hedron_compile_commands_setup()
(2) 在根目录下的 BUILD.bazel 中添加下面语句
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
load("@hedron_compile_commands//:refresh_compile_commands.bzl", "refresh_compile_commands")
refresh_compile_commands(
name = "refresh_compile_commands",
# 指定目标 target 及其编译选项/参数,例如 `mlir-opt` 、`config=clangd`
targets = {
"//:my_output_1": "--important_flag1 --important_flag2=true"
# "//tools:triton-opt": "--config=debug --config=clang",
},
)
(3) 运行 bazel run :refresh_compile_commands
2.然后,配置vscode的clangd插件
(1)ctrl + p 输入 clangd,先点击 下载language server;
如果 clangd 下载失败,那么手动安装:下载链接:https://github.com/clangd/clangd/releases/tag/19.1.2
scp到服务器上的挂载目录
1
scp Downloads/clangd-linux-19.1.2.zip ruantingfeng@xxx:/home/ruantingfeng/projects
在docker unzip它,然后更换 “设置->Clangd:Path” 成对应的clangd二进制 clangd -> /projects/clangd/bin/clangd。然后 reload windows
(2)然后 加 settings.json , ctrl + p 打开工作区设置json,将以下内入加入
triton 默认的位置在 python/build/cmake.linux-x86_64-cpython-3.9/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
{
"clangd.arguments": [
"--header-insertion=never",
"--compile-commands-dir=${workspaceFolder}/build/",
"--query-driver=**",
]
}
使用compile_commands.json主要是方便索引文件,特别是td生成的 inc 文件,但也可以人为从 build/tools/mlir/include/mlir/xxx/xxx 中找到编译出的 inc。
代码格式
一般使用 clang-format 工具(或者基于此的 lint.sh)。
安装
1
apt-get install clang-format
创建.clang-format
1
2
BasedOnStyle: LLVM
ColumnLimit: 80
格式化
1
2
3
4
# 单个文件
clang-format -i path/to/your/file.cpp
# 整个目录
find path/to/your/project -name '*.cpp' -o -name '*.h' | xargs clang-format -i
Adaptor
只有operands没有results的中间态,可以从adaptor中获得很多基础信息
ConversionPattern 相比 RewriterPattern 需要多传递一个 adaptor
OpAdaptor的作用:封装了op的operands
CoversionPattern 可能需要运行多遍直到 legal,过程中可能存在非法的 ir,所以推荐从 adaptor 中去取 operand 的信息。
You are supposed to lookup operands in the adaptor during a dialect conversion. 来自。
ConversionPattern和RewritePattern
1.相同点
- 都会依赖对应的
rewrite pattern driver - pattern 写好后都会分配
benefit并使用RewritePatternSet收集,然后 apply
2.不同点
- ConversionPattern
- 延时生效,往往需要多次才能legal,所以不要获取其他op的信息,可能还处于改变过程中
- adaptor, type converter, ConversionPatternRewriter
- 常配合 applyFullConversion/applyPartialConversion 使用,用于dialect2dialect的op之间变换
- RewritePattern
- 即时生效,通常需要一遍完成,所以不能用在 dialect-to-dialect 的 conversion 中
- PatternRewriter
- 一般用于优化变换,常配合 applyPatternsAndFoldGreedily 使用
- 当 pattern 可能 failed 时,千万不能修改 ir(create / earse)
- 修改ir之前,一定要确保pattern可以成功
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// OpConversionPattern
struct AbsOpToMathAbsConverter : public OpConversionPattern<mhlo::AbsOp> {
using OpConversionPattern<mhlo::AbsOp>::OpConversionPattern;
LogicalResult
matchAndRewrite(mhlo::AbsOp op, OpAdaptor adaptor,
ConversionPatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {
...
// OpRewritePattern
struct TransposeSliceLayoutPattern : public OpRewritePattern<mhlo::SliceOp> {
using OpRewritePattern<mhlo::SliceOp>::OpRewritePattern;
LogicalResult
matchAndRewrite(mhlo::SliceOp op,
OpRewritePattern &rewriter) const override {
Analysis
Analisys Manager
1
mlir/include/mlir/Pass/AnalysisManager.h
Analyses 是独立于其他设施的数据结构,可以将相关的信息 perserve 起来。
例如 Transforms/CSE.cpp 中就将一些 Analyses 信息保存给下一次分析。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// If there was no change to the IR, we mark all analyses as preserved.
if (!changed)
return markAllAnalysesPreserved();
// We currently don't remove region operations, so mark dominance as
// preserved.
markAnalysesPreserved<DominanceInfo, PostDominanceInfo>();
但使用 markAnalysesPreserved 在 pass 间传递信息的行为是不可取的,因为该功能只是为了减少编译时间,要在 pass 间传递信息最合理的方法是设计一套 Attribute 挂在 op上。
Dataflow Analysis
概念
以下相关概念引自 南大软件分析 课程。
基础概念:
- statement
statement 是 CFG(control flow grap) 中的基本程序块。可以把IR当成statement。
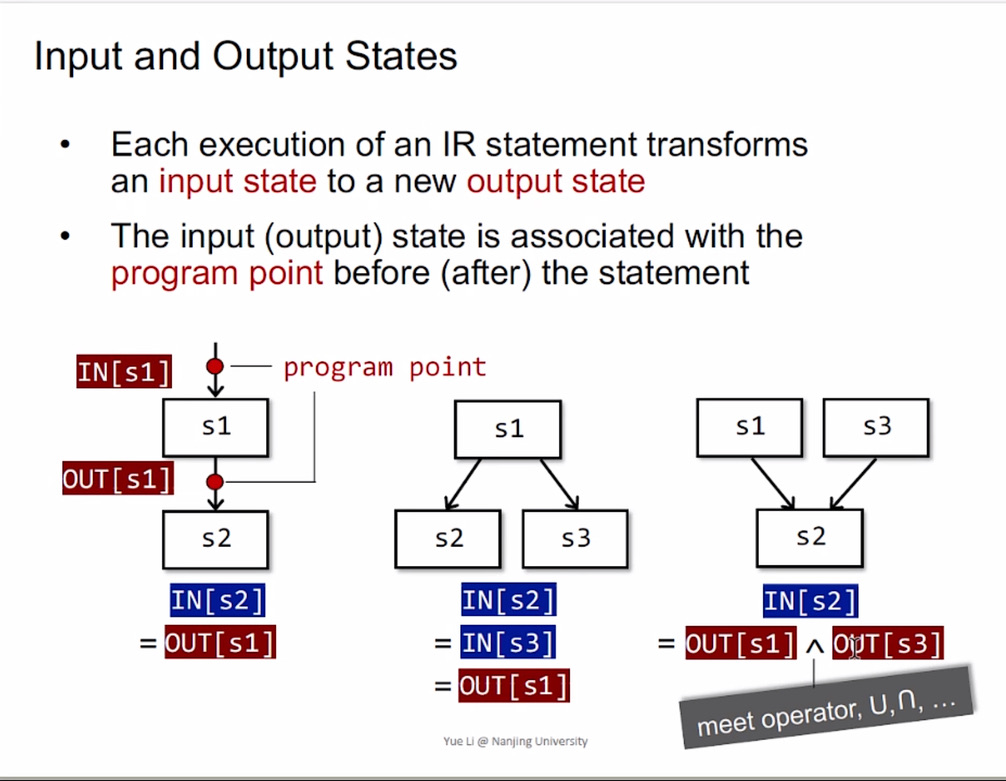
- program point
program state 是每个 statement(一般是一个ir) 前后(被观察)变量的状态。
数据流分析理论中,每个 program state 都关联了一个 program point 点,如下图,图源南大软件分析课程。
ProgramPoint 是 DataFlowAnalysis 中的基石,每次分析都是从一个 point 对象出发,visit 到更多的 point 对象。
- data flow values
静态分析完成标志:给每个program point都关联一个值(data flow values),这个值表示这个program state在那个点所有可能值的抽象
- fix point
在数据流分析中,用来描述数据数据流中信息的变化和融合的是 SemiLattice 理论。例如,在进行活跃性分析时,使用交半格可以跟踪不同数据流中变量活跃性的最小公共集合。这部分的内容可以参考南大《软件分析》课程的数据流分析。
fixedpoint 即 所有 program point 都关联一个值(data flow values),这个值表示 program state 在那个点所有可能值的抽象。
SemiLattice 是用来做两个 program point 的 data flow values 的 交汇(meet)操作(对于集合来说,就是并集/交集)。
所谓 fixedpoint iteration 算法其实是利用了 SemiLattice 的特性,保证迭代过程中一定存在一个上界(并集)/下界(交集),即 fixpoint。
- 设计一个 data flow analysis
三要素:Data Flow Values,Transfer Function和Control-flow Handing
(1) Data Flow Values: 定义 Lattice 中需要包含哪些 value,除了集合,也可能是一个值
(2) Transfer Function:定义如何前进,前向分析一般就是 out[s] = func(in[s])
(3) Control-flow Handing: 定义 Lattice 交汇时的行为,并集还是交集需要具体问题具体分析
也有某些地方称为五要素 “方向(D)、值(V)、转换函数(F)、初始值(I)和交运算(Λ)”,其中方向一般有 forward 和 backward。不同方向下转换一般不同。
流程举例
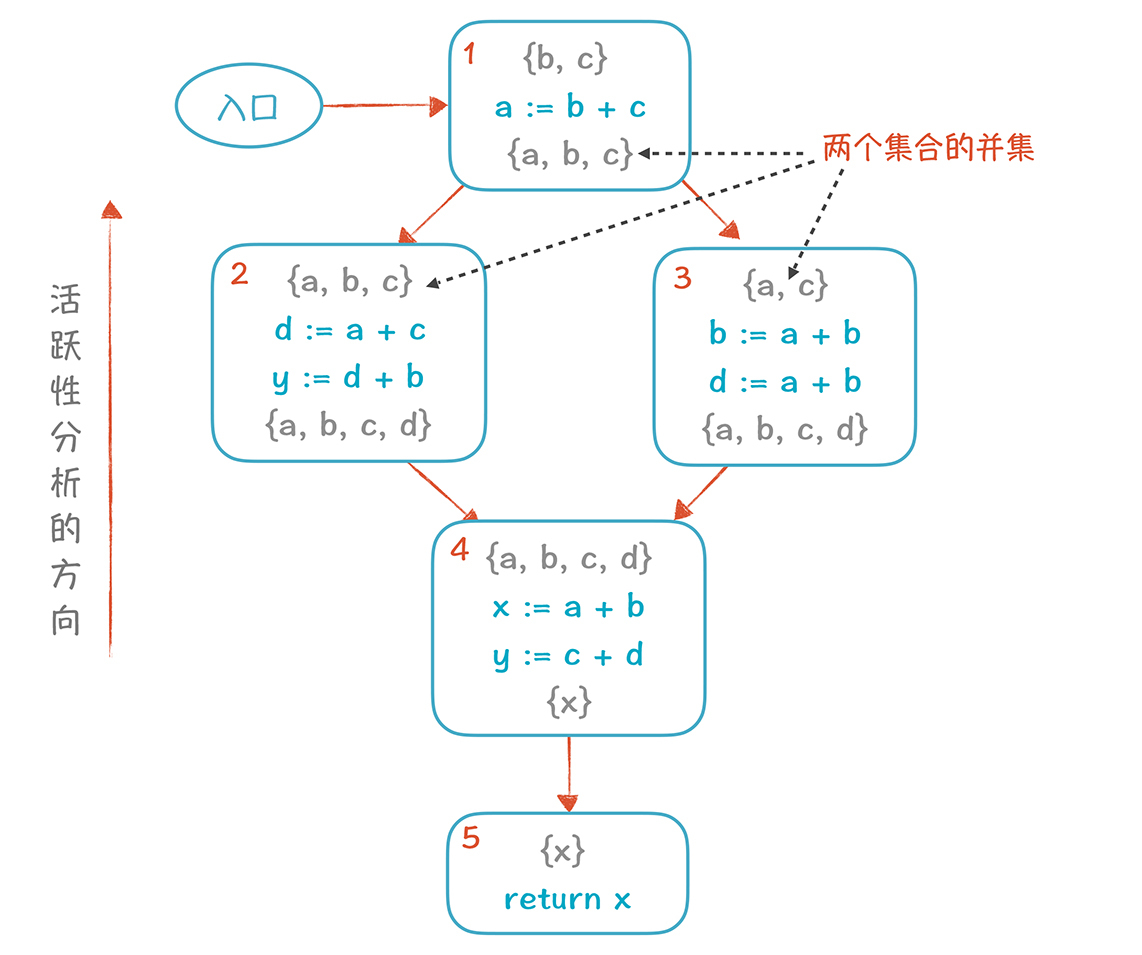
引用编译原理之美28博客中的相关内容补充说明一下相关概念。
下图是对一个CFG的 liveness 分析结果,每个块当作是一个 program point,每个 point 前后(前: 输入变量,后: 输出变量)是可以观察到的所有元素集合(data flow values)。
当分支相遇的时,需要取两个分支的并集。即图中块4的入口 program point 的 value 等于 块2、块3出口 program point 的 value 的并集。
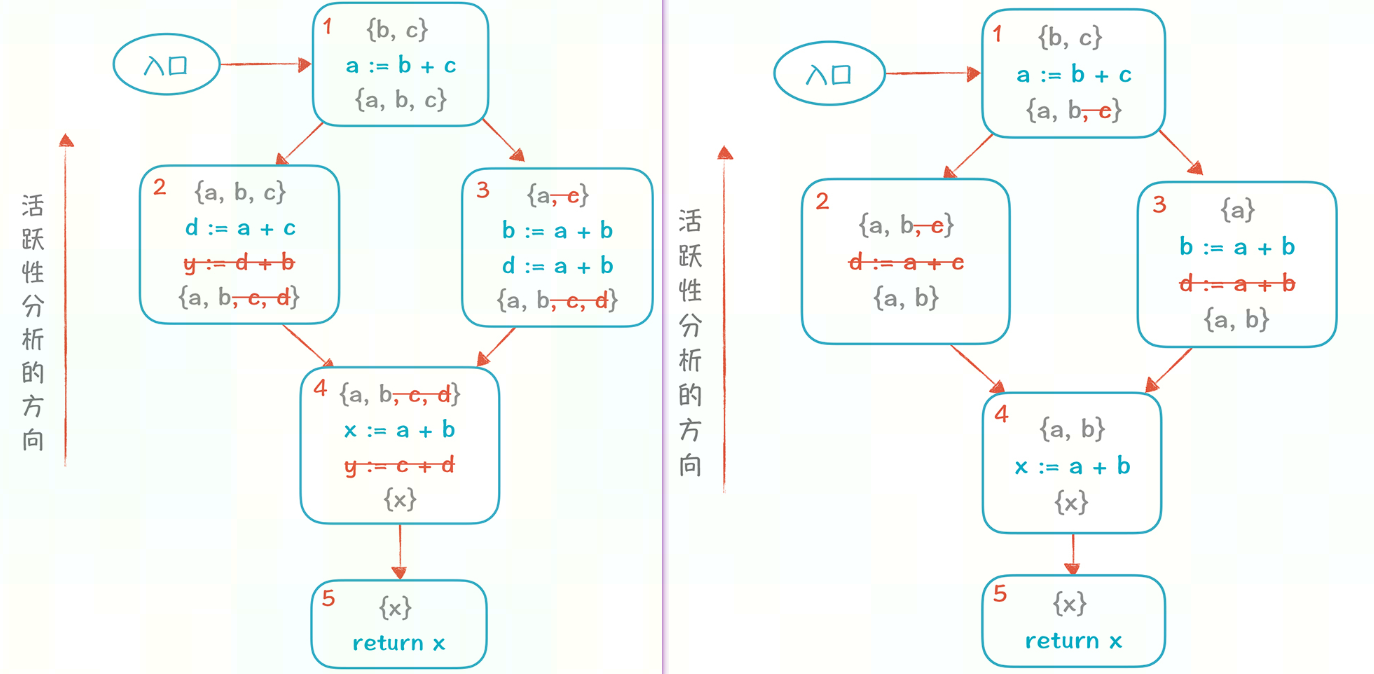
当然基于上述图,所有 data flow values 中可以删除掉和变量 y 以及相关内容
依次删除掉不活跃变量(y 和 d)后,CFG可简化为下图
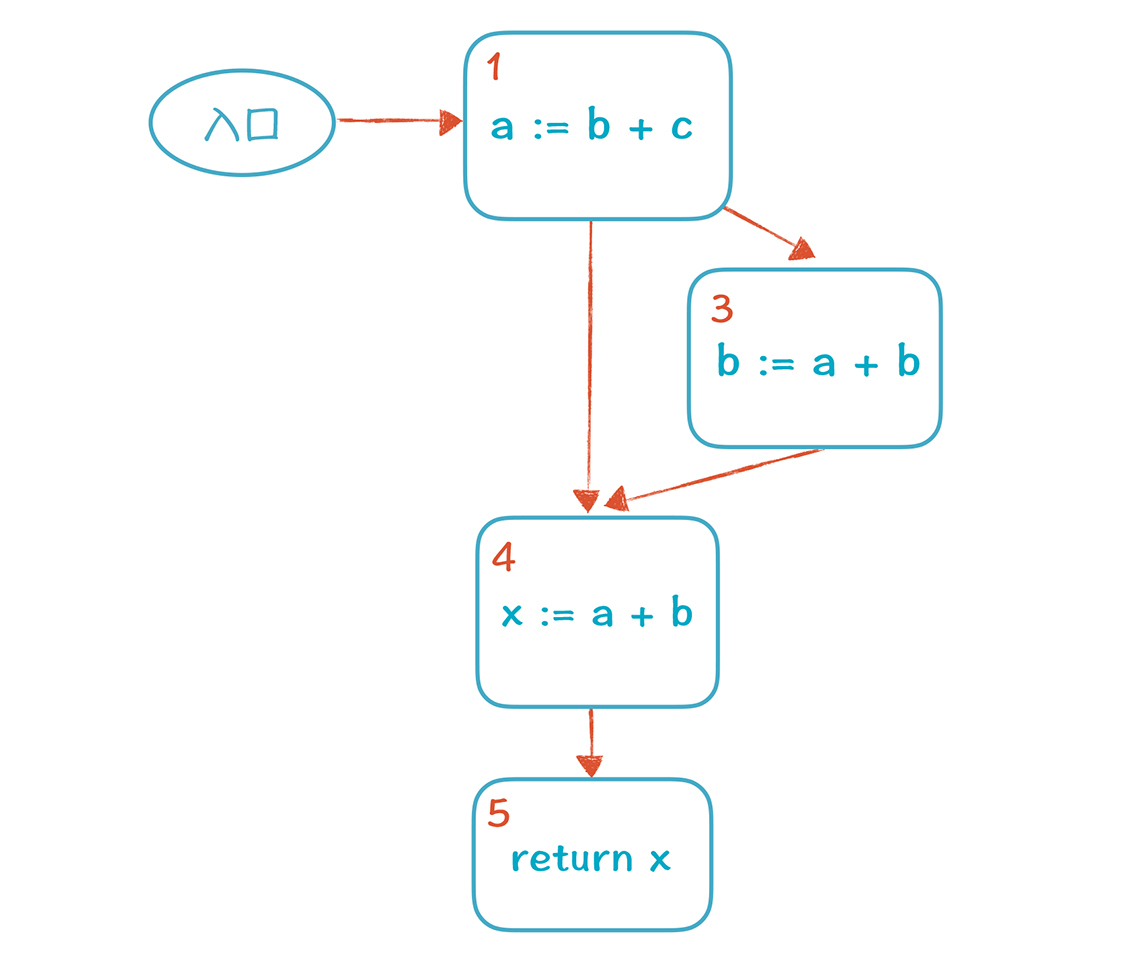
这就针对当前的 CFG 完成了 DCE(Dead Code Eliminate)。
但如果 CFG 中存在回路,例如 for 循环操作(在 MLIR 中常常表现为 RegionBranchOpInterface) 时,相关 program point 中 value 将会增加很多(对所有节点进行多次计算,直到所有value中内容稳定为止)。
Dataflow Framework
1
2
3
4
include/mlir/Analysis/DataFlowFramework.h
include/mlir/Analysis/DataFlow/
lib/Analysis/DataFlowFramework.cpp
lib/Analysis/DataFlow/
1.ChangeResult
1
2
3
4
enum class [[nodiscard]] ChangeResult {
NoChange,
Change,
};
lattice 有 join(const ValueT &rhs) 方法,会合并rhs包含的信息,返回当前lattice是否更改
[[nodiscard]]来标记函数的返回值不应该被忽略。也就是说,当调用一个被标记为[[nodiscard]]的函数时, 如果返回值没有被使用,编译器会发出警告。
2.ProgramPoint
MLIR 中的 ProgramPoint 是一个 PointerUnion,可以是 Operation *, Value, Block *
3.AnalysisState
所有程序状态的基类,附加到程序点并随着分析迭代而演变的数据流信息,例如经典的 AbstractSparseLattice。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class AnalysisState {
public:
AnalysisState(ProgramPoint point) : point(point) {}
...
protected:
virtual void onUpdate(DataFlowSolver *solver) const {}
...
ProgramPoint point;
friend class DataFlowSolver;
};
4.DataFlowSolver
实现 child data-flow analyses,使用的是 fixedpoint iteration 算法。一直维护 AnalysisState 和 ProgramPoint 信息。
多种 Analysis 是同时运行的,但结果会互相影响
数据流分析的流程:
(1) 加载并初始化 children analyses
例如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
std::unique_ptr<mlir::DataFlowSolver> createDataFlowSolver() {
auto solver = std::make_unique<mlir::DataFlowSolver>();
solver->load<mlir::dataflow::DeadCodeAnalysis>();
solver->load<mlir::dataflow::SparseConstantPropagation>();
solver->load<mlir::dataflow::IntegerRangeAnalysis>();
...
return solver;
}
(2) 配置并运行分析,直到达到设置的 fixpoint
solver根据IR来调用子分析(children analysis),直到达到 fixpoint
1
2
3
4
if (failed(solver->initializeAndRun(root))) {
LLVM_DEBUG(llvm::dbgs() << " - XXX analysis failed.\n");
return failure();
}
initializeAndRun 的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// mlir/lib/Analysis/DataFlowFramework.cpp
LogicalResult DataFlowSolver::initializeAndRun(Operation *top) {
// 加载所有当前context下的 analysis,进行初始化
for (DataFlowAnalysis &analysis : llvm::make_pointee_range(childAnalyses)) {
DATAFLOW_DEBUG(llvm::dbgs()
<< "Priming analysis: " << analysis.debugName << "\n");
if (failed(analysis.initialize(top)))
return failure();
}
// 执行 fixpoint 迭代:一直运行,直到 fixpoint
do {
while (!worklist.empty()) {
auto [point, analysis] = worklist.front();
worklist.pop();
DATAFLOW_DEBUG(llvm::dbgs() << "Invoking '" << analysis->debugName
<< "' on: " << point << "\n");
// 在 visit 过程还会不断地遇到新的符合条件的 point,需要加入 worklist,一直遍历下去,直到到达 fixpoint
if (failed(analysis->visit(point)))
return failure();
}
// Iterate until all states are in some initialized state and the worklist
// is exhausted.
} while (!worklist.empty());
return success();
}
理论上一定会到达 fixpoint,每个 analysis 都获得一个稳定的 Lattice。当 ProgramPoint 的 AnalysisState 发生变化时,这个信息会被添加到 worklist,这样不断迭代。
如果该过程的时间过慢,说明相关的 analysis 处理 ProgramPoint 的行为存在问题。
(3) 从 solver 中 query analysis state results
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// 当不存在时, lookupState 会返回 null
auto analysisState = solver->lookupState<xxLattice>(Value/Op)
// 当不存在时, getOrCreateState 会创建一个未初始化的 state
auto analysisState = solver->getOrCreateState<xxLattice>(Value/Op)
auto *maybeInferredRange =
solver.lookupState<IntegerValueRangeLattice>(val);
if (!maybeInferredRange || maybeInferredRange->getValue().isUninitialized())
return failure();
(4) 其他:重要的数据成员
using WorkItem = std::pair<ProgramPoint, DataFlowAnalysis *>, std::queueworklist solver的工作队列 - SmallVector<std::unique_ptr
> childAnalyses - DenseMap<std::pair<ProgramPoint, TypeID>, std::unique_ptr
> analysisStates,表示每个 `std::pair<ProgramPoint, TypeID>`对应一个分析状态(AnalysisState)
Liveness
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Liveness.h
mlir/bin/Analysis/Liveness.cpp
对 op -> Liveness(Operation *op)
对 block -> liveness.getLiveness(block) -> LivenessBlockInfo
LocalAliasAnalysis
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/AliasAnalysis/LocalAliasAnalysis.h
mlir/lib/Analysis/AliasAnalysis/LocalAliasAnalysis.h
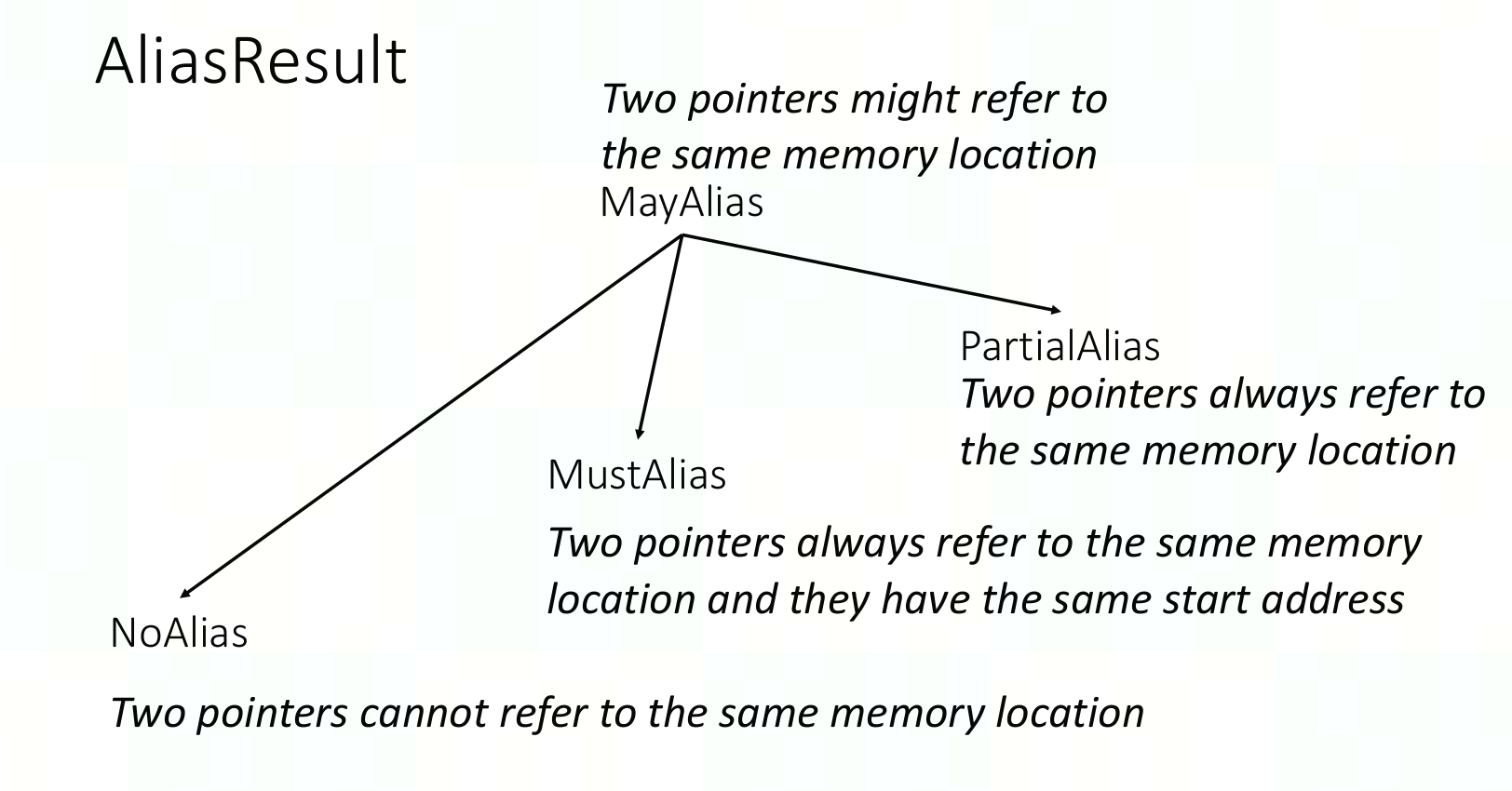
1.AliasResult: 两个location之间是否有关系
- Kind
- NoAlias
- MayAlias
- PartialAlias : 两个loc互相alias,但是部分重叠
- MustAlias
- isNO / isMay / isPartial / isMust -> bool
2.AliasResult alias(Value lhs, Value rhs);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// 确定一个op是否对一个value有读/写行为
bool isOpReadOrWriteInplace(Operation *op, Value val) {
auto memInterface = llvm::dyn_cast<MemoryEffectOpInterface>(op);
if (!memInterface)
return false;
llvm::SmallVector<MemoryEffects::EffectInstance> effects;
memInterface.getEffects(effects);
bool readOnVal = false;
bool writeOnVal = false;
LocalAliasAnalysis analysis;
for (MemoryEffects::EffectInstance effect : effects) {
if (llvm::isa<MemoryEffects::Read>(effect.getEffect()) &&
!analysis.alias(val, effect.getValue()).isNo()) {
readOnVal = true;
}
if (llvm::isa<MemoryEffects::Read>(effect.getEffect() &&
!analysis.alias(val, effetc.getValue()).isNo()) {
writeOnVal = true;
}
}
return readOnVal || writeOnVal;
}
3.collectUnderlyingAddressValues
重载了多种形式,常用的有以下输入:
(Value, SmallVectorImpl
&output) - (OpResult result, unsigned maxDepth, DenseSet
&visited, SmallVectorImpl &output) - result.getOwner() -> ViewLikeOpInterface -> 继续调用 viewOp.getViewSource()
- result.getOwner() -> RegionBranchOpInterface
- (BlockArguement arg, unsigned maxDepth, DenseSet
&visited, SmallVectorImpl &output)
SliceAnalysis
用来遍历 use-def 链的 analysis 一般可以将 use-def 理解为
- def : 写
- use : 读
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
____
\ / defs (in some topological order)
\/
op
/\
/ \ uses (in some topological order)
/____\
1.getSlice
(1)getForwardSlice : 获得root op的use链 (向ir的结尾找)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
从 0 开始追,可以获得 {9, 7, 8, 5, 1, 2, 6, 3, 4}
0
___________|___________
1 2 3 4
|_______| |______|
| | |
| 5 6
|___|_____________|
| |
7 8
|_______________|
|
9
输入, root可以是op,也可以是value
1
2
3
4
5
void getForwardSlice(Operation *op, SetVector<Operation *> *forwardSlice,
const ForwardSliceOptions &options = {});
void getForwardSlice(Value root, SetVector<Operation *> *forwardSlice,
const ForwardSliceOptions &options = {});
(2)getBackWardSlice : 获得root op的def链 (向ir的开头找)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
从 node 8 开始, 可以获得 {1, 2, 5, 3, 4, 6}
1 2 3 4
|_______| |______|
| | |
| 5 6
|___|_____________|
| |
7 8
|_______________|
|
9
输入, root可以是op,也可以是value。
如果是op,那么会追踪组成该op的其所有operand;如果是value,那么会追踪该value的产生链,使用value就可以从BlockArguement开始追。
1
2
3
4
5
void getBackwardSlice(Operation *op, SetVector<Operation *> *bac
const BackwardSliceOptions &options = {});
void getBackwardSlice(Value root, SetVector<Operation *> *backwa
const BackwardSliceOptions &options = {});
2.SliceOptions
TransitiveFilter filter : 设置遍历条件,当遍历到的节点不符合 filter 时停止(注意第一个遍历对象就是 rootOp)
bool inclusive : 返回的 sliceSetVec中 是否包含 root(op / value)
ForwardSliceOptions : using ForwardSliceOptions = SliceOptions;
BackwardSliceOptions : 相比 SliceOptions 多一个参数 ` bool omitBlockArguments`,这个参数控制是否避免遍历 blockArguement
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
BackwardSliceOptions sliceOptions;
// 不遍历 blockArg(可以理解为到blockArg这就结束)
sliceOptions.omitBlockArguments = true;
// 所有加入backwardSlice的op都需要满足以下条件
// 第一下会遍历本身
sliceOptions.filter = [rootOp](Operation *slice) -> bool {
return !llvm::isa<arith::ConstantOp, tensor::EmptyOp, memref::AllocOp,
scf::ForallOp, scf::ForOp, scf::IfOp>(slice)
&& rootOp->isProperAncestor(slice);
};
SetVector<Operation *> backwardSlice;
getBackwardSlice(targetOp, &backwardSlice, sliceOptions);
Attribute
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Attribute.h
常见类型:
- StringAttr
- UnitAttr / IntegerAttr / IndexAttr
- BoolAttr
- ArrayAttr
- DictionaryAttr
- DenseElementsAttr
1
2
auto value = constantOp.getValue().dyn_cast<DenseElementsAttr>();
if (value && value.isSplat()) // 一个 DenseElementsAttr 如果是 splat 的,那么所有值都相同
常用方法:
1.使用 OpBuilder 可以创建这类 Attr,例如
rewriter.getI64IntegerAttr 或builder.getI64IntegerAttr。
2.src: AttrTy
- get() 例如从SmallVector
变成ArrayAttr
1
2
SmallVector<Attribute, 8> mappings;
ArrayAttr tmp = ArrayAttr::get(context, mappings)
getName()
setValue()
getValue() 对于IntegertAttr会返回APInt,之后一般可以接
getSExtValue(),来将APInt转为int64_tsrc : operation*
getAttr / getAttrOfType ,一般get完之后要dyn_cast(可能cast失败,所以要判空)到对应的AttrType,例如
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
op->getAttr(getAliasAttrKey()).dyn_cast_or_null<mlir::IntegerAttr>() op->getAttrOfType<DenseI64ArrayAttr> constexpr llvm::StringLiteral getXXXAttrKey() { return llvm::StringLiteral("sadkjasd"); } auto attr = op->getAttrOfType<BoolAttr>(getXXXAttrKey()); if (attr) return attr.getValue();
hasAttr / hasAttrOfType
- setAttr(StringRef name, Attribute value)
- name可以
constexpr llvm::StringLiteral形式定义在头文件中 - funcOp→setAttr(attrName, IntegerAttr::get(intType, 1));
- 例如
1 2 3
// 为 `arith::FastMathInterface op` 设置 `fastmathAtrr` op->setAttr(op.getFastMathAttrName(), mlir::arith::FastMathFlagsAttr::get( op->getContext(), arith::FastMathFlags::fast));
- name可以
removeAttr
- func::FuncOp::setResultAttr
operation、attribute、type关系
| 专用指针 | 通用指针 | 值 |
|---|---|---|
| AddOp | Operation * | Operation |
| IntegerType | Type | TypeStorage |
| IntegerAttr | Attribute | AttributeStorage |
Block
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Block.h
Block 包含 BlockArgument(使用getArguements()获得)和 BlockOperand
BlockArgument
继承自 Value。
Block *getOwner() 返回该arg属于哪个block。
unsigned getArgNumber() 返回该arg的index。
BlockOperand
继承自IROperand。
unsigned getOperandNumber() 返回该operand的index。
使用
1.返回 Block
Operation *->getBlock()Value->getParentBlock()
2.遍历block
walk
1
block->walk([&](Operation *op) {...
只遍历同层op
1
Operation &workOp : rootBlock->getOperations()
Builder
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Builders.h
mlir/lib/IR/Builders.cpp
Builder 用于创建新的 MLIR 操作,例如各种 Type, Attr, Affine Expressions 等
OpBuilder
OpBuilder 继承自 Builder 类,额外提供了struct Listener和class InsertPoint
ImplicitLocOpBuilder继承自 OpBuilder,并不需要 Location 信息。
InsertPoint
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Listener *getListener() const { return listener; }
void clearInsertionPoint();
InsertPoint saveInsertionPoint();
// insertionPoint设在block内的iterator处
void setInsertionPoint(Block *block, Block::iterator insertPoint);
// insertionPoint设到op前面,本质上还是找到op在block内的iterator
void setInsertionPoint(Operation *op) {
setInsertPointPoint(op->getBlock(), Block::iterator(op));
}
// insertionPoint设到op后面
void setInsertionPointAfter(Operation *op) {
setInsertPointPoint(op->getBlock(), ++Block::iterator(op));
}
// insertionPoint设到value后面
void setInsertionPointAfterValue(Value val) {
if (Opeartion *op = val.getDefiningOp()) {
setInsertionPointAfter(op);
} else {
auto blockArg = llvm::cast<BlockArguement>(val);
setInsertionPointToStart(blockArg.getOwner());
}
}
// insertionPoint设到block开头
void setInsertionPointToStart(Block *block);
// insertionPoint设到block结尾
void setInsertionPointToEnd(Block *block);
create
1
2
3
4
5
6
Block *createBlock(Region *parent, Region::iterator insertPt = {},
TypeRange argTypes = std::nullopt,
ArrayRef<Location> locs = std::nullopt);
// createBlock(®ion, /*insertPt=*/{}, argTypes, argLocs);
Operation *insert(Operation *op);
Operation *create(const OperationState &state);
- OpTy create(loc, Args &&..args);
先创建 OperationState 对象,再调用 OpTy::build 方法创建 Operation 对象
- createOrFold
返回值是 Value (也可以直接作为 OpFoldResult 使用,会有一个隐式转换)
创建op后立即尝试fold,一般在创建某些有xxxOp.cpp中有opFoldPattern的op时使用,例如一些arith dialect 中的op 以及 memref.dim
参见: mlir/lib/Dialect/Complex/IR/ComplexOps.cpp
clone
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Operation *clone(Operation &op, IRMapping &mapper);
Operation *clone(Operation &op);
Operation *cloneWithoutRegions(Operation &op, IRMapping &mapper) {
return insert(op.cloneWithoutRegions(mapper));
}
Operation *cloneWithoutRegions(Operation &op) {
return insert(op.cloneWithoutRegions());
}
例:使用linalg.reduce的region创建一个linalg.map
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
// op 是 linalg.reduce
Value emptyOp = rewriter.create<tensor::EmptyOp>(
loc, initDims, dstType.getElementType());
auto mapOp = rewriter.create<linalg::MapOp>(
loc, ValueRange(op.getDpsInputs()), emptyOp,
[&](OpBuilder &b, Location loc, ValueRange args) {});
// 下面的代码等价于 rewriter.inlineRegionBefore(op->getRegion(0), mapOp->getRegion(0), mapOp->getRegion(0)->begin());
Block *opBody = op.getBody();
llvm::SmallVector<Value> bbArgs;
for(Operation *opOperand : op.getOpOperandsMatchingBBargs()) {
bbArgs.emplace_back(opBody->getArgument(
opOperand->getOperandNumber()));
}
Block *mapOpBody = mapOp.getBlock();
SmallVector<BlockArgument> mapOpBbargs;
for (OpOperand *opOperand : mapOp.getOpOperandsMatchingBBargs()) {
mapOpBbargs.emplace_back(mapOpBody->getArgument(opOperand->getOperandNumber());
}
assert(mapOpBbargs.size() == bbArgs.size());
IRMapping bvm;
for (auto [bbarg, newBBarg] : llvm::zip(bbArgs, mapOpBbargs)) {
bvm.map(bbarg, newBBarg); // 这个操作其实就是在 DenseMap<Value, Value> 中建立映射关系。
}
rewriter.setInsertionPointToStart(mapOpBody);
for (Operation &operation : *reduceOpBody) {
rewriter.clone(operation, bvm);
}
Listener
Listener用于hook到OpBuilder的操作,Listener继承自 ListenerBase,ListenerBase有两种 kind
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// Listener() : ListenerBase(ListenerBase::Kind::OpBuilderListener)
struct ListenerBase {
enum class Kind {
OpBuilderListener = 0,
RewriterBaseListener = 1
};
...
}
Listener常用两个函数为 notifyOperationInserted(Operation *Op) 和 notifyBlockCreated(Block *block)。自定义rewriter时,一般需要 override 这两个函数。
RewriterBase
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/IR/PatternMatch.h
mlir/lib/IR/PatternMatch.cpp
继承自 OpBuilder,且将 Listener 设置为 RewriterBaseListener
1
2
3
4
5
6
class RewriterBase : public OpBuilder {
public:
struct Listener : public OpBuilder::Listener {
Listener() : OpBuilder::Listener(Kind::RewriterBaseListener) {}
};
}
常用函数:
1.notify : 在正式对op修改前都需要调用notify,以便listener监听
notifyOperationModified : in-place 修改
notifyOperationReplaced : 调用 replaceOp时触发
1 2 3 4 5
if (auto *listener = dyn_cast_if_present<RewriteBase::Listener>(rewriter.getListener())) { listener->notifyOperationReplaced(op, existing); } rewriter.replaceAllUsesWith(op->getResults()) opsToErase.push_back(op);
notifyOperationErased : 调用 earseOp时触发
2.modifyOpInPlace : 会调用 startOpModification 和 finalizeOpModification
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
struct PrintOpLowering : public OpConversionPattern<toy::PrintOp> {
using OpConversionPattern<toy::PrintOp>::OpConversionPattern;
LogicalResult
matchAndRewrite(toy::PrintOp op, OpAdaptor adaptor,
ConversionPatternRewriter &rewriter) const final {
// We don't lower "toy.print" in this pass, but we need to update its
// operands.
rewriter.modifyOpInPlace(op,
[&] { op->setOperands(adaptor.getOperands()); });
return success();
}
};
3.replaceAllUsesWith
ForwardingListener
可以将所有 notify 发送给另外一个 OpBuilder::Listener,用于创建监听链条
1
2
struct ForwardingListener : public RewriterBase::Listener {
ForwardingListener(OpBuilder::Listener *listener) : listener(listener) {}
IRRewriter
继承自 RewriteBase,当 PatternRewriter 不可用时才使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
class IRRewriter : public RewriterBase {
public:
explicit IRRewriter(MLIRContext *ctx, OpBuilder::Listener *listener = nullptr)
: RewriterBase(ctx, listener) {}
explicit IRRewriter(const OpBuilder &builder) : RewriterBase(builder) {}
};
PatternMatch
PatternBenefit
一般配合 Pattern 使用,表示一个pattern的benefit,benefit越高越先apply
1
patterns.add<DoWhileLowering>(patterns.getContext(), /*benefit=*/2);
benefit的取值范围为 0到65535
Pattern
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
class Pattern {
/// This enum represents the kind of value used to select the root operations
/// that match this pattern.
enum class RootKind {
Any,
OperationName,
InterfaceID,
TraitID
};
...
有match、rewrite、matchAndRewrite这些函数,也会设置 PatternBenefit (默认为1)
RewritePattern
继承自pattern
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
virtual LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(Operation *op,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const {
if (succeeded(match(op))) {
rewrite(op, rewriter);
return success();
}
return failure();
}
一些子类:
1.OpOrInterfaceRewritePatternBase
OpRewritePattern : 使用 SourceOp::getOperationName() 来match
OpInterfaceRewritePattern : 使用 SourceOp::getInterfaceID() 来match
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
struct AddOpPat : public OpRewritePattern<AddOp> {
using OpRewritePattern<AddOp>::OpRewritePattern;
LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(AddOp op,
PatternRewriter & rewriter) const override{
static EraseDeadLinalgOp : public OpInterfaceRewritePattern<LinalgOp> {
using OpInterfaceRewritePattern<LinalgOp>::OpInterfaceRewritePattern;
LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(LinalgOp op,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override{
2.OpTraitRewritePattern
使用 TypeID::get
() 来match 例如某些elementwiseTrait :
OpTraitRewritePattern<OpTrait::Elementwise>
RewritePatternSet
1
2
3
4
5
RewritePatternSet(MLIRContext *context,
std::unique_ptr<RewritePattern> pattern)
: context(context) {
nativePatterns.emplace_back(std::move(pattern));
}
1.新建pattern
所以一般新建 RewritePatternSet 对象时都得传入 context
1
RewritePatternSet patterns(&getContext());
然后再一些函数来归类pattern
1
2
3
4
populateAffineToStdConversionPatterns(patterns);
void mlir::populateAffineToStdConversionPatterns(RewritePatternSet &patterns) {
...
}
也可以通过PDLL来写pattern(包含constrict和rewrite)
1
2
RewritePatternSet(PDLPatternModule &&pattern)
: context(pattern.getContext()), pdlPatterns(std::move(pattern)) {}
2.add : 向set中添加pattern
1
2
add(LogicalResult (*implFn)(OpType, PatternRewriter &rewriter),
PatternBenefit benefit = 1, ArrayRef<StringRef> generatedNames = {})
3.clear : 清空set中的pattern
PatternRewriter
继承自 RewriteBase, 用于重写(transform)现有 MLIR 操作的工具。它提供了一组方法,允许用户在遍历操作并修改它们时进行规则匹配和替换。在rewrite pattern中才使用
PatternRewriter &rewriterConversionPatternRewriter &rewriter: 相比pattern rewriter要多传入一个adaptor,详细见 Conversion 节
常用操作
1.设置插入点(与builder同)
- setInsertionPoint(Operantion *)
- setInsertionPointAfter
2.block
getBlock()
3.创建
- create
(…) create(OperationState)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
OperationState state(op->getLoc(), op->getName().getStringRef(), {newInput, newKernel, newInit}, {resTy}, op->getAttrs(), op->getSuccessors()); for (Region &r : op->getRegions()) { Region *newRegion = state.addRegion(); b.cloneRegionBefore(r, *newRegion, newRegion->begin()); } Operation *newOp = b.create(state);
4.替换
replaceOp(Operation *op, Operation *newOp)
replaceOp(Operation *op, ValueRange newValues())
例如getResults()作为ValueRange输入
replaceAllOpUsesWith(Operation *from, ValueRange to) / replaceAllOpUsesWith(Opeation *from, Operation *to )
replaceUsesWithIf(Value from, Value to, func_ref) / replaceUsesWithIf(ValueRange from, Value to, func_ref) / replaceUsesWithIf(Operation *op, Value to, func_ref)
1 2 3 4 5 6
// 替换forallOp外的使用 rewriter.replaceUsesWithIf(workOp->getResult(0), forallOp->getResults(idx), [&](OpOperand use) {return !forallOp->isProperAncestor(use.getOwner()) // 仅替换当前op的使用 rewriter.replaceUsesWithIf(emptyOp->getResult(), newEmptyOp->getResult(), [&](OpOperand use) { return use.getOwner() == op; });
replaceAllUsesExcept(Value from, Value to, Operation *exceptedUser) 本质是使用
replaceUsesWithIf来实现1 2
rewriter.replaceUsesWithIf(from, to, [&](OpOperand use) { return use.getOwner() != exceptedUser; });
5.消除
earseOp(Operation *op) : 如果要在pattern中删除op,最好使用
rewriter.earseOp,使用op自带的erase函数代码运行时会在debug模式出问题earseBlock(Block *block)
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
struct AddOpPat : public OpRewritePattern<AddOp> {
using OpRewritePattern<AddOp>::OpRewritePattern;
LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(AddOp op,
PatternRewriter & rewriter) const override{
xxx
return success();
}
};
class AddOpPatPass : public impl::AddOpPatPassBase<AddOpPatPass> {
explicit AddOpPatPass() = default;
void runOnOperation() override {
RewriterPatternset patterns(&getContext());
patterns.add<AddOpPat>(patterns.getContext());
if (failed(applyPatternAndFlodGreedily(getoperation(), std::move(patterns))))
return signalPassFailure();
};
}
std::unique_ptr<pass> mlir::createAddOpPatPass() {
return std::make_unique<AddOpPatPass>;
}
Bufferize
bufferization dialect
bufferization:将逻辑计算语义的tensor转为物理内存语义的buffer
- bufferize::AllocTensorOp
申请一块空间,使用给定shape创建一个bufferize allocation。常会传入一个可选的 srcOp,表示从这个srcOp拷贝出的数据,此时就传入的 ValueRange dynamicShape就应为空。
该op主要是帮助bufferization过程提供一个 handler,并且这样产生的alloc_tensor op没有不会产生 read-after-write 冲突,也不会alias其他buffer,可以再进行 in-place bufferize
- bufferization.to_tensor
将memref转为转为tensor语义下的操作
- bufferization.materialize_in_destination
相当于在tensor层面的copy
one-shot-bufferize
(copy from大佬)
1
mlir/lib/Dialect/Bufferization/IR/BufferizableOpInterface.cpp
1.OneShotBufferize pass
对于每个有 BufferizableOpInterface 的op都进行bufferize
- 声明:mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/Bufferization/Transforms/Passes.td
- 先基于tensor的SSA use-def链进行原位分析来确认哪些operand可以in-place bufferize.(尽量减少alloc和copy, 提高性能)
- destination-passing style op(继承
DestinationStyleOpInterface): 某一个operand和dst的buffer可复用,所以分配了该operand的buffer后,无需再分配dst的buffer:eg: %t0 = tensor.insert %f into %dest[%idx], buffer(%t0)和buffer(%dest)是完全一致的; - 非destination-passing style op:对每个OpOperand产生一个新的buffer allocation, eg:tensor.generate
- 所有新allocate的buffer后续都会deallocate,不然会内存泄露
- destination-passing style op(继承
- TensorCopyInsertion:对确定是out-of-place的operands插入 copies,insertTensorCopies()函数。
- 调用bufferize接口bufferize()函数来实现bufferize. bufferizeOp()函数。
- 函数签名的layout map由
function-boundary-type-conversion选项单独控制,可选的参数有3种:infer-layout-map,fully-dynamic-layout-mapandidentity-layout-map, 默认是infer-layout-map。无法精确推测时,函数参数类型为fully dynamic layout maps。 bufferize-function-boundaries是一个用来对funcOp、returnOp、callOp进行bufferize的flag- funcArg一般可以bufferize,除非有
bufferization.writable = false
- 先基于tensor的SSA use-def链进行原位分析来确认哪些operand可以in-place bufferize.(尽量减少alloc和copy, 提高性能)
- 实现:mlir/lib/Dialect/Bufferization/Transforms/Bufferize.cpp
- struct OneShotBufferizePass {void runOnOperation() override }
- Configure type converter, 先获得 unknownTypeConversionOption:
- 若是LayoutMapOption::IdentityLayoutMap, bufferization::getMemRefTypeWithStaticIdentityLayout(tensorType, memorySpace);
- 否则,只能是LayoutMapOption::FullyDynamicLayoutMap,bufferization::getMemRefTypeWithFullyDynamicLayout(tensorType,memorySpace);
- Configure op filter. 依据编译选项设置不可bufferize的op
- 依据编译选项是否激活bufferizeFunctionBoundaries确定调用哪个函数进行bufferize:
- 若激活了,runOneShotModuleBufferize(moduleOp, opt, &statistics)
- 反之,runOneShotBufferize(moduleOp, opt, &statistics)
- createCanonicalizerPass()
- createCSEPass()
- createLoopInvariantCodeMotionPass()
- Configure type converter, 先获得 unknownTypeConversionOption:
- struct OneShotBufferizePass {void runOnOperation() override }
- 示例:mlir/test/Dialect/Bufferization/Transforms/one-shot-module-bufferize-out-params.mlir, mlir/test/Dialect/Bufferization/Transforms/one-shot-module-bufferize.mlir
2.transform IR : transform.bufferization.one_shot_bufferize 有很多可选的参数
- layout{IdentityLayoutMap} { bufferize_function_boundaries = true }
- {bufferize_function_boundaries = true }
- 定义:mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/Bufferization/TransformOps/BufferizationTransformOps.td
- 实现:transform.bufferization.one_shot_bufferize的代码:
- mlir/lib/Dialect/Bufferization/TransformOps/BufferizationTransformOps.cpp: transform::OneShotBufferizeOp::apply()函数,从transform IR提供的各个参数中获得OneShotBufferizationOptions options,之后主要调用
- runOneShotModuleBufferize()
- insertTensorCopies(moduleOp, options)
- bufferizeOp() 会调用
BufferizableOpInterface::bufferize()函数来对每个op进行具体的bufferize
- runOneShotBufferize()
- insertTensorCopies(target, options)
- bufferizeOp() 会调用
BufferizableOpInterface::bufferize()函数来对每个op进行具体的bufferize
- runOneShotModuleBufferize()
- mlir/lib/Dialect/Bufferization/TransformOps/BufferizationTransformOps.cpp: transform::OneShotBufferizeOp::apply()函数,从transform IR提供的各个参数中获得OneShotBufferizationOptions options,之后主要调用
- 示例:mlir/test/Dialect/Bufferization/Transforms/transform-ops.mlir
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// 编译命令:mlir-opt --test-transform-dialect-interpreter
func.func @matmul(%A: tensor<12x9xf32>, %B: tensor<9x6xf32>, %C: tensor<12x6xf32>) -> tensor<12x6xf32> {
%D = linalg.matmul ins(%A, %B: tensor<12x9xf32>, tensor<9x6xf32>) outs(%C: tensor<12x6xf32>) -> tensor<12x6xf32>
return %D : tensor<12x6xf32>
}
// use identity layout at function boundaries.
transform.sequence failures(propagate) {
^bb0(%arg1: !pdl.operation):
transform.bufferization.one_shot_bufferize layout{IdentityLayoutMap} %arg1 {bufferize_function_boundaries = true }
}
// result is 连续的memref
func.func @matmul(%arg0: memref<12x9xf32>, %arg1: memref<9x6xf32>, %arg2: memref<12x6xf32>) -> memref<12x6xf32> {
linalg.matmul ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<12x9xf32>, memref<9x6xf32>) outs(%arg2 : memref<12x6xf32>)
return %arg2 : memref<12x6xf32>
}
// use default at function boundaries.
transform.sequence failures(propagate) {
^bb0(%arg1: !pdl.operation):
transform.bufferization.one_shot_bufferize %arg1 {bufferize_function_boundaries = true }
}
// result is 非连续的memref(所有func.func的args和返回值均是非连续的)
func.func @matmul(%arg0: memref<12x9xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>, %arg1: memref<9x6xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>, %arg2: memref<12x6xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>) -> memref<12x6xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>> {
linalg.matmul ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<12x9xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>, memref<9x6xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>) outs(%arg2 : memref<12x6xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>)
return %arg2 : memref<12x6xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>
}
Canonicalize
Canonicalize 的形式是进行 IR 的等价变换,目的是让 compiler 更方便分析(使 DAG 中的节点和连接减少),而不是为了性能考虑。 例如某些情况下 x + x 可能比 x * 2 性能更好,但 x * 2 在 DAG 中表现的 Deps 关系更加清晰简单。
有需要的 op 自己注册,需要在 td 中加上 let hasCanonicalizer = 1;, 然后在对应的 cpp 中添加相关方法,例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
namespace {
struct FoldAdjacentBitcast : public OpRewritePattern<BitcastOp> {
using OpRewritePattern<BitcastOp>::OpRewritePattern;
LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(BitcastOp op,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {
if (auto parentOp = op.getSrc().getDefiningOp<BitcastOp>()) {
// The adjacent bitcast must have only use.
if (parentOp->hasOneUse()) {
auto src = parentOp.getSrc();
RankedTensorType dstTy = op.getDest().getType();
auto newBitcast =
rewriter.createOrFold<BitcastOp>(op.getLoc(), dstTy, src);
rewriter.replaceOp(op, newBitcast);
return success();
}
}
return failure();
}
};
} // namespace
void BitcastOp::getCanonicalizationPatterns(RewritePatternSet &results,
MLIRContext *context) {
results.add<FoldAdjacentBitcast>(context);
}
在 Canonicalizer pass 执行时,会贪心(greedy apply,一般是达到最大iter次数)地调用所有 loaded dialects 中 op 的 CanonicalizationPatterns
此外,类似的还有 fold 方法,同样需要在 td 中添加 let hasFolder = 1;
1
2
3
4
5
6
OpFoldResult BitcastOp::fold(FoldAdaptor) {
if (getSrc().getType() == getDest().getType()) {
return getSrc();
}
return {};
}
fold 和 canonicalize 的区别:
- fold 方法一般只跟 op 本身相关,且是一定会带来收益
- canonicalize 方法一般需要分析 op 连接关系,且主要目标是简化后序分析,而非带来收益
- PassManager 在运行时会先尝试调用 op 的 fold 方法,而 canonicalize 方法需要显式调用 canonicalize
CRTP
CRTP (Curiously Recurring Template Pattern,奇异递归模版模式),在 MLIR 的类型定义中十分常见。
1
2
class DialectFoldInterface
: public DialectInterface::Base<DialectFoldInterface>
表现形式为:将派生类(DialectFoldInterface)传给基类(DialectInterface)
作用:为基类提供一些派生类信息,再通过基类中实现方法继承来扩展派生类本身。 这种方法区别于虚函数继承,可以避免运行时虚函数表为了动态分派而进行查找的开销,实现静态多态(零运行时开销)
推荐一个博客:C++ CRTP 简介
其他 CPP in MLIR 相关内容见:https://tfruan2000.github.io/posts/cpp-in-mlir/
Conversion
形式:将写好的pattens加入RewriterPatternSet并设置benefit,再apply
1
2
3
4
5
6
void runOnOperation() override {
RewritePatternSet patterns(&getContext());
patterns.add<xxxx>(patterns.getContext(), /*benefit*/2)
if (failed(applyPatternsAndFoldGreedily(getOperation(), std::move(patterns))));
return signalPassFailure();
}
常见的apply形式:
applyPartialConversion:如果结果是合法(以ConversionTarget参数来判断)则保留。如果有未转换的illegal操作,并不会转换失败,将混合存在。applyFullConversion:调用pattern对目标进行转换,直至IR满足ConversionTarget设置的目标合法,pattern必须成功才会产生合法的target。要求所有illegal都被转换applyPatternsAndFoldGreedily:尽可能地多次修改,pattern可以失败
前两种常用于dialect conversion,需要多传入一个ConversionTarget参数,greedilyConversion一般用于优化pass
ConversionTarget
常用定义op
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
MLIRContext &ctx = getContext();
ConversionTarget target(ctx);
target.addIllegalDialect<SparseTensorDialect>();
target.addLegalDialect
target.addDynamicallyLegalDialect
target.addLegalOp
target.addDynamicallyLegalOp
例如只对标量op进行转换的pattern
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
target.markUnknownOpDynamicallyLegal([](Operation *op) {
if (isa<math::MathDialect>(op->getDialect()) &&
llvm::isa<math::LogOp, math::ExpOp,...>(op)) {
return op->getResultTypes().front().isa<ShapedType>();
}
return true;
});
RewritePatternSet patterns(&ctx);
patterns.add<xxx>(patterns.getContext());
if(failed(applyParticalCpnversion(getOperation(), target,
std::move(patterns))))
return signalPassFailure();
ConversionPattern相比RewriterPattern一般多一个adaptor参数,用于访问op的opernads
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// 常用于op的dialect2dialect下降
struct AbsOpToMathAbsConverter : public OpConversionPattern<mhlo::AbsOp> {
using OpConversionPattern<mhlo::AbsOp>::OpConversionPattern;
LogicalResult
matchAndRewrite(mhlo::AbsOp op, OpAdaptor adaptor,
ConversionPatternRewriter &rewriter) const final {
// 常用于op的优化行为,也可以用于dialect2dialect中的op下降
struct TransposeSliceLayoutPattern : public OpRewritePattern<mhlo::SliceOp> {
using OpRewritePattern<mhlo::SliceOp>::OpRewritePattern;
LogicalResult
matchAndRewrite(mhlo::SliceOp op,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {
dialect conversion
1
mlir/lib/Transforms/Utils/DialectConversion.cpp
即dialect_a中的op对应转换到dialect_b中,例如vector dialect → gpu dialect
dialect conversion一般包含op conversion和type conversion
op conversion
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/PatternMatch.h
1.OpRewritePattern
以vector2gpu为例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// mlir/lib/Conversion/ArithToSPIRV/ArithToSPIRV.cpp
// namespace内定义许多op conversion patterns
namespace{
// final 跟在类后面,说明该类不能再被继承
// const 修饰 matchAndRewrite 方法,说明该方法不能改变类的成员变量。
struct ConstantCompositeOpPattern final
: public OpConversionPattern<arith::ConstantOp> {
using OpConversionPattern::OperationConversionPattern;
LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(arith::ConstantOp op,
opAdaptor adaptor,
ConversionPatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {
...
}
}
...
void mlir::populateArithToSPIRVPatterns(RewritePatternSet &patterns) {
patterns.add<ConstantCompositeOpPattern>(patterns.getContext());
// 可以设置pattern的/*benefit=*/
// patterns.add<ConstantCompositeOpPattern>(patterns.getContext(), /*benefit=*/2);
...
}
} // namespace
当 OpRewritePattern match 的是 template 时
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
template<class OpTy> // 有些函数要调用时要用 template
struct XXXPattern : public OpRewritePattern<OpTy> {
using OpRewritePattern<OpTy>::OpRewritePattern;
LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(OpTy op,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {
// 判断是否是想处理的op
// 1. 用isa: 此时 isa 中不能放多种,只能一个一个判断
if (!llvm::isa<xxx>(Op1) || !llvm::isa<xxx>(Op2))
return failure();
// 2. 用 std::is_same_v
if (!std::is_same_v(OpTy, Op1))
return failure();
}
};
2.OpInterfaceRewritePattern
专门匹配某种 OpInterface 的pattern。例如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
struct ViewLikeOpXXXPattern
: public OpInterfaceRewritePattern<ViewLikeOpInterface> {
ViewLikeOpXXXPattern(MLIRContext *ctx)
: OpInterfaceRewritePattern<ViewLikeOpInterface>(ctx) {}
LogicalResult mathAndRewrite(ViewLikeOpInterface viewOp,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {
...
}
}
type conversion
1
mlir/Conversion/LLVMCommon/TypeConverter.h
对type对改写一般通过 typeConverter ,常配合 ConversionTarget 使用。其一般包含三个主要函数
addConversion:定义通用的类型转换规则,当调用convertType方法时,会依次检查addConversion中注册的规则。- 当调用
getTypeConverter()->convertType(inputType)时启用
- 当调用
addTargetMaterialization:sourceType→targetType- 例如,op2 以 op1 作为 operand,当 op1 和 op2 的 resType 被转换后, op2 期望其 operandType 和 op1 给出的并不符合,所以就需要将中间类型值转换为目标类型值。
addSourceMaterialization:targetType→sourceTypeaddArgumentMaterialization
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
static Value materializeToXXXCallback(OpBuilder &builder, Type type, ValueRange values) {
if (xxx)
...
return nullptr;
}
class MyTypeConvert : public TypeConverter {
public:
MyTypeConvert() {
addConversion([](Type type)) -> Type {
if (isSomeType(type))
return ...;
return type;
});
addTargetMaterialization([](OpBuilder &builder, Type type, ValueRange values) {
if (...)
return builder.create<SomeOp>(type, values);
return nullptr;
});
addSourceMaterialization(materializeToXXXCallback);
addArgumentMaterialization(materializeToXXXCallback);
// 可以默认使用 unrealized_conversion_cast,如下
auto addUnrealizedCast = [](OpBuilder &builder, Type type, ValueRange inputs,
Location loc) {
auto cast = builder.create<UnrealizedConversionCastOp>(loc, type, inputs);
return std::optional<Value>(cast.getResult(0));
}
addSourceMaterialization(addUnrealizedCast);
addTargetMaterialization(addUnrealizedCast);
addArgumentMaterialization(addUnrealizedCast);
}
};
Dataflow
MLIR中的数据流图是由Operation和Value构成的:(use-def chain)
- Value的值要么来自于Operation的result,要么来自于BlockArgument
- 调用getDefiningOp时,BlockArgument会返回null
- 每个Operation的Operand都是到Value的指针
Operation都包含Results和Operands;Results中包含多个OpResult实例,Operands中包含多个OpOperand实例
- 修改Operand时,实际是修改OpOperand,对应value的use-chain也会被修改
Operation找Value
- getOperands() / getResults()
1
2
3
4
5
6
for (auto operand : op.getOperands()) {
if (auto *def = op.getDefiningOp()) {
} else {
// BlockArgument
}
}
- getOpOperands() 用于需要修改operand时
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
IRMapping mapping;
mapping().map(op1.getResults(), op2.getResults());
for (auto &opOperand : op3.getOpOperands()) {
// 将 op3 的参数里含有 op1 results 的替换为 op2 的 mapping
// mapping.lookupOrDefault(a): 如果mapping中存在就用结果,反之用 a
opOperand.set(mapping.lookupOrDefault(opOperand.get()));
}
value找op
getDefiningOp:可能返回null
- getUses :返回OpOperand迭代器,即使用了这个value的OpOperand集合
- OpOperand &operand : value.getUses()
- getUsers :返回Operation迭代器,即直接依赖于该value的operation集合
- user_iterator相当于对use_iterator使用getOwner()
- use.getOwner() → Operation*
dataflow framework
见 Analysis 节
DataType
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/BuiltinTypes.h
从ShapedType使用getElementType()获得
类型:
- FloatType
- getF32
- getWidth
- IndexType :target word-size integer(一般是64位)
- IntegerType
- Signless: 单纯表示64位的数据,是否当作有无符号,完全根据前后ir运算
- Signed
- UnSigned
用法
- 判断类型
- isInteger
- isInteger(unsigned width)
- isIndex
- isIntOrIndex
- isIntOrFloat
- isInteger
- 生成 get
- RankedTensorType::get(ArrafRef
shapes, elemType) 例如 RankedTenorType newType = RankedTensorType::get({srcDims[0], 1}), srcType.getElementType) - IntegerType::get(op→getContext(), 64);
- RankedTensorType::get(ArrafRef
Debug
1
2
3
4
#include "llvm/include/llvm/Support/Debug.h"
LLVM_DEBUG(llvm::dbgs() << "Original loop:\n"
<< *region->getParentOp() << "\n");
LLVM_DEBUG(llvm::dbgs() << "Checking op: " << *op << "\n");
Dianostic
1
2
3
mlir/docs/Diagnostics.md
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Diagnostics.h
mlir/lib/IR/Diagnostics.cpp
当rewrite-pattern使用op的verify(rewrite出的op是否合法)来判断pattern是否match-and-rewrite成功时,那apply-pattern时的报错就是不必要的,可以通过去除handler的办法消除掉这些不必要的报错
使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
auto *context = &getContext();
auto handlerID =
context->getDiagEngine().registerHandler([](Diagnostic &) { return; });
...
RewritePatternSet patterns(context);
patterns.add<xxx>(patterns.getContext());
(void)applyPatternsAndFoldGreedily(getOperation(), std::move(patterns));
...
context->getDiagEngine().eraseHandler(handlerID);
Dialect
新增一个dialect可以参考最近mlir中新增的polynomial dialect ,然后就是补充各种dialect2dialect的conversion了
组成
详见 MLIR Survey 一文 的第二节 dialect 和 operation 相关的介绍
DialectRegistry
The DialectRegistry maps a dialect namespace to a constructor for the matching dialect :为dialect中的op外挂新的属性
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/DialectRegistry.h
例如为linalg的op挂上新的interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
void mlir::xxx::utils::registerLinalgAggregatedOpInterfaceModel(
DialectRegistry ®istry) {
registry.addExtension(+[](MLIRContext *ctx, LinalgDialect *dialect) {
linalg::MapOp::attachInterface<MapOpInterface>(*ctx);
MatmulOp::attachInterface<
MatmulOpInterface<MatmulOp, linalg::Conv2DNhwcFhwcOp>>(*ctx);
BatchMatmulOp::attachInterface<
MatmulOpInterface<BatchMatmulOp, linalg_ext::BatchConv2DNhwcFhwcOp>>(
*ctx);
ReduceOp::attachInterface<ReduceOpInterface>(*ctx);
});
}
// 定义上例如,其中AggregatedOpInterface需要在LinalgExtInterface.td定义
template <typename SrcOpTy, typename DstOpTy>
struct MatmulOpInterface : public AggregatedOpInterface::ExternalModel<
MatmulOpInterface<SrcOpTy, DstOpTy>, SrcOpTy> {
FailureOr<SmallVector<Operation *>>
decomposeOperation(Operation *op, Operation *value,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const {
}
};
Affine
op
op定义详见 affine dialect ops
- affine.apply
- affine.max / affine.min
- affine.index
- affine.for
- affine.if
op相关的一些函数
1
mlir/lib/Dialect/Affine/IR/AffineOps.cpp
AffineMap
1
2
3
mlir/inlcude/mlir/IR/AffineMap.h
mlir/lib/IR/AffineMap.cpp
mlir/Dialect/Affine/IR/AffineOps.h
getFilteredIdentityMap创建条件过滤affinemap
1
2
3
/// getFilteredIdentityMap(3, [false, false, true]) -> affine_map<(d0, d1, d2) -> (d2)>
AffineMap getFilteredIdentityMap(MLIRContext *ctx, unsigned numDims,
llvm::function_ref<bool(AffineDimExpr)> keepDimFilter);
getPermutationMap创建一个permutation的affinemap
1
2
3
/// ArrrayRef<int64_t>
static AffineMap getPermutationMap(ArrayRef<unsigned> permutation,
MLIRContext *context);
getMultiDimMapWithTargets创建一个指定输出行为的affinemap,没有计算,只是排序。输入的numDims>=targets.size()
1
2
3
/// * getMultiDimMapWithTargets(3, [2, 1])
/// -> affine_map<(d0, d1, d2) -> (d2, d1)>
static AffineMap getMultiDimMapWithTargets(unsigned numDims, ArrayRef<unsigned> targets, MLIRContext *context);
bool isEmpty() : Returns true if this affine map is an empty map, i.e., () -> ().
bool isSingleConstant() : Returns true if this affine map is a single result constant function.
int64_t getSingleConstantResult()
bool isConstant() : Returns true if this affine map has only constant results.
SmallVector
getConstantResults() : Returns the constant results of this map. This method asserts that the map has all constant results. - unsigned getNumDims() : AffineMap的numDims属性
- unsigned getNumSymbols()
- unsigned getNumResults()
unsigned getNumInputs()
- **ArrayRef
getResults()** 返回每个result的计算affineExpr AffineExpr getResult(unsigned idx)
- getDimPosition : 返回result的pos,要求这个idx对应的result是一个 AffineDimExpr。
AffineDimExpr 意味着这个result不是计算出来的,一般是等于某个输入。
例如affine_map<(d0, d1) -> (d1, d0)>,这个 AffineMap有两个输出,对其getDimPosition(0) = 1, getDimPosition(1) = 0。这个函数一般用在 permutation 的 AffineMap 上。
1
2
3
unsigned AffineMap::getDimPosition(unsigned idx) const {
return cast<AffineDimExpr>(getResult(idx)).getPosition();
}
- getResultPosition : 返回输入input是当前AffineMap的第几个输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
std::optional<unsigned> AffineMap::getResultPosition(AffineExpr input) const {
if (!isa<AffineDimExpr>(input))
return std::nullopt;
for (unsigned i = 0, numResults = getNumResults(); i < numResults; i++) {
if (getResult(i) == input)
return i;
}
return std::nullopt;
}
- isFunctionOfDim
1
2
3
4
5
6
/// Return true if any affine expression involves AffineDimExpr `position`.
bool isFunctionOfDim(unsigned position) const {
return llvm::any_of(getResults(), [&](AffineExpr e) {
return e.isFunctionOfDim(position);
});
}
- 创建 affine.max / affine.min
makeComposedFoldedAffineMin, makeComposedFoldedAffineMax
例如下面的代码会创建一个 affine.min affine_map<(d0) -> (256, d0)>(%operand)
1
2
3
4
OpFoldResult c256 = rewriter.createOrFold<arith::ConstantIndexOp>(loc, 256);
OpFoldResult minVal = mlir::affine::makeComposedFoldedAffineMin(
rewriter, loc, AffineMap::getMultiDimIdentityMap(2, loc.getContext()),
ArrayRef({getAsOpFoldResult(operand), c256}));
MutableAffineMap
可以set一些属性,比如
void setResult(unsigned idx, AffineExpr result) { results[idx] = result; }simplify()
使用 analysis 简化affinemap,大体是折叠常量相关的计算
AffineExpr
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/IR/AffineExpr.h
mlir/lib/IR/AffineExpr.cpp
- AffineExprKind getKind() : 返回kind
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Add,
/// RHS of mul is always a constant or a symbolic expression.
Mul,
/// RHS of mod is always a constant or a symbolic expression with a positive
/// value.
Mod,
/// RHS of floordiv is always a constant or a symbolic expression.
FloorDiv,
/// RHS of ceildiv is always a constant or a symbolic expression.
CeilDiv,
/// This is a marker for the last affine binary op. The range of binary
/// op's is expected to be this element and earlier.
LAST_AFFINE_BINARY_OP = CeilDiv,
/// Constant integer.
Constant,
/// Dimensional identifier.
DimId,
/// Symbolic identifier.
SymbolId,
- AffineBinaryOpExpr 继承自 AffineExpr
- AffineExpr getLHS()
- AffineExpr getRHS()
- AffineDimExpr
- unsigned getPosition()
- AffineConstantExpr
- int64_t getValue()
例: affine_map (d1, d2) -> (d1 - d2) 这是一个 AffineBinaryOpExpr,kind是add,表达为(1 * d1, -1 * d2)。lhs和rhs都是 AffineConstantExpr,value分别是(1, -1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/// Return "true" if `candidate` is a negated expression, i.e., Mul(-1, expr).
/// If so, also return the non-negated expression via `expr`.
static bool isNegatedAffineExpr(AffineExpr candidate, AffineExpr &expr) {
auto mulExpr = dyn_cast<AffineBinaryOpExpr>(candidate);
if (!mulExpr || mulExpr.getKind() != AffineExprKind::Mul)
return false;
if (auto lhs = dyn_cast<AffineConstantExpr>(mulExpr.getLHS())) {
if (lhs.getValue() == -1) {
expr = mulExpr.getRHS();
return true;
}
}
if (auto rhs = dyn_cast<AffineConstantExpr>(mulExpr.getRHS())) {
if (rhs.getValue() == -1) {
expr = mulExpr.getLHS();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
Linalg
Linalg is designed to solve the High-level Hierarchical Optimization
Linalg IR 比较常见的 transfroms:
- Progressive Buffer Allocation
- Parametric Tiling
- Tiled Producer-Consumer Fusion with Parametric Tile-And-Fuse
- Map to Parallel and Reduction Loops and Hardware
Linalg Dialect 是很重要的一个层级,在这之前的 dialect 更多得是对计算的描述,表达原有的 ML 程序。而从 Linalg 开始,就会经过一系列变换(tile, fuse, promotion, bufferize)贴近目标硬件。
op
- linalg.generic:其实是以完美嵌套循环表示的计算
- linalg.fill
- linalg.map{ arith.op / math.op }
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
auto mapOp = rewriter.create<linalg::MapOp>(
loc, adaptor.getOperands().front(), emptyTensor,
[&](OpBuilder &b, Location loc, ValueRange args) {
Type elementType = getElementTypeOrSelf(emptyTensor);
Value operand = args.front();
Value innerResult =
elementType.isa<FloatType>()
? rewriter.create<math::AbsFOp>(loc, elementType, operand)
.getResult()
: rewriter.create<math::AbsIOp>(loc, elementType, operand)
.getResult();
b.create<linalg::YieldOp>(loc, innerResult);
});
- linalg.matmul
- linalg.batch_matmul
function
- LinalgInterface
- bool hasDynamicShape()
SmallVector
getIndexingMapsArray() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
// 判断linalgOp是ElementwiseOp auto isElementwiseLinalg = [](linalg::LinalgOp linalgOp) -> bool { if (linalgOp.getNumDpsInints() != 1) return false; return llvm::all_of(linalgOp.getIndexingMapsArray(), [](AffineMap map) { return map.isIdentity(); }) && hasOnlyScalarElementwiseOp(linalgOp->getRegion(0)); };
LinalgInterface
1
2
mlir/lib/Dialect/Linalg/IR/LinalgInterfaces.cpp
mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/Linalg/IR/LinalgInterfaces.td
- getNumLoops() -> unsigned
即返回 getIteratorTypesArray().size()
- getNumParallelLoops
返回 loops 中 parallel轴的数量,这些轴一般可以并行(用scf.forall来tile),而reduction轴都只能用scf.for来tile
- getIndexingMapsArray
返回region内的计算。generic op内部是由一堆的计算组成的,即可以看成一个AffineMap。
- getRegionOutputArgs
返回region内的outArg,配合 SliceAnalysis 的 matchReduction 可以收集 reductions op
1
2
3
4
5
SmallVector<Operation *, 4> combinerOps;
if (!matchReduction(op.getRegionOutputArgs(), 0, combinerOps) ||
combinerOps.size() != 1)
return failure();
Operation *payloadOp = combinerOps[0];
例如 linalg.reduce {addf} 将会返回 arith.addf
- payloadUsesValueFromOperand
输入是 OpOperand,返回这个 OpOperand 是否被使用,由此来获得准确 Memory-Effect。(inputOperand有user则有read,initOperand必被write,若有user则有read)
例如 https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/pull/92079/files 中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
static void getGenericEffectsImpl(
SmallVectorImpl<SideEffects::EffectInstance<MemoryEffects::Effect>>
&effects,
LinalgOp linalgOp) {
SmallVector<Value> inputOperands = linalgOp.getDpsInputs();
for (auto [index, operand] : llvm::enumerate(inputOperands)) {
if (!llvm::isa<MemRefType>(operand.getType()))
continue;
if (linalgOp.payloadUsesValueFromOperand(&linalgOp->getOpOperand(index))) {
effects.emplace_back(MemoryEffects::Read::get(), operand, /*stage=*/0,
/*effectOnFullRegion=*/true,
SideEffects::DefaultResource::get());
}
}
unsigned inputOperandSize = inputOperands.size();
for (auto [index, operand] : llvm::enumerate(linalgOp.getDpsInits())) {
if (!llvm::isa<MemRefType>(operand.getType()))
continue;
if (linalgOp.payloadUsesValueFromOperand(
&linalgOp->getOpOperand(index + inputOperandSize))) {
effects.emplace_back(MemoryEffects::Read::get(), operand, /*stage=*/0,
/*effectOnFullRegion=*/true,
SideEffects::DefaultResource::get());
}
effects.emplace_back(MemoryEffects::Write::get(), operand, /*stage=*/0,
/*effectOnFullRegion=*/true,
SideEffects::DefaultResource::get());
}
}
conversion
强烈推荐项目 triton-linalg,大佬们的力作
SCF
1
mlir/lib/Dialect/SCF/IR/SCF.cpp
op
scf.for : 循环body必须串行执行,因为每次迭代返回值会写回blockarg,所以下一次使用 blockarg的值受上次迭代的影响
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
%alloc = memref.alloc() : memref<16xi32> %1 = scf.for %arg0 = %c0_i32 to %c8_i32 step %c1_i32 iter_args(%arg1 = %alloc) -> (memref<16xi32>) { %allco_new = memref.alloc() : memref<16xi32> use %arg1 ... scf.yield %alloc_new : memref<16xi32> }scf.forall / scf.parallel :循环body的程序是可以的并发执行,没有前后依赖的 可以使用多线程的方式来执行,线程的id就是循环的迭代变量 从scf到launch这种转换是可以通过代码自动完成的,需要的额外信息就是每一个循环的轴到launch的轴的映射关系
1 2 3 4
scf.forall (%thread_id_1, %thread_id_2) in (%num_threads_1, %num_thread_2) { // ... } }创建一个新的 forall
1 2 3 4 5
auto newforallOp = rewriter.create<scf::ForallOp>( loc, forallOp.getMixedLowerBound(), forallOp.getMixedUpperBound(), forallOp.getMixedStep(), forallOp.getOutputs(), forallOp.getMapping()); rewriter.eraseBlock(newforallOp.getBody()); newforallOp.getRegion().takeBody(forallOp.getRegion());
scf.if
1
2
3
4
5
6
Block *IfOp::thenBlock() { return &getThenRegion().back(); }
YieldOp IfOp::thenYield() { return cast<YieldOp>(&thenBlock()->back()); }
auto cond = op.getCondition();
auto thenYieldArgs = op.thenYield().getOperands();
auto elseYieldArgs = op.elseYield().getOperands();
有一个 scf.if 的canonicalize pattern,叫 ConvertTrivialIfToSelect,可以尽量消除 else region
经常在 bufferize 后的 canonicalize 起效,因为bufferize 后 scf.yield 的operand更关系更明确了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
// ./build/bin/mlir-opt test_if.mlir --split-input-file --one-shot-bufferize --canonicalize
// 不能命中,因为thenRegion的yield value属于thenRegion
// %1 = arith.cmpi slt, %arg1, %c0_i32 : i32
// %2 = scf.if %1 -> (memref<2xi32>) {
// %alloc_0 = memref.alloc() {alignment = 64 : i64} : memref<2xi32>
// linalg.map { math.absi } ins(%0 : memref<2xi32, strided<[?], offset: ?>>) outs(%alloc_0 : memref<2xi32>)
// scf.yield %alloc_0 : memref<2xi32>
// } else {
// scf.yield %alloc : memref<2xi32>
// }
func.func @test_if (%arg0 : tensor<2xi32>, %arg1 : i32) -> tensor<2xi32> {
%cst = arith.constant 0 :i32
%0 = tensor.empty() : tensor<2xi32>
%1 = linalg.fill ins(%cst : i32) outs(%0 : tensor<2xi32>) -> tensor<2xi32>
%2 = arith.cmpi slt, %arg1, %cst : i32
%3 = scf.if %2 -> tensor<2xi32> {
%4 = tensor.empty() : tensor<2xi32>
%5 = linalg.map{math.absi} ins(%arg0 : tensor<2xi32>) outs(%4: tensor<2xi32>)
scf.yield %5 : tensor<2xi32>
} else {
scf.yield %1 : tensor<2xi32>
}
return %3 : tensor<2xi32>
}
// -----
// 可以命中,但不产生select,因为trueVal == falseVal
// %1 = arith.cmpi slt, %arg1, %c0_i32 : i32
// scf.if %1 {
// linalg.map { math.absi } ins(%0 : memref<2xi32, strided<[?], offset: ?>>) outs(%alloc : memref<2xi32>)
func.func @test_if (%arg0 : tensor<2xi32>, %arg1 : i32) -> tensor<2xi32> {
%cst = arith.constant 0 :i32
%0 = tensor.empty() : tensor<2xi32>
%1 = linalg.fill ins(%cst : i32) outs(%0 : tensor<2xi32>) -> tensor<2xi32>
%2 = arith.cmpi slt, %arg1, %cst : i32
%3 = scf.if %2 -> tensor<2xi32> {
%5 = linalg.map{math.absi} ins(%arg0 : tensor<2xi32>) outs(%1: tensor<2xi32>)
scf.yield %5 : tensor<2xi32>
} else {
scf.yield %1 : tensor<2xi32>
}
return %3 : tensor<2xi32>
}
// -----
// 产生select
// %1 = arith.cmpi slt, %arg1, %c0_i32 : i32
// %2 = arith.select %1, %alloc, %alloc_0 : memref<2xi32>
// scf.if %1 {
// linalg.map { math.absi } ins(%0 : memref<2xi32, strided<[?], offset: ?>>) outs(%alloc : memref<2xi32>)
func.func @test_if (%arg0 : tensor<2xi32>, %arg1 : i32) -> tensor<2xi32> {
%cst = arith.constant 0 :i32
%0 = tensor.empty() : tensor<2xi32>
%1 = linalg.fill ins(%cst : i32) outs(%0 : tensor<2xi32>) -> tensor<2xi32>
%cst1 = arith.constant 1 :i32
%6 = tensor.empty() : tensor<2xi32>
%7 = linalg.fill ins(%cst1 : i32) outs(%6 : tensor<2xi32>) -> tensor<2xi32>
%2 = arith.cmpi slt, %arg1, %cst : i32
%3 = scf.if %2 -> tensor<2xi32> {
%5 = linalg.map{math.absi} ins(%arg0 : tensor<2xi32>) outs(%1: tensor<2xi32>)
scf.yield %5 : tensor<2xi32>
} else {
scf.yield %7 : tensor<2xi32>
}
return %3 : tensor<2xi32>
}
Tensor
1
mlir/Dialect/Tensor/IR/Tensor.h
op
tensor.empty
1
2
3
4
auto srcShape = srcType.getShape();
SmallVector<int64_t> sizes(srcShape.begin(), srcShape.end())
Value input = rewriter.create<tensor::EmptyOp>(loc, sizes, srcType.getElementType());
// RankedTenorType newType = RankedTensorType::get({srcDims[0], 1}), srcType.getElementType)
tensor.extract_slice [$offsets] [$sizes] [$strides]- getSource()
- getResult()
- getType() → getResult().getType()
tensor.collapse_shape
1
2
3
SmallVector<int64_t> srcDims;
RankedTensorType collapseType = RankedTensorType::get(srcDims, srcType.getElementType());
rewriter.create<tensor::CollapseShapeOp>(loc, collapseType, collapseIn, collapseIndices);
tensor.expend_shape
应用上可以使用tensor.collapse_shape和tensor.expand_shape消除operands中dimSize=1的维(往往这些维度不会影响数据的layout),创建降维后的op时候需要为某些op set额外的属性,例如linalg.transpose的permutation、linalg.reduce和linalg.broadcast的dimensions
tensor.parallel_insert_slice
创建 scf.forall 时,如果有 output,就需要使用 tensor.parallel_insert_slice 来返回
- forallOp.getTerminator() -> 返回
scf.forall_in_parallel - forallOp.getTerminator().getYieldingOps() -> 返回
scf.forall_in_parallel内的tensor.parallel_insert_slice
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
// forallOp.getTerminator() 返回的是 scf.forall.in_parallel op
rewriter.setInsertPointToTheEnd(forallOp.getTerminator().getBody());
// 如果 forall 循环只进行一次(即 ub - lb = 1),那么返回的行为就和 scf.forall 的 inductionVar 无关
auto zero = rewriter.getIndexAttr(0);
auto one = rewriter.getIndexAttr(1);
// 记返回值为 returnVal,对应 forall 的第idx个输出
Value returnVal;
int64_t idx;
auto rankTy = llvm::dyn_cast<RankedTensorType>(returnVal.getType());
assert(rankTy && "expected returnVal has a RankedTensorType");
SmallVector<OpFoldResult> sizes;
for (const auto &shape : llvm::enumerate(rankTy.getShape())) {
if (ShapedType::isDynamic(shape.value())) {
sizes.emplace_back(rewriter.createOrFold<tensor::DimOp>(
loc, collapseRes, shape.index()));
continue;
}
sizes.emplace_back(rewriter.getIndexAttr(shape.value()));
}
SmallVector<OpFoldResult> offsets(rank, zero);
SmallVector<OpFoldResult> strides(rank, one);
rewriter.create<tensor::ParallelInsertSliceOp>(
loc,
/*source=*/resVal,
/*dest=*/forallOp.getOutputBlockArguments()[idx],
/*offsets=*/offsets,
/*sizes=*/sizes,
/*strides=*/strides);
MemRef
更详细介绍见后文
tensor章节,说明了 MLIR 中 tensor 和 memref 的关系
%a = memref.view/subview %b:a相当于是b的别名,二者具有相同的baseptr,指向同一块内存,修改b/a时,也会影响a/b。
getMixedOffsets / getMixedSizes / getMixedStrides → SmallVector
memref addr的分配:MemRef的内存分配是由MLIR运行时系统负责的,它会根据MemRef的大小和数据类型在内存中分配一段连续的内存空间,并将其地址存储在MemRef的指针中。
1
getStridesAndOffset(MemRefType t, SmallVectorImpl<int64_t> &strides, int64_t &offset);
如果使用 memref.reinterpret_cast 将 memref<axbxi64, stride<[s1, s2], offset: off>> 从 i64 转为 i32,那么输出的 memref 应为
1
memref<axbx2xi32, stride<[2 * s1, 2 * s2, 1], offset: 2 * off>>
memref 在组织上可以视为一维数组,判断其连续性时需要从最内维(innermost)开始判断。 需要满足 stride[rank - 1] == 1, 并且 stride[i + 1] * shape[i + 1] = shape[i] (0 <= i < rank)。
那如果行主序的存储模式是从最低维开始判断memref的连续性,那列主序的存储模式是从最高维开始吗?
-> 并不是的,行主序和列主序是内存中数据的组织模式,并不影响 memref 表达的形式,所以列主序也是一样从最内维开始判断的。最终硬件会负责解释这个memref。如果内存中数据排布是以行为主序的,那么列主序数据存储后在硬件中会有类似 transpose 的行为将其转为硬件组织数据的模式。
memrefType
MemRefType 主要由 layout 描述: offset, size, stride, memrefspace
- getElementType() → Type
- getShape() → ArrayRef
- getLayout() → MemRefLayoutAttrInterface
1
auto strided = dyn_cast<MemRefLayoutAttrInterface>(t.getLayout());
- getMemorySpace() → Attribute
- MemRefType::get() 提供了多种构造的方法
1
2
3
4
// 如果只有 shape 和 elemTy 两个属性,但想构造一个包含 memory space 的 memref,那么可以额外使用 Builder
MemRefType resTy =
MemRefType::get(dstType.getShape(), dstType.getElementType());
resTy = MemRefType::Builder(resTy).setMemorySpace(srcTy.getMemorySpace());
offset / stride / size
获得memrefType的offset / stride / size的方法
1.自定义dialect支持OffsetOp和StrideOp
类似:[mlir][memref] Introduce memref.offset and memref.stride ops
2.getStridesAndOffset
注意:现在变成 MemRefType.getStridesAndOffset()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// mlir/lib/IR/BuiltinTypes.cpp
LogicalResult mlir::getStridesAndOffset(MemRefType t,
SmallVectorImpl<int64_t> &strides,
int64_t &offset) {
if (auto strided = llvm::dyn_cast<StridedLayoutAttr>(t.getLayout())) {
llvm::append_range(strides, strided.getStrides());
offset = strides.getOffset();
return success();
}
AffineExpr offsetExpr;
SmallVector<AffineExpr, 4> strideExprs;
if (failed(::getStridesAndOffset(t, strideExprs, offsetExpr)))
return failure();
if (auto cst = dyn_cast<AffineConstantExpr>(offsetExpr))
offset = cst.getValue();
else
offset = cst.getValue();
for (auto e : strideExprs) {
if (auto c = dyn_cast<AffineConsantExpr>(e))
strides.push_back(c.getValue());
else
strides.push_back(c.getValue());
}
return success();
}
3.MemRefDescriptor
1
#include "mlir/Conversion/LLVMCommon/MemRefBuilder.h"
1
2
3
4
MemRefDescriptor memrefDesc(csrc);
Value offsetval = memrefDesc.offset(builder, loc);
// stride(OpBuilder &builder, Location loc, unsigned pos);
Value strideVal = memrefDesc.stride(builder, loc, 0);
4.Range
1
2
3
4
5
struct Range {
OpFoldResult offset;
OpFoldResult size;
OpFoldResult stride;
};
Range数据结构一般使用以下方法获得
1
2
auto tileInfo = cast<TilingInterface>(op);
SmallVector<Range> domain = op.getInterationDomain(rewriter);
由于是 OpFoldResult 类型,访问时使用getValueOrCreateConstantIndexOp方法
取size的时候也经常先dyn_cast为Attribute
1
2
3
if (inAttr = range.size.dyn_cast<Attribute>()) {
tileSize =inAttr.cast<IntegerAttr>().getInt();
}
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
// mlir/lib/Dialect/SCF/Transforms/TileUsingInterface.cpp
FailureOr<SmallVector<scf::ForOp>>
mlir::scf::lowerToLoopsUsingSCFForOp(RewriterBase &rewriter,
TilingInterface op) {
if (op->getNumResults() > 0) {
return rewriter.notifyMatchFailure(
op, "unable to lower to loops operations with return values");
}
SmallVector<Range> domain = op.getIterationDomain(rewriter);
SmallVector<Value> ivs;
SmallVector<scf::ForOp> loops;
Location loc = op.getLoc();
for (auto loopRange : domain) {
Value offsetVal =
getValueOrCreateConstantIndexOp(rewriter, loc, loopRange.offset);
Value sizeVal =
getValueOrCreateConstantIndexOp(rewriter, loc, loopRange.size);
Value strideVal =
getValueOrCreateConstantIndexOp(rewriter, loc, loopRange.stride);
auto loop = rewriter.create<scf::ForOp>(op.getLoc(), offsetVal, sizeVal,
strideVal, ValueRange{});
loops.push_back(loop);
ivs.push_back(loop.getInductionVar());
rewriter.setInsertionPoint(loop.getBody()->getTerminator());
}
if (failed(op.generateScalarImplementation(rewriter, op.getLoc(), ivs))) {
return failure();
}
return loops;
}
Diagnostic
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Diagnostics.h
Dominance
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Dominance.h
mlir/lib/IR/Dominance.cpp
DominanceInfo
class DominanceInfo : public detail::DominanceInfoBase</*IsPostDom=*/false>
返回一个 region-like 的 dominance
常见函数
下面的 T 可以是 Operation * 或 Value *
1.bool dominates(T *a, Operation *b): 判断a是否支配b
如果a是Operation,则返回
a == b || properlyDominates(a, b)如果a是Value,则返回
(Operation *)a.getDefiningOp() == b || properlyDominates(a, b)
2.Bool properlyDominates(T *a, Operation *b)
如果a是Operation,则直接调用 properlyDominatesImpl
- 如果a是Value(BlockArguement / OpResult)
- a是BlockArgument,则
dominates(blockArg.getOwner(), b->getBlock()); - 反之
properlyDominates((Operation *)a.getDefiningOp(), b)
- a是BlockArgument,则
- properlyDominatesImpl(Operation *a, Operation *b, bool enclosingOpOk)
- 当 a 和 b 位于不同区域且 a 包含 b,此时 a 并不会被视为支配 b(enclosingOpOk = false)
- 其实当 block 相同时,是检查 “在 block 中 a 的位置在 b 之前” (
a->isBeforeInBlock(b))是否成立
例如下面的例子中:
- properlyDominatesImpl(opA, opB, true) = true
- properlyDominatesImpl(opA, opB, false) = false
- properlyDominatesImpl(opA, opC, true) = true
- properlyDominatesImpl(opA, opC, false) = true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
region0 {
^bb0 {
opA
(opA)region1 {
^bb1 {
opB
}
}
opC
}
}
这个 dominance 方法注意和 isProperAncestor 区别开,前者要求判断前后次序,后者是判断是否在子region中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
bool Operation::isProperAncestor(Operation *other) {
while ((other = other->getParentOp()))
if (this == other)
return true;
return false;
}
当寻找一个 op 是否在一个 region 内部时,可以使用 Operation *Region::findAncestorOpInRegion
3.bool hasSSADominance(Block *block) -> hasSSADominance(block->getParent())
4.bool hasSSADominance(Region *region)
判断region中的ops是否都满足SSA支配关系
如果region中不满足,则无法分析出dominanceInfo,遍历order需要修改
5.DominanceInfoNode *getRootNode(Region *region)
- 获得给定region的root dominance node,输入的region必须有多block
DominanceInfoNode
支配树节点 llvm::DomTreeNodeBase<Block>
有一个 SmallVector<DomTreeNodeBase *, 4> Children;
begin() / end() 都是以 Children 为对象。下面的代码是CSE pass遇见多block的region的遍历行为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// currentNode->node 就是 DominanceInfoNode,即 llvm::DomTreeNodeBase<Block>
while (!stack.empty()) {
auto ¤tNode = stack.back();
// 检查当前node是否被处理
if (!currentNode->processed) {
// 处理该节点
currentNode->processed = true;
// getBlock() 会返回当前Block
simplifyBlock(knownValues, currentNode->node->getBlock(),
hasSSADominance);
}
// 遍历该node的子节点
if (currentNode->node->begin() != currentNode->node->end()) {
auto *childNode = *(currentNode->childIterator++);
stack.emplace_back(
std::make_unique<CFGStackNode>(knownValues, childNode));
} else {
// 如果当前节点和其子节点都被处理了,移除它
stack.pop_back();
}
}
Func
所有dialect的funcOp都继承了 FunctionOpInterface , 该interface提供许多方法来获得func的信息
- Type getFunctionType()
- Region &getFunctionBody()
- BlockArgListType getArguments()
- bool isDeclaration() 如果为 true 则表示该func只是一个声明,而没有具体的实现
IRMapping
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/IRMapping.h
用法:
1.构造(建立映射关系)
- map(Value from, Value to)
- 在使用 old region 创建新的 region 常用,尤其是 region 上存在 bbarg 且 数量该变了,需要重新建立 bbarg 和 region 内部计算的映射关系
bv.map(oldArg, newArg),注意oldArg和newArg之间是否存在计算变换关系- 然后 builder.clone(op, bvm) for op in region 即可
- map(Block *from, Block *to)
- map(Operation *from, Operation *to)
2.lookupOrValue(from, value);
mapping.lookupOrValue(from, value): mapping中找到就用from,找不到就用value
- lookupOrDefault <=> lookupOrValue(from, from);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
IRMapping mapping;
mapping().map(op1.getResults(), op2.getResults());
for (auto &opOperand : op3.getOpOperands()) {
// 将 op3 的参数里含有 op1 results 的替换为 op2 的
// lookupOrDefault 指找不到 mapping 就用原来的
opOperand.set(mapping.lookupOrDefault(opOperand.get()));
}
- lookupOrNull <=> lookupOrValue(from, nullptr);
Interface
Op 相关的 Interface (例如 DestinationStyleOpInterface)其实就是一个 Op 的封装。
AttrInterface
- ElementsAttrInterface
- DenseIntOrFPElements
- DenseIntElementsAttr:
mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr::get(\*ShapedType*\ shaped, \APInt\ val);
- DenseIntElementsAttr:
- DenseStringElements
- DenseResourceElements
- SparseElements
- DenseIntOrFPElements
- MemRefLayoutAttrInterface
- TypeAttrInterface
DialectInlinerInterface
(像 inliner 和 canonicalize 这样的函数,每个dialect都需要支持上, inline 有统一的实现可以继承,而 canonicalize 需要编写相关的fold函数即可)
为自定义的Dialect继承该interface以实现inliner的操作,然后在额外重载一点函数就行,例如 isLegalToInline
1
2
3
// mlir/lib/Dialect/SCF/IR/SCF.cpp
struct SCFInlinerInterface : public DialectInlinerInterface {
using DialectInlinerInterface::DialectInlinerInterface;
在调inline这个pass时,遍历每个op的时候会使用 getInterfaceFor函数获得该op所属dialect重载的inline相关interface和函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
bool InlinerInterface::isLegalToInline(Operation *op, Region *dest,
bool wouldBeCloned,
IRMapping &valueMapping) const {
if (auto *handler = getInterfaceFor(op))
return handler->isLegalToInline(op, dest, wouldBeCloned, valueMapping); // 跳转到对应 dialect 中去
return false;
}
每个 dialect 继承 DialectInlinerInterface 后,根据需求重写 部分虚函数 (如isLegalToInline)
1
2
3
4
5
6
struct SCFInlinerInterface : public DialectInlinerInterface {
using DialectInlinerInterface::DialectInlinerInterface;
bool isLegalToInline(Region *dest, Region *src, bool wouldBeCloned,
IRMapping &valueMapping) const final {
bool isLegalToInline(Operation *, Region *, bool, IRMapping &) const final {
void handleTerminator(Operation *op, ValueRange valuesToRepl) const final {
DestinationStyleOpInterface
linalOp都包含该interface
1
2
OpOperandVector getDpsInputOperands()
OpOperandVector getDpsInitOperands()
其中每个元素为 OpOperand * ,使用opOperand->get()即可得到alue
相关函数:
1.hasPureTensorSemantics
所有operand都不为memref,至少有一个为tensor
2.hasPureBufferSemantics
3.isScalar
!llvm::isa<BaseMemRefType, TensorType>(opOperand->get().getType());
TilingInterface
对于有该interface的op可以cast成该interface llvm::cast<TilingInterface>(op)。要求被tile的op都要实现该interface。
自定义的Dialect以及op并新增TilingTnterface可以参考Triton-Linalg中的LinalgExtOpTilingInterface
1.TilingResult类
1
2
3
4
struct TilingResult {
SmallVector<Operation *> tiledOps;
SmallVector<Value> tiledValues; // 作为被tiled value的result
}
2.getLoopIteratorTypes:每个元素为utils::IteratorType,表示为utils::IteratorType::parallel或utils::IteratorType::reduction
3.getIterationDomain:每个元素是一个Range
1
2
3
if (auto intAttr = range.size.dyn_cast<Attribute>()) {
tileSize = std::min(setTileSize, intAttr.cast<IntegerAttr>().getInt());
}
MemoryEffectOpInterface
- getEffects
- hasEffect
- hasNoEffect
EffectInstance
EffectInstance 是描写 MemoryEffects 行为的对象,有四种
- Allocate
- Free : 对alloc resource的free行为
- Read
- Write
例如判断某个op是否有read/write effect
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
static bool hasReadOrWriteEffect(Operation *op) {
WalkResult ret = op->walk([&](Operation *innerOp) ->WalkResult {
if (auto interface = dyn_cast<MemoryEffectOpInterface>(innerOp)) {
if (interface.hasEffect<MemoryEffects::Read>() ||
interface.hasEffect<MemoryEffects::Write>())
return WalkResult::interrupt();
}
return WalkResult::advance();
});
return ret.wasInterrupted();
}
MemoryEffects::EffectInstance 的常用方法
- Value getValue(): 返回这个effect是apply到哪个value,当不知道是apply到谁时就返回 nullptr
1
2
copy A -> B
copy op 有 read 和 write,其中 read 的 apply value 是A(读A), write 的 apply value 是B(写B)
EffectT *getEffect() 返回四种类型
int getStage() : 返回这个 effect的发生阶段,值越小说明其发生更早。例如
copy A -> B中 read 比 write 早,那么Readeffect 的 stage 就比Writeeffect的 stage 小bool getEffectOnFullRegion() : 返回该 side effect 是否作用于region内的每个value,一般是带 region 内有计算的op,比如 linalg.generic / linalg.map / linalg.reduce
常用方法
isPure(Operation *op)
op.getEffect()
一般传入一个 SmallVector<SideEffects::EffectInstance<MemoryEffects::Effect>, 4>
1
2
3
void mlir::MemoryEffectOpInterface::getEffects(::llvm::SmallVectorImpl<::mlir::SideEffects::EffectInstance<::mlir::MemoryEffects::Effect>> & effects) {
return getImpl()->getEffects(getImpl(), getOperation(), effects);
}
当然,更直接的是判断 Operation * 能否转为 MemoryEffectOpInterface,一般在 op 的 td 中标识该op是否可以有该interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
class LinalgStructuredBase_Op<string mnemonic, list<Trait> props>
: Op<Linalg_Dialect, mnemonic, !listconcat([
SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<"YieldOp">,
DeclareOpInterfaceMethods<MemoryEffectsOpInterface>,
DestinationStyleOpInterface,
LinalgStructuredInterface,
...
以及,需要额外注意带有 MemWriteAt<0, PartialEffect>的 op,因为如果writeeffect是full,那么后一次写就能覆盖前一次,但如果是partial,就不能因为有后一次写而删除前一次写。
使用
DeclareOpInterfaceMethods声明的interface时需要被重写覆盖,而其他都是默认继承(采用默认实现),解释见讨论。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
def LoadOp : MemRef_Op<"load", [...] {
...
// 这意味着是部分读,只读一部分数据
let arguments = (ins Arg<AnyMemRef, "the reference to load from",
[MemReadAt<0, PartialEffect>]>:$memref,
Variadic<Index>:$indices,
DefaultValuedOptionalAttr<BoolAttr, "false">:$nontemporal);
...
}
使用上
1
2
3
4
if (auto memEffect = llvm::dyn_cast<MemoryEffectOpInterface>(op)) {
SmallVector<MemoryEffects::EffectInstance> effects;
memEffect.getEffects(effects); // 这样effects中就会收集到op的MemoryEffects.
}
- isMemoryEffectFree(Operation *op)
- NoMemoryEffect
- HasRecursiveMemoryEffects 且 所有 nested ops 都是 MemoryEffectFree
- hasEffect
(Operation *op, Value value = nullptr) : 判断op是否对value有副作用,如果没提供value,则判断op是否有副作用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
template <typename... EffectTys>
auto memOp = dyn_cast<MeoryEffectOpInterface>(op);
if (!memOp)
return false;
SmallVector<SideEffects::EffectInstance<MemoryEffects::Effect>, 4> effects;
memOp.getEffects(effects);
return llvm::any_of(effects, [&](MemoryEffects::Effect effect) {
if (value && effect.getValue() != value)
return false;
return isa<EffectTys...>(effect.getEffect());
});
- onlyHasEffect
例如判断只有read effect
1
2
3
4
5
if (!isMemoryEffectFree(op)) {
auto memEffects = dyn_cast<MemoryEffectOpInterface>(op);
if (!memEffects || !memEffects.onlyHasEffect<MemoryEffects::Read>())
return failure();
}
- isOpTriviallyDead(Operation *op) : 当op没有使用者且不会引起副作用时,op就是trivially dead
1
2
3
bool mlir::isOpTriviallyDead(Operation *op) {
return op->use_empty() && wouldOpBeTriviallyDead(op);
}
- getEffectsRecursively(Operation *rootOp) : 获得该root op和其nest op(一般指root op的region内的所有op)的memory Effect
1
2
std::optional<llvm::SmallVector<MemoryEffects::EffectInstance>>
mlir::getEffectsRecursively(Operation *rootOp)
- bool isSpeculatable(Operation* op)
判断一个op是否是用于判断相关的语意,会先尝试判断op是否有 ConditionallySpeculatable的OpInterface
然后会根据 conditionallySpeculatable.getSpeculatability() 来判断
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
switch(conditionallySpeculatable.getSpeculatability()) {
case Speculation::RecursivelySpeculatable:
// 遍历op->getRegions()中的所有op,判断
case Speculation::Speculatable:
return true;
case Speculation::NotSpeculatable:
return false;
}
BranchOpInterface
1
mlir/include/mlir/Interfaces/ControlFlowInterfaces.td
所以分支类型的op都继承了该interface,例如cf.br、cf.cond_br等。对它们的处理需要额外考虑其 successors。
例子:collect blocks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
SmallVector<Block *, 4> blocks;
if (isa<RegionBranchOpInterface>(op)) {
// When the op is a `RegionBranchOpInterface`, like an `scf.for` or an
// `scf.index_switch` op, its branch operand controls the flow into this
// op's regions.
for (Region ®ion : op->getRegions()) {
for (Block &block : region)
blocks.push_back(&block);
}
} else if (isa<BranchOpInterface>(op)) {
// When the op is a `BranchOpInterface`, like a `cf.cond_br` or a
// `cf.switch` op, its branch operand controls the flow into this op's
// successors.
blocks = op->getSuccessors();
}
使用:
- mlir::SuccessorOperands getSuccessorOperands(unsigned index)
Operation 的 Successors 可以理解成该op的后续 Block 例如下面的ir中,cf.br 的 Successors 就是 {^bb3}。
RegionSuccessor表示后续的region
getSuccessorOperands 函数会返回 branchOp 传给 Successors 中第 index 个 successor 的 operand,下面的ir中,cf.br的getSuccessorOperands(0)会得到 %2
1
2
cf.br ^bb3(%2 : tensor<*xf32>)
^bb3(%3: tensor<*xf32>):
例如获得 BranchOpInterface 对应的 successors 和 successorOperands
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// terminator -> Operation *
BranchOpInterface branchOp = dyn_cast<BranchOpInterface>(terminator);
if (!branchOp)
return;
for (unsigned succI = 0, usccE = terminator->getNumSuccessors(); succI < succE; ++succI) {
SuccessOperands successOperands = branchOp.getSuccessorOperands(succI);
Block *successor = terminator->getSuccessor(succI);
}
- std::optional<::mlir::BlockArgument> getSuccessorBlockArgument(unsigned operandIndex)
返回 BranchOpInterface 对应的第 operandIndex operand 所对应的 successor BlockArg。下面这段ir中cf.br的getSuccessorBlockArgument(0)会得到 %3
1
2
cf.br ^bb3(%2 : tensor<*xf32>)
^bb3(%3: tensor<*xf32>):
跨 block 的RE:
(1)首先需要获取 %t 的所有 aliasChilds。从 %t 开始找 uses,若 use 的 owner 是 viewLike,则继续遍历 viewLike 的 result;若 use 的 owner 是 BranchOpInterface,则使用 getSuccessorBlockArgument 获得对应的 blockArg,再继续往前找,直到%1。
(2)再获得 %1 到 %s 的 viewLike 链条,一步步找 defineOp,如果遇见 blockArg 的情况
(3)再利用 aliasChilds 中的对应关系 *(llvm::find(%val) + 1) 来跨 block。
获取
aliasChilds的方法类似LocalAliasAnalysis中的collectUnderlyingAddressValues。区别在于,此时我只需要获得%arg对应的BranchOpInterface的operand,而不需要考虑其他冗余的operand。
1
2
3
4
copy %s -> %t
cf.br ^bb1(%t : tensor<*xf32>)
^bb1(%1: tensor<*xf32>):
use %1
RegionBranchOpInterface
1
mlir/include/mlir/Interfaces/ControlFlowInterfaces.td
带region的且会自动跳转region的op,比如 scf.if、scf.for。对它们的处理需要考虑它们 region 内的op。
像
linalg许多op虽然有region,但并不属于RegionBranchOpInterface
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
SmallVector<Operation &, 4> ops;
if (isa<RegionBranchOpInterface>(op)) {
for (Region ®ion : op->getRegions()) {
for (Block &block : region)
for (Operation &inner : block)
ops.push_back(&inner);
}
}
- RegionBranchPoint
这个 class 表示 RegionBranchOpInterface 中 branch(理解为跳转) 的点,一般是
parentOp -> 即这个 RegionBranchOpInterface,常用 RegionBranchPoint::parent() 获得
Region * -> 这个 RegionBranchOpInterface 中的 region 即可,常用 block->getParent() 获得
- RegionSuccessor
表示 a successor of a region,可以是 RegionBranchOpInterface(parentOp) 本身,也可以是其 region。
getSuccessor() 获得 Region *, getSuccessorInputs() 获得该 region 的 input。
- void getSuccessorRegions(mlir::RegionBranchPoint point, mlir::SmallVectorImpl
successors)
返回 RegionBranchOpInterface 的 RegionSuccessor,例如 scf.if 就会返回 then region 和 else region。
1
2
3
SmallVector<RegionSuccessor, 2> successors;
// pred -> RegionBranchPoint
branch.getSuccessorRegions(pred, successors);
- OperandRange getEntrySuccessorOperands(mlir::RegionBranchPoint point)
对于下面的ir,使用 getEntrySuccessorOperands(RegionBranchPoint::parent()) 会获得 %init。
1
2
3
4
%0 = scf.for %i = %arg0 to %arg0 step %c2 iter_args(%arg = %init) -> (i32) {
%1 = "test.op"(%i, %arg) : (index, i32) -> i32
scf.yield %1 : i32
}
用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
SmallVector<RegionSuccessor> successors;
SmallVector<Attribute> operands(op->getNumOperands(), nullptr);
branch.getEntrySuccessorRegions(operands, successors);
for (RegionSuccessor &successor : successors) {
OperandRange operands = branch.getEntrySuccessorOperands(successor);
ValueRange inputs = successor.getSuccessorInputs();
LoopLikeOpInterface
在 Ops.td 中定义op时使用,例如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
def AffineForOp : Affine_Op<"for",
[AttrSizedOperandSegments, AutomaticAllocationScope,
ImplicitAffineTerminator, ConditionallySpeculatable,
RecursiveMemoryEffects, DeclareOpInterfaceMethods<LoopLikeOpInterface,
// 定义函数
["getSingleInductionVar", "getSingleLowerBound", "getSingleStep",
"getSingleUpperBound", "getYieldedValuesMutable",
"replaceWithAdditionalYields"]>,
DeclareOpInterfaceMethods<RegionBranchOpInterface,
["getEntrySuccessorOperands"]>]> {
相关op
1
2
3
4
5
6
scf.for : 使用 scf.yield 返回
scf.forall : 使用 scf.forall.in_parallel + tensor.parallel_insert_slice
scf.paralle
scf.while
affine.for
affine.parallel
方法
- 下界、上界、step
std::optional<::mlir::OpFoldResult> getSingleLowerBoundstd::optional<::mlir::OpFoldResult> getSingleUpperBoundstd::optional<::mlir::OpFoldResult> getSingleStep
mlir::Block::BlockArgListType getRegionIterArgsmlir::ValueRange getYieldedValues()
返回yield给下一个iteration的值,可以返回为 {}
std::optional<::mlir::ResultRange> getLoopResults()void moveOutOfLoop(op)将op移出loopbool isDefinedOutsideOfLoop(mlir::Value value)
判断输入value是否在loop region外定义
- FailureOr
replaceWithAdditionalYields(RewiterBase &rewriter, ValueRange newInitOperands, bool replaceInitOperandUsesInLoop, NewYieldValuesFn newYieldValuesFn)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
if (extractionOp && insertionOp) {
// Create a new loop with an additional iter_arg.
NewYieldValuesFn newYieldValuesFn =
[&](OpBuilder &b, Location loc,
ArrayRef<BlockArgument> innerNewBBArgs) -> SmallVector<Value> {
return {insertionOp.getSourceOperand().get()};
};
// 新的yield对应的bbArg的initOp是extractionOp.getResult()
// 再以insertOp的source作为该yeild的operand
FailureOr<LoopLikeOpInterface> newLoop =
loopLike.replaceWithAdditionalYields(
rewriter, extractionOp.getResult(),
/*replaceInitOperandUsesInLoop=*/true, newYieldValuesFn);
- OpResult getTiedLoopResult(BlockArgument bbArg) / OpResult getTiedLoopResult(OpOperand *opOperand)
获得 loopResults(由getLoopResults()获得) 中该bbArg对应的值。下面的ir中 %a 对应 %res#0, %b 对应 %res#1
1
%res:2 = scf.forall(%arg3) in (1) shared_outs(%a = %empty0, %b =%empty1) -> (tensor<?xf32>, tensor<?xf32>)
- OpOperand *getTiedLoopInit(BlockArgument bbArg)
获得这个bbArg对应的loopInit,例如上面代码中 %a 对应的 loopInit 就是 %empty0
SubsetOpInterface
用法
bool operatesOnEquivalentSubset(SubsetOpInterface candidate, function_ref<bool(Value, Value)> equivalenceFn)
判断this op 是否和 candidate 一起负责一个subset
bool operatesOnDisjointSubset(SubsetOpInterface candidate, function_ref<bool(Value, Value)> equivalenceFn)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
// 获得loop中的 SubsetExtractionOpInterface 和 SubsetInsertionOpInterface 对应
SmallVector<SubsetExtractionOpInterface> extractions;
SmallVector<SubsetInsertionOpInterface> insertions;
void insertExtractionOp(SubsetExtractionOpInterface extractionOp) {
for (auto it : llvm::enumerate(insertions)) {
if (!it.value())
continue;
auto other = cast<SubsetOpInterface>(it.value().getOperation());
if (other.operatesOnEquivalentSubset(extractionOp, isEquivalent)) {
extractions[it.index()] = extractionOp;
return;
}
}
// There is no known equivalent insertion op. Create a new entry.
extractions.push_back(extractionOp);
insertions.push_back({});
}
void insertInsertionOp(SubsetInsertionOpInterface insertionOp) {
for (auto it : llvm::enumerate(extractions)) {
if (!it.value())
continue;
auto other = cast<SubsetOpInterface>(it.value().getOperation());
if (other.operatesOnEquivalentSubset(insertionOp, isEquivalent)) {
insertions[it.index()] = insertionOp;
return;
}
}
// There is no known equivalent extraction op. Create a new entry.
extractions.push_back({});
insertions.push_back(insertionOp);
}
子interface
- SubsetExtractionOpInterface
OpOperand getSourceOperand()
- SubsetInsertionOpInterface
OpOperand getSourceOperand()OpOperand getDestinationOperand()OpResult getUpdatedDestination(): 返回该op的result_tensor
相关使用:将extractOp和insertOp提升到loop外
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// mlir/lib/Transforms/Utils/LoopInvariantCodeMotionUtils.cpp
// Hoist the extraction/insertion ops.
// LoopLikeOpInterface loopLike
iterArg = loopLike.getRegionIterArgs()[iterArgIdx];
OpResult loopResult = loopLike.getTiedLoopResult(iterArg);
OpResult newLoopResult = loopLike.getLoopResults()->back();
extractionOp->moveBefore(loopLike);
insertionOp->moveAfter(loopLike);
// insertOp外提后,就需要使用loop内还有的value来替换yield的输出
rewriter.replaceAllUsesWith(insertionOp.getUpdatedDestination(),
insertionOp.getDestinationOperand().get());
// extractOp提到loop外后,就需要使用对应的loopInitOp作为sourceOp
extractionOp.getSourceOperand().set(loopLike.getTiedLoopInit(iterArg)->get());
// 使用insertOp的result替换func.return的使用
rewriter.replaceAllUsesWith(loopResult, insertionOp.getUpdatedDestination());
// insertOp提出loop后,source要变成newLoopResult,dst要变成loopResult
insertionOp.getSourceOperand().set(newLoopResult);
insertionOp.getDestinationOperand().set(loopResult);
以下面的代码为例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
iterArg : %t
loopResult : %5#0
newLoopResult : %5#1
loopLike.getTiedLoopInit(iterArg)->get() : %arg0
对extractOp而言
- getSourceOperand() -> %t
对insertOp而言
- getSourceOperand() -> %2
- getDestinationOperand() -> %t
- getUpdatedDestination() -> %3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
%0 = scf.for %iv = %lb to %ub step %step iter_args(%t = %arg0) -> (tensor<?xf32>) {
%standalone = tensor.extract_slice %t[9][5][1] : tensor<?xf32> to tensor<5xf32>
"test.foo"(%standalone) : (tensor<5xf32>) -> ()
%1 = tensor.extract_slice %t[0][5][1] : tensor<?xf32> to tensor<5xf32>
%2 = "test.foo"(%1) : (tensor<5xf32>) -> (tensor<5xf32>)
%3 = tensor.insert_slice %2 into %t[%sub][5][1] : tensor<5xf32> into tensor<?xf32>
scf.yield %3 : tensor<?xf32>
}
return %0 : tensor<?xf32>
// convert to
%extracted_slice = tensor.extract_slice %arg0[0] [5] [1] : tensor<?xf32> to tensor<5xf32>
%5:2 = scf.for %arg1 = %0 to %1 step %2 iter_args(%arg2 = %arg0, %arg3 = %extracted_slice) -> (tensor<?xf32>, tensor<5xf32>) {
%extracted_slice_0 = tensor.extract_slice %arg2[9] [5] [1] : tensor<?xf32> to tensor<5xf32>
"test.foo"(%extracted_slice_0) : (tensor<5xf32>) -> ()
%6 = "test.foo"(%arg3) : (tensor<5xf32>) -> tensor<5xf32>
scf.yield %arg2, %6 : tensor<?xf32>, tensor<5xf32>
}
%inserted_slice = tensor.insert_slice %5#1 into %5#0[%4] [5] [1] : tensor<5xf32> into tensor<?xf32>
return %inserted_slice : tensor<?xf32>
ViewLikeOpInterface
memref.expand_shape, memref.collapse_shape, memref.view, memref.reshape, memref.reshape, memref.reinterpret_cast, memref.cast 等
这些的src都是单operand,但是offset / size / stride属性是 OperandRange
Value getViewSource()
判断两个view是否相同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
static bool isSameView(ViewLikeOpInterface a, ViewLikeOpInterface b) { if (a->getName() != b->getName() || a->getAttrs() != b->getAttrs() || a->getNumOperands() != b->getNumOperands()) { return false; } for (auto [operand1, operand2] : llvm::zip(a.getOperands(), b.getOperands())) { if (operand1 == a.getViewSource() && operand2 == b.getViewSource()) continue; if (operand1 != operand2) return false; } return true; }
OffsetSizeAndStrideOpInterface
也属于 ViewLikeOpInterface ,可以通过 llvm::cast<OffsetSizeAndStrideOpInterface>(op) 获得。
主要用来获取 offeset/size/stride 信息,常用以下方法:
mlir::OperandRange getOffsets() / getSizes() / getStrides()
llvm::ArrayRef
getStaticOffsets() / getStaticSizes() / getStaticStrides() llvm::SmallVector<mlir::OpFoldResult, 4> getMixedOffsets() / getMixedSizes() / getMixedStrides()
bool isDynamicOffset(idx) / isDynamicSize(idx) / isDynamicStride(idx)
int64_t getStaticOffset(idx) / getStaticSize(idx) / getStaticStride(idx)
mlir::Value getDynamicOffset(idx) / getDynamicSize(idx) / getDynamicStride(idx)
isSameAs(::mlir::OffsetSizeAndStrideOpInterface, ::llvm::function_ref<bool, (::mlir::OpFoldResult, ::mlir::OpFoldResult)>)
1
2
auto isSame = [](OpFoldResult, OpFoldResult) { return a == b};
if (prevInsertOp.isSameAs(insertOp, isSame))
AllocOpInterface
常见的alloc op都继承了该interface,常见 memref.alloc
常用
- Value getSource()
- Value getTarget()
FunctionOpInterface
各种 func op都继承了该interface,常见 func.func
常见于pass中的遍历处理,在 .td 中不设置其target,直接在 runOnOperation() 中锚定为 funcOp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
void processOnFunc(FunctionOpInterface func) {};
namespace {
struct ...
void runOnOperation() override {
Operation *input = getOperation();
input->walk([](FunctionOpInterface func) {
processOnFunc(func);
})
}
}
CallOpInterface
调用 function 的 op,例如
1
2
3
// mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/SPIRV/IR/SPIRVControlFlowOps.td
def SPIRV_FunctionCallOp : SPIRV_Op<"FunctionCall", [
InFunctionScope, DeclareOpInterfaceMethods<CallOpInterface>]> {
从 callOp 找 funcOp
1
2
ModuleOp m = getOperation();
triton::FuncOp matrixFunc = m.lookupSymbol<triton::FuncOp>(callOp.getCallee());
llvm
很多下面的函数都在 c++ 中有相应实现,但 LLVM 重新实现了一遍,例如工具类 cast / dyn_cast 等, 数据结构类 SmallVector / DenseMap 等, 这种设计是出于性能、灵活性和代码一致性的考虑。
1.性能问题
c++ 的 dynamic_cast 是 RTTI (运行时类型识别机制的一种),依赖编译器生成的类性信息 (如虚表) 来完成类型检查和类型转换,这种机制会造成额外的运行时开销。 而 dyn_cast 是一个轻量级实现,避免了 RTTI 导致的开销。
其实 LLVM的代码中 RTTI 通常是禁用的,方便减小二进制文件大小。
SmallVector 这类数据结构利用栈的特性优化。
2.类型层次较深
LLVM 的众多类有深层次的类继承结构和众多的类型检查需求。
LogicalResult
函数内用 success() / failure() 作为返回
外部调用判断 succeeded / failed
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
static LogicalResult getXXX(Value &res, ...) {
if (xxx) {
value = newValue
return success();
}
return failure();
}
// 使用
Value res = nullptr;
LogicalResult a = getXXX(res, ...);
if (failed(a)) {
DBGS() << "Get value failed.";
}
但如果不想判断该函数是否 successed,或直接使用返回值(某些数据类型直接返回开销不大,没必要传入引用),可以考虑使用 FailureOr<Ty>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
static FailureOr<Value> getXXX(...) {
if (xxx) {
return newValue;
}
return failure();
}
// 使用
FailureOr a = getXXX(res, ...);
if (failed(a))
DBGS() << "Get value failed.";
Value res = *a
isa
1.isa : 不能在cast之后使用isa,有类似场景请用dyn_cast
2.isa_and_nonnull / isa_and_present:允许op为null作为输入,返回null
两者作用完全相同,未来的llvm将弃用
isa_and_nonnull,推荐使用isa_and_present
cast
一般 cast 都是用在从基类向(具体)派生类转换。
1.cast :直接转换,失败时报错(assert)
c++ 中都 static_cast 会在编译期检查 cast 的合法性,和 llvm::cast 类似。
c++ 中的 reinterpret_cast 用于任意 指针/引用 之间的类型转换,不检查安全性,只是重新解释。
c++ 中的 const_cast 用于去除变量的 const 属性
c++ 中的 dynamic_cast 类似 llvm::dyn_cast,如果 cast 失败会返回一个 nullptr。
2.cast_or_null :允许op为null作为输入,返回null
3.dyn_cast : 尝试转换,失败时返回null,op为null时报错
4.dyn_cast_if_present / dyn_cast_or_null :尝试转换,失败时返回null,op为null时返回null
1
2
3
template <class X, class Y> auto dyn_cast_or_null(const Y &Val) {
return dyn_cast_if_present<X>(Val);
}
例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Value mlir::getValueOrCreateConstantIndexOp(OpBuilder &b,
Location loc,
OpFoldResult ofr) {
if (auto value = llvm::dyn_cast_if_present<Value>(ofr))
return value;
auto attr = dyn_cast<IntegerAttr>(llvm::dyn_cast_if_present<Attribute>(ofr));
assert(attr && "expected the op fold result casts to an integer attribute");
return b.create<arith::ConstantIndexOp>(loc, attr.getValue().getSExtValue());
}
all_of / any_of / for_each
1
llvm/include/llvm/ADT/STLExtras.h
1.all_of :判断是否所有元素都满足条件
用法
1
2
3
if (llvm::all_of(inputs, [](Value input) {
return input.getType().isa<ShapedType>();
});
实现
1
2
3
4
template <typename R, typename UnaryPredicate>
bool all_of(R &&Range, UnaryPredicate P) {
return std::all_of(adl_begin(Range), adl_end(Range), P);
}
2.any_of :判断是否有元素满足条件
用法
1
2
3
4
if (llvm::any_of(op->getRegions(), [](Region &r) {
return r.getBlocks().size > 1;
}))
return failure();
实现
1
2
3
4
template <typename R, typename UnaryPredicate>
bool any_of(R &&Range, UnaryPredicate P) {
return std::any_of(adl_begin(Range), adl_end(Range), P);
}
3.none_of :判断是否没有元素满足条件
4.for_each :对每个元素执行操作
1
llvm::for_each(outputs, [&](Value val) { types.emplace_back(val.getType()); });
5.llvm::enumerate
返回一个pair,first是index,second是value,直接对元素使用
.index()和.value()即可也可以使用
auto [idx, val] : llvm::enumerate(inputs)/auto [idx, val1, val2] : llvm::enumerate(inputs, outputs)用法
1
2
3
4
5
auto isConsecute [](ArrayRef<int64_t> array) -> bool {
return llvm::all_of(llvm::enumerate(array), [array](auto iter)) {
return iter.index() + array.front() == iter.value();
});
};
6.llvm::zip
- 遍历时使用
std::get<0>和std::get<1>来获得值
1
2
3
for (const auto &it :llvm::enumerate(llvm::zip(valAVec, valBVec))) {
Value aVal = std::get<0>(it.value());
Value bVal = std::get<1>(it.value());
- 比较
1
2
3
4
5
for (const auto &[operand, arg] :
llvm::zip(op->getOperands(), body->getArguements())) {
if (operand != arg)
return failure();
}
7.llvm::is_contained
判断 Element 是否在 Range 中,比用 llvm::find 更简洁(底层实现也是find判断有没有到container::end)。
1
bool is_contained(R &&Range, const E &Element)
function
1.llvm:function_ref 定义inline func,用于传递函数指针
using function_ref = llvm::function_ref<Fn>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
size_t mlir::moveLoopInvariantCode(
ArrayRef<Region *> regions,
function_ref<bool(Value, Region *)> isDefinedOutsideRegion, // 调用点
...
size_t mlir::moveLoopInvariantCode(LoopLikeOpInterface loopLike) {
return moveLoopInvariantCode(
loopLike.getLoopRegions(),
[&](Value value, Region *) {
return loopLike.isDefinedOutsideOfLoop(value);
}, // 定义点,传递了一个lambda函数
Array / Vector / Set / hash
1.llvm:ArrayRef
- 轻量级数组引用,不进行内存分配或拷贝,适用于对已有数组进行访问而不修改的场景,是一个只读工具
- 常传入SmallVector或std::vector构造
- tips:
const &SmallVector<==>ArrayRef
2.llvm:SmallVector
- SmallVector
srcDims(2, 1) 表示 初始化了两个元素,每个元素的值都是 `1`。 SmallVector<int64_t, 2>表示包含int64_t元素的SmallVector类型,其中2是指定的初始大小- tips:如果能预先知道需要的size,就使用reserve先分配
其他
1 2 3 4 5
llvm::reverse() llvm::to_vector() // SmallVector<int64_t> res{llvm::to_vector(llvm::seq((int64_t)0, size))}; llvm::make_filter_range() llvm::map_range()
3.llvm::SmallVectorImpl
- SmallVector构造时调用的是
SmallVector() : SmallVectorImpl<T>(N) {} - 写一个以SmallVector为参数的函数,如果传入的元素个数是固定的,建议使用
SmallVectorImpl作为形参,来避免对堆栈元素的隐式数量进行硬编码
SmallVector有一个参数N表示该堆栈开辟了多少空间(元素),函数上直接使用SmallVectorImpl作形参能减少拷贝。SmallVectorImpl<Value> &
4.llvm::SetVector
- 即有set的存储行为,又有vector的存储顺序
- 常用方法
- insert
- contains / count
- erase
- clear
- size
- empty
5.llvm:to_vector
- 将数组类型的对象转为SmallVector,常用来解决用ArrayRef构造SmallVector
用法
1 2
// 构造一个[0, 1, windowTy.getShape()-1]的数组 SmallVector<int64_t> dstShape(llvm::to_vector(windowTy.getShape()));
源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
template <typename R> SmallVector<ValueTypeFromRangeType<R>> to_vector(R &&Range) { return {std::begin(Range), std::end(Range)}; } template <typename RangeType> // std::remove_const_t 用于移除模板参数类型的const修饰符 // std::remove_reference_t 用于移除模板参数类型的引用修饰符 // decltype 用于推断表达式的类型 // std::declval 用于创建模板类型的临时值 using ValueTypeFromRangeType = std::remove_const_t<std::remove_reference_t<decltype(*std::begin( std::declval<RangeType &>()))>>;
6.llvm::seq
- 生成一个连续的序列,包含起始值,不包含结束值。
seq_inclusive既包含起始值,也包含结束值。 - 用法
- 循环的范围
for (auto idx : llvm::seq<int>(0, rank)) - 创建个连续的
SmallVector<int64_t> res{llvm::to_vector(llvm::seq((int64_t)0, size))};
- 循环的范围
源码
1 2 3 4 5 6
auto seq(T Begin, T End) { return iota_range<T>(Begin, End, false); } auto seq(T Size) { return seq<T>(0, Size); }
7.llvm:DenseSet
- set和map都是基于hash的,都是无序的
- 常用方法
insert(const ValueT &V)
1 2 3 4
// insert是有返回值 std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const ValueT &V) - first: 插入后的iterator - bool: 是否插入
- erase(Iterator I)
- count(const ValueT &V)
- contains(const_arg_type_t
V) using const_arg_type_t = typename const_pointer_or_const_ref<T>::type;
8.llvm:DenseMap
- 和std::map类似, <key, value>
- find(返回iterator) / lookup(返回value或null)
- contains(返回true/false) / count(返回1/0)
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert / try_emplace : 返回值的second为true时,表示原本的map中不能找到key,已新插入一个<key, val>的pair,并以该pair的iterator作为返回值的first
1
launchInfo.insert({candidateOp, replacementIndexes})
9.llvm::DenseMapInfo
- hash表,只存key,
DenseMapInfo<T*> - 使用
getHashValue来获得hash值,最原始的方法是使用指针地址偏移计算的。但如果要实现自定义的hash,可以继承该类并重载getHashValue和isEqual方法 例如:CSE中确定Op是否相同的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
// mlir/lib/Transform/CSE.cpp struct SimpleOperationInfo : public llvm::DenseMapInfo<Operation *> { static unsigned getHashValue(const Operation *opC) { return OperationEquivalence::computeHash( const_cast<Operation *>(opC), /*hashOperands*/OperationEquivalence::directHaseValue, /*hashResults*/OperationEquivalence::ignoreHaseValue, OperationEquivalence::IngoreLocations); } } static bool isEqual(const Operation *lhsC, const Operation *rhsC) { auto *lhs = const_cast<Operation *>(lhsC); auto *rhs = const_cast<Operation *>(rhsC); if (lhs == rhs) return true; // 防止lsh/rhs是hash表中的特异值 if (lhs == getTombstoneKey() || lhs == getEmptyKey() || rhs == getTombstoneKey() || rhs == getEmptyKey()) return false; return OperationEquivalence::isEquivalentTo( const_cast<Operation>(lhsC), const_cast<Operation>(rhsC), OperationEquivalence::IngoreLocations); }
10.llvm::ScopedHashTable
需要包含 key, value, keyInfo, AllocatorTy 四个参数,例如 CSE.cpp 中构造该类型:
1 2 3 4
using ScopedMapTy = llvm::ScopedHashTable<Operation *, Operation *, SimpleOperationInfo, AllocatorTy> // SimpleOperationInfo 继承自 DenseMapInfo<Operation *> // using AllocatorTy = llvm::RecyclingAllocator<llvm::BumpPtrAllocator, llvm::ScopedHashTableVal<Operation *, Operation *>>;
实例化
using ScopeTy = ScopedHashTableScope<K, V, KInfo, AllocatorTy>;1
ScopedMapTy::ScopeTy scope(knownValues);
使用函数
- V lookup(K key) : 在其中尝试查找key。一般来说
SimpleOperationInfo都会有有自己的getHashValue和isEqual函数,这样就能根据key找到对应的value
- V lookup(K key) : 在其中尝试查找key。一般来说
11.StringRef
StringRef 没有存储在其中数据的所有权 的 string,可以是 constant 也可以是 dynamic,想要存储一个 StringRef 往往是不安全的。(因为data的真实memory可能随时被修改)
但也因为如此, StringRef 十分轻量,避免了 const char* 这类的在堆上开辟空间。
This class does not own the string data. The start of the string, in an external buffer.
const char *Data = nullptr;
此外, StringLiteral (继承自 StringRef) 也很常见,必须配合 constexpr 使用,作为编译器常量,用来表示字符串字面量:
1
static constexpr StringLiteral xxxAttrName = "............";
等效于 static const char *const
make_range
1.llvm::map_range
- 将一个range映射到另一个range
用法
1 2 3 4 5 6
// 将 srcDims 中的每个元素都乘以2 auto res = llvm::map_range(srcDims, [&](int64_t dim) { return dim * 2; }); // 判断所有的operand的shape都相同 assert(llvm::all_equal(llvm::map_range(op.getOperandTypes(), [](Type t) { return t.cast<TensorType>().getShape(); })));
源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
template <typename ContainerTy, class FuncTy> auto map_range(ContainerTy &&C, FuncTy F) { return make_range(map_iterator(std::begin(C), F), map_iterator(std::end(C), F)); } template <typename ItTy, class FuncTy> inline mapped_iterator<ItTy, FuncTy> map_iterator(ItTy I, FuncTy F) { return mapped_iterator<ItTy, FuncTy>(std::move(I), std::move(F)); }
2.llvm::make_early_inc_range
- 允许range中的元素被修改,且不影响iterator。例如遍历DenseMap对符合条件的iterator进行erase
1
2
3
for (Block *block : llvm::make_early_inc_range(blockVec)) {
... // earse/replace ops in block
}
注意在遍历 getUsers() 或 getUses() ,且要修改时,要么用 SmallVector 包起来,要么用 make_early_inc_range,即
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
for (OpOperand &currUse : llvm::make_early_inc_range(op->getUses())) {
auto newOp = rewriter.create<...>(...)
rewriter.replaceUsesWithIf(
op.getResult(), newOp.getResult(),
[&](OpOperand &use) { return use == currUse; });
}
if (llvm::any_of(llvm::to_vector(src->getUsers()), [&](auto user) {
if (hasEffect<MemoryEffects::Write>(user, src)) {
return !dom.dominates(user, copyOp);
}
return false;
})) {
continue;
}
因为 getUsers() 或 getUses() 返回的数据类型是 use_range 或 user_range,这些都是 iterator_range !!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// uses
using use_range = result_range::use_range;
// using use_range = iterator_range<use_iterator>;
use_range getUses() { return getResults().getUses(); }
// users
using user_iterator = ValueUserIterator<use_iterator, OpOperand>;
using user_range = iterator_range<user_iterator>;
user_iterator user_begin() { return user_iterator(use_begin()); }
user_iterator user_end() { return user_iterator(use_end()); }
user_range getUsers() { return {user_begin(), user_end()}; }
find
- llvm::find
1
llvm::find(a.begin(), a.end(), val)
- llvm::find_if
1
2
3
llvm::find_if(shapeIndexs, [&](int64_t shapeIndex) {
return !oneSizeDimIndexsSet.count(shapeIndex);
});
tip: 如果需要在循环中查找,建议使用 DenseSet, DenseMap 类数据结构, contains, find, count等操作开销都小
switch
- llvm:TypeSwitch
常用在模板输入的pattern中,某些op需要额外的处理,例如构建某些op的时候需要额外set一些属性
记得第一个参数如果是算子,要使用 getOperation() 方法转为 Operation*
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
auto newOp = clone(rewriter, op, TypeRange{newResType}, newOperands);
auto inWhiteList = llvm::TypeSwitch<Operation *, bool>(newOp)
.Case([&](linalg::BroadcastOp updateOp) {
auto srcOp = cast<linalg::BroadcastOp>(op);
updateOp.setDimensions...
return true;
})
.Case([&](linalg::ReduceOp updateOp) {
auto srcOp = cast<linalg::ReduceOp>(op);
updateOp.setDimensions...
return true;
})
.Case([&](linalg::TransposeOp updateOp) {
auto srcOp = cast<linalg::TransposeOp>(op);
updateOp.setPermutation...
return true;
})
.Default([&](Operation *noNeedUpdate) { return false; });
STL_Extra func
1.llvm::count_if
用法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
llvm::count_if(inputs.getType(), [](Type type) { return type.isa<ShapedType>(); }); int64_t = numUsesInContainingOp = llvm::count_if(producerOp->getUsers(), [&](Operation *op) { return containingOp->isAncestor(op); });
实现
1 2 3 4
template <typename R, typename UnaryPredicate> auto count_if(R &&Range, UnaryPredicate P) { return std::count_if(adl_begin(Range), adl_end(Range), P); }
2.llvm::transform
- 对一个range应用特殊的方法
使用
1 2
llvm::transform(srcDims, std::back_inserter(resDims) [&](int64_t dim) { return dim * 2; });
3.llvm::hasSingleElement
使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
auto containingOps = state.getPayloadOps(getContainingOp()); if (!llvm::hasSingleElement(containingOps)) { return emitDefiniteFailure() << "requires exactly one containing_op handle (got " << llvm::range_size(containingOps) << ")"; } Operation *containingOp = *containingOps.begin();
实现
1 2 3 4 5
template <typename ContainerTy> bool hasSingleElement(ContainerTy &&C) { auto B = std::begin(C), E = std::end(C); return B != E && std::next(B) == E; }
4.drop_begin / drop_end
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
template <typename T>
auto drop_begin(T &&RangeOrContainer, size_t N = 1) {
make_range(std::next(adl_begin(RangeOrContainer), N), adl_end(RangeOrContainer));
}
auto drop_begin(T &&RangeOrContainer, size_t N = 1) {
make_range(adl_begin(RangeOrContainer), adl_prev(adl_end(RangeOrContainer), N));
}
setOperation
1
llvm/include/llvm/ADT/SetOperations.h
- llvm::set_union(A, B): 计算集合A与集合B的并集,并将结果赋值给集合A
- llvm::set_intersection(A, B): 计算集合A与集合B的交集,并将结果赋值给集合A
- llvm::set_subtract(A, B): 计算集合A与集合B的差集(在A中但不在B中),并将结果赋值给集合A
LLVM Dialect
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/Target/LLVMIR
mlir/lib/Target/LLVMIR
LLVM Dialect 是 mlir 设置的最后一个出口, 和 LLVM IR 映射密切,提供了许多公共的 api,某些 arch special 的信息需要同时定义一个同级的 Dialect 来辅助下降,例如 NVVM Dialect
下面以一段 gpu dialect 表示的内容进行下降说明
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
module attributes {gpu.container_module} {
gpu.module @copy {
gpu.func @copy(%arg0: memref<1024xf32>, %arg1: memref<1024xf32>) kernel {
%thread = gpu.thread_id x
%idx = affine.apply affine_map<()[s0] -> (s0 * 4)>()[%thread]
%v = vector.load %arg0[%idx] : memref<1024xf32>, vector<4xf32>
vector.store %v, %arg1[%idx] : memref<1024xf32>, vector<4xf32>
gpu.return
}
}
}
to llvm dialect: 由于没有 gpu arch,得用点骚办法 mlir-opt -gpu-lower-to-nvvm-pipeline --mlir-print-ir-after-all 把最后的 llvm dialect 表示抠出来,如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
llvm.func @copy(%arg0: !llvm.ptr, %arg1: !llvm.ptr, %arg2: i64, %arg3: i64, %arg4: i64, %arg5: !llvm.ptr, %arg6: !llvm.ptr, %arg7: i64, %arg8: i64, %arg9: i64) attributes {gpu.kernel, nvvm.kernel} {
%0 = llvm.mlir.constant(4 : index) : i64
%1 = nvvm.read.ptx.sreg.tid.x : i32
%2 = llvm.sext %1 : i32 to i64
%3 = llvm.mul %2, %0 overflow<nsw> : i64
%4 = llvm.getelementptr %arg1[%3] : (!llvm.ptr, i64) -> !llvm.ptr, f32
%5 = llvm.load %4 {alignment = 4 : i64} : !llvm.ptr -> vector<4xf32>
%6 = llvm.getelementptr %arg6[%3] : (!llvm.ptr, i64) -> !llvm.ptr, f32
llvm.store %5, %6 {alignment = 4 : i64} : vector<4xf32>, !llvm.ptr
llvm.return
}
to llvm ir: mlir-translate --mlir-to-llvmir tmp.mlir
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
; ModuleID = 'LLVMDialectModule'
source_filename = "LLVMDialectModule"
define ptx_kernel void @copy(ptr %0, ptr %1, i64 %2, i64 %3, i64 %4, ptr %5, ptr %6, i64 %7, i64 %8, i64 %9) {
%11 = call i32 @llvm.nvvm.read.ptx.sreg.tid.x()
%12 = sext i32 %11 to i64
%13 = mul nsw i64 %12, 4
%14 = getelementptr float, ptr %1, i64 %13
%15 = load <4 x float>, ptr %14, align 4
%16 = getelementptr float, ptr %6, i64 %13
store <4 x float> %15, ptr %16, align 4
ret void
}
; Function Attrs: nocallback nofree nosync nounwind speculatable willreturn memory(none)
declare noundef i32 @llvm.nvvm.read.ptx.sreg.tid.x() #0
attributes #0 = { nocallback nofree nosync nounwind speculatable willreturn memory(none) }
!llvm.module.flags = !{!0}
!0 = !{i32 2, !"Debug Info Version", i32 3}
后续专为 ptx,用 llc -march=nvptx64 -mcpu=sm_XX output.ll -o output.ptx 即可
参考 llvm/test/CodeGen/NVPTX/load-store-vectors.ll 中的测试
一般 MLIR-LLVM CodeGen 的 pipeline:
mix mlir dialect -> llvm dialect -> llvm ir -> hardware intrinsics(llvm/include/llvm/IR/Intrinsics.td) -> hardware assembly
intrinsic 其实是 LLVM 中一些根据硬件后端预定义的 vairable 和 function。
mix mlir dialect -> llvm(+nvvm) dialect -> llvm ir -> ptx assembly -> 通过cuda-rt binary 转为 sass ,而不用转为 intrinsics
Matcher
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Matchers.h
matchPattern
用来确定输入对象符合某种特性(Pattern)
- matchPattern(Value, Pattern)
1
2
auto val = getValueOrCreateConstantIndexOp(...)
if (mathPattern(val, m_Zero())) // 判断 val 是否是立即数0 或 constant(0)
- matchPattern(val, m_Zero())
- matchPattern(Operation *, Pattern)
- matchPattern(Attribute, Pattern)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
/// %cst = arith.constant 4.0 : f32
/// %0 = arith.divf %arg0, %cst : f32
auto divisor = op.getRhs();
FloatAttr divisorAttr;
if (matchPattern(divisor, m_Constant(divisorAttr))) {
// 如果 match 成功了,divisorAttr 会被赋值
auto divisorVal = divisorAttr.getValue().convertToDouble(); // APFloat -> Double
...
}
实现形式例如: (对于不同类型的输入,都有一个 match 函数)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
template <typename Pattern>
inline bool matchPattern(Attribute attr, const Pattern &pattern) {
static_assert(llvm::is_detected<detail::has_compatible_matcher_t, Pattern,
Attribute>::value,
"Pattern does not support matching Attributes");
if (!attr)
return false;
return const_cast<Pattern &>(pattern).match(attr);
}
Pattern
一些常见的 Pattern
- m_Constant() : 对于operation*而言,需要满足
op->hasTrait<OpTrait::ConstantLike>() - m_AnyZeroFloat() : 是0且是APFloat,则匹配成功
- m_Zero() : 是0且是APInt,则匹配成功
- m_OneFloat() : 是1且是APFloat,则匹配成功
- m_One() : 是1且是APInt,则匹配成功
- m_ConstantFloat(FloatAttr::ValueType *bind_value) : 会把值写入bind_value(binds the constant integer value)
- m_ConstantInt(IntegerAttr::ValueType *bind_value)
判断一个 OpFoldResult 的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
/// Copy from mlir/lib/Dialect/Linalg/Transforms/ElementwiseOpFusion.cpp.
static bool opFoldIsConstantValue(OpFoldResult ofr, int64_t value) {
if (auto attr = llvm::dyn_cast_if_present<Attribute>(ofr))
return cast<IntegerAttr>(attr).getInt() == value;
llvm::APInt actual;
return matchPattern(ofr.get<Value>(), m_ConstantInt(&actual)) &&
actual.getSExtValue() == value;
}
Operand
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Operation.h
方法(src: Operation *)
- getDpsInputOperand
- getOperands
- getOpOperands:在需要修改operand时用,配合opOperand.set()
OpOperand
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Value.h
每个Operation的Operand都是到Value的指针,这就意味着可以通过修改 OpOperand 来修改 Value。
1
2
3
4
5
OpOperand a;
Value b = a->get();
unsigned idx = a.getOperandNumber(); // 返回operation中该operand的idx,一般想要获得operand的idx也是通过其OpOperand
Value value;
a.assign(value);
Operation都包含Results和Operands;Results中包含多个OpResult实例,Operands中包含多个OpOperand实例
- 获得operands
Operation * 的 getOpOperands() 将返回
MutableArrayRef<OpOperand>。相比 getOperands 获得的是OperandRange,一般不可修改,常常当ArrayRef<Value>来用。
某些op中一般实现了 getxxx 和 getxxxMutable 两种方法来获得 operands
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// scf.forall 的 相关方法
::mlir::Operation::operand_range getDynamicLowerBound();
::mlir::Operation::operand_range getDynamicUpperBound();
::mlir::Operation::operand_range getDynamicStep();
::mlir::Operation::operand_range getOutputs();
::mlir::MutableOperandRange getDynamicLowerBoundMutable();
::mlir::MutableOperandRange getDynamicUpperBoundMutable();
::mlir::MutableOperandRange getDynamicStepMutable();
::mlir::MutableOperandRange getOutputsMutable();
还有许多op在 mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/xxx/IR/xxxOps.h 中定义有op的一些方法
1
2
Value getTagMemRef() { return getOperand(0); }
OpOperand &getTagMemRefMutable() { return getOperation()->getOpOperand(0); }
Value 的
getUses()方法返回的就是OpOperandreplaceUsesWithIf常用的写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
// 例如使用 to 替换 from 在 userBlock中的使用
Value from, to;
Block *userBlock;
rewrite.replaceUsesWithIf(from, to, [&](OpOperand &use) {
return userBlock == use.getOwner()->getBlock();
});
OpResult
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Value.h
继承自 Value,和 OpOperand 的用法基本一致,基础的方法有:
- Operation *getOwner()
- unsigned getResultNumber()
Operation
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/IR/OperationSupport.h
mlir/lib/IR/Operation.cpp
每个op本质上都是一个 Operation 的指针
Operation 里面存了 OpName 和所有的 operands, results, attributes 和其它的东西
在不修改 IR 的情况下,每个 Operation 有唯一地址 ,如果只是对ir分析,可以使用 llvm::DenseMap<Operation*, size_t> numberOfReference; 来统计
常用方法
OperationName opName = op->getName();
- 获得父op
- getParentOp():返回该operation的最近的上一级op 如果要判断某个op的父op就用该方法
getParentOfType
():返回该operation的最近的上一级的为OpTy的op 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
template <typename OpTy> OpTy getParentOfType() { auto *op = this; while (op = op->getParentOp()) { if (auto parentOp = dyn_cast<OpTy>(op)) return parentOp; return OpTy; } }
getParentRegion 返回包含该op的region,也可以返回nullptr
getBlock() 返回父block,而不是当前op的block
getBody() 返回当前op内部的block或region
- getOperands()
- 如果operand没有defineOp,则代表是BlockArgument
bool isBeforeInBlock(Operation *other) 判断这个op是否在other之前,要求当前op和other都在同一block内
getResults() / getResult(unsigned idx)
- 转换为目标op
- cast
(op) - dyn_cast
(op)
- cast
- getUses() / getUsers()
相当于这个operation的所有result的use / user(其实就是operation *)的集合
walk : 遍历 op 所有内部的 innerOp,第一次遍历的是本身
emitOpError
1
2
3
4
if (xxx) {
op->emitOpError() << "error info" << "."
return signalPassFailure();
}
注册op
例如想新建一个linalg_ext.xxop
参考:linalg.map的注册方法
- 首先在
td中注册
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
// mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/Linalg/IR/LinalgStructuredOps.td
def TensorOrMemref :
AnyTypeOf<[AnyMemRef, AnyRankedTensor], "", "::mlir::ShapedType">;
def MapOp : LinalgStructuredBase_Op<"map", [
DeclareOpInterfaceMethods<OpAsmOpInterface, ["getAsmResultNames"]>,
DeclareOpInterfaceMethods<OpAsmOpInterface, ["getAsmBlockArgumentNames"]>,
SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<"YieldOp">]> {
let summary = "Elementwise operations";
let description = [{
Models elementwise operations on tensors in terms of arithmetic operations
on the corresponding elements.
Example:
```
%add = linalg.map
ins(%lhs, %rhs : tensor<64xf32>, tensor<64xf32>)
outs(%init: tensor<64xf32>)
(%lhs_elem: f32, %rhs_elem: f32) {
%0 = arith.addf %lhs_elem, %rhs_elem: f32
linalg.yield %0: f32
}
```
Shortened print form is available. Applies to simple maps with one
non-yield operation inside the body.
The example above will be printed as:
```
%add = linalg.map { arith.addf }
ins(%lhs, %rhs : tensor<64xf32>, tensor<64xf32>)
outs(%init: tensor<64xf32>)
```
}];
let arguments = (ins
// Input args
Variadic<TensorOrMemref>:$inputs,
// Output arg
TensorOrMemref:$init
);
// 把result只限制在tensor语意上,memref时候就没有result
let results = (outs Variadic<AnyTensor>:$result);
let regions = (region SizedRegion<1>:$mapper);
let builders = [
OpBuilder<(ins "ValueRange":$inputs, "Value":$init,
"function_ref<void(OpBuilder &, Location, ValueRange)>",
CArg<"ArrayRef<NamedAttribute>", "{}">:$attributes)>
];
let extraClassDeclaration = structuredOpsBaseDecls # [{
// Implement functions necessary for LinalgStructuredInterface.
SmallVector<utils::IteratorType> getIteratorTypesArray();
ArrayAttr getIndexingMaps();
std::string getLibraryCallName() {
return "op_has_no_registered_library_name";
}
// Implement functions necessary for DestinationStyleOpInterface.
MutableOperandRange getDpsInitsMutable() { return getInitMutable(); }
SmallVector<OpOperand *> getOpOperandsMatchingBBargs() {
return getDpsInputOperands();
}
bool payloadUsesValueFromOperand(OpOperand * opOperand) {
if (isDpsInit(opOperand)) return false;
return !getMatchingBlockArgument(opOperand).use_empty();
}
static std::function<void(mlir::ImplicitLocOpBuilder &, mlir::Block &,
mlir::ArrayRef<mlir::NamedAttribute>)>
getRegionBuilder() {
return nullptr;
}
}];
let hasCustomAssemblyFormat = 1;
let hasVerifier = 1;
}
- 然后在
xxxDialectOps.cpp中写 build 等方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// mlir/lib/Dialect/Linalg/IR/LinalgOps.cpp
void MapOp::build(
OpBuilder &builder, OperationState &result, ValueRange inputs, Value init,
function_ref<void(OpBuilder &, Location, ValueRange)> bodyBuild,
ArrayRef<NamedAttribute> attributes) {
build(builder, result, TypeRange{}, inputs, init);
result.addAttributes(attributes);
// Add output types for `RankedTensorType` output arguments.
// 配合 td 中 `let results = (outs Variadic<AnyTensor>:$result);`
Type initType = init.getType();
if (llvm::isa<RankedTensorType>(initType))
result.addTypes(initType);
if (bodyBuild)
buildGenericRegion(builder, result.location, *result.regions.front(),
inputs, /*outputs=*/{}, bodyBuild);
}
创建op
使用 OpBuilder 来 create
1.根据op的build函数create
create
/mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/XXX/IR/XXXOps.tdbuild/tools/mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/XXX/IR/XXXOps.h.inc中对应op的build函数
2.根据operationState来create
create(OperationState state)
1
2
3
OperationState state(op->getLoc(), op->getName().getStringRef(), operands,
newResults, op->getAttrs(), op->getSuccessors());
Operation *newOp = rewriter.create(state);
使用 OperationState 可以用来写一些模板函数pattern或者 TypeConvert 的naive_pattern,创建op会更加简单
例: 当op的mask来自于特殊情况,将起专为 scf.if + op 的形式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
static std::optional<Value> getBaseMaskVal(Value maskVal) {
if (mask) {
if (...)
return ...;
}
return std::nullopt;
}
/// access_op(with mask) --> scf.if + access_op(without mask)
template<typename OpTy>
class FoldMaskAccessPattern : public OpRewritePattern<OpTy> {
using OpRewritePattern<OpTy>::OpRewritePattern;
LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(OpTy op,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {
std::optional<Value> maskBaseVal = getMaskBaseVal(op.getMask());
if (!maskBaseVal.has_value())
return failure();
auto resTypes = op->getResultTypes();
auto loc = op->getLoc();
// If else region is empty, it will be fold in canonicalize.
auto ifOp = rewriter.create<scf::IfOp>(loc,
/*resultTypes*/resTypes,
/*cond*/maskBaseVal.value(),
/*addElseBlock*/true);
// 下面这种实现是比较危险的,建议使用 getMaskMutable() 来直接将值clear掉
// Then region.
auto maskIndex = llvm::find_if(op.getOperand(), [&](Value operandVal) {
return operandVal == op.getMask(); }) - op.getOperand().begin();
SmallVector<Value> operand;
operand.reserve(maskIndex);
operand.append(op->operand_begin(), op->operand_begin() + maskIndex - 1);
rewriter.setInsertionPointToStart(&ifOp.getThenRegion().front());
OperationState state(loc, op->getName().getStringRef(), operands,
resTypes, op->getAttrs(), op->getSuccessors());
auto newOp = rewriter.create(state);
rewriter.create<scf::YieldOp>(loc, newOp->getResults());
// Else resgion.
if (!resTypes.empty()) {
// Fill with zero.
rewriter.setInsertionPointToStart(&ifOp.getElseRegion().front());
auto zeroVal = rewriter.create<arith::ConstantOp>(
loc, resTypes.front(), rewriter.getZeroAttr(resTypes.front()));
rewriter.create<scf::YieldOp>(loc, zeroVal);
rewriter.replaceOp(op, ifOp);
return success();
}
rewriter.eraseOp(op);
return success();
}
};
但如果 op 存在 operandSegmentSizes 属性,还需要额外修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
if (auto attr = op->getAttrOfType<DenseI32ArrayAttr>("operandSegmentSizes")) {
auto segments = attr.asArrayRef();
SmallVector<int32_t> newSegments;
newSegments.assign(segments.begin(), segments.end());
for (size_t i = maskIdx; i < segments.size(); ++i) {
newSegments[i] = 0;
}
op->setAttr("operandSegmentSizes",
builder.getDenseI32ArrayAttr(newSegments));
}
但是直接修改 operandSegmentSizes 属性的方法十分危险,且不利于维护,建议使用 MutableOperandRange(见 mlir/include/mlir/IR/ValueRange.h) 直接丢弃该 operand,同时也会修改 operandSegmentSizes 属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// Then region.
op.getMaskMutable().clear();
// For load op, drop the `ohter` operand as well.
if (llvm::isa<triton::LoadOp>(op))
op.getOtherMutable().clear();
auto newOp = rewriter.clone(&op);
...
OpFoldResult
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/OpDefinition.h
OpFoldResult是一个PointUnion,可以是Value,Attribute,也可能是空的(使用其前记得 isNull 函数判断下)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class OpFoldResult : public PointerUnion<Attribute, Value> {
using PointerUnion<Attribute, Value>::PointerUnion;
public:
void dump() const { llvm::errs() << *this << "\n"; }
MLIRContext *getContext() const {
return is<Attribute>() ? get<Attribute>().getContext()
: get<Value>().getContext();
}
};
常见用法:
1
mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/Utils/StaticValueUtils.h
1.Attribute / Value 转为 OpFoldResult
直接包起来
OpFoldResult{b.getI64IntegerAttr(1)}使用
getAsOpFoldResult函数1 2 3
OpFoldResult getAsOpFoldResult(Value val); SmallVector<OpFoldResult> getAsOpFoldResult(ValueRange values); SmallVector<OpFoldResult> getAsOpFoldResult(ArrayAttr arrayAttr);
2.一些op的fold行为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// mlir/lib/Dialect/Complex/IR/ComplexOps.cpp
OpFoldResult NegOp::fold(FoldAdaptor adaptor) {
// complex.neg(complex.neg(a)) -> a
if (auto negOp = getOperand().getDefiningOp<NegOp>())
return negOp.getOperand();
return {};
}
OpFoldResult LogOp::fold(FoldAdaptor adaptor) {
// complex.log(complex.exp(a)) -> a
if (auto expOp = getOperand().getDefiningOp<ExpOp>())
return expOp.getOperand();
return {};
}
3.getAsOpFoldResult(ValueRange values)
遍历values,尝试将value转化为constant Attribute,如果失败则返回value
1
2
3
4
Attribute attr;
if (matchPattern(value, m_Constant(&attr)))
return attr;
return value;
4.std::optional
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
std::optional<int64_t> getConstantIntValue(OpFoldResult v) {
if (auto val = llvm::dyn_cast_if_present<Value>(ofr)) {
APSInt intVal;
if (matchPattern(val, m_ConstantInt(&intVal)))
return intVal.getSExtValue();
return std::nullopt;
}
Attribute attr = llvm::dyn_cast_if_present<Attribute>(ofr);
if (auto intAttr = llvm::dyn_cast_if_present<IntegerAttr>(attr)
return intAttr.getValue().getSExtValue();
return std::nullopt;
}
5.bool isConstantIntValue(OpFoldResult ofr, int64_t value)
PDLL
1
mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/PDL/IR/PDLTypes
常见用法
auto pdlOpType = pdl::OperationType::get(context);
用pdll来实现pattern的match和rewrite
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// PatternRuleImpl.cpp
// 定义这些rewrite和constrain实现
static Operation *tileOpImpl(PDLResultList &results, Value value) {
// insert special rewrite logic here.
Operation *resultOp = ...;
return resultOp;
}
void registerRuleFunctions(RewritePatternSet &patterns) {
auto &patternModule = patterns.getPDLPatterns();
// 这些 pattern 的实现见后文
patternModule.registerRewriteFunction("tileOp", tileOpImpl);
patternModle.registerConstraintFunction("tilingLoopSizeLimit", tilingLoopSizeLimitImpl)
...
}
rewrite pattern impl
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
// help func
static FailureOr<Value> getLastMatchOpAndSetRewriter(
PatternRewriter &rewriter, Operation *op) {
if (auto moduleOp = op->getParentOfType<ModuleOp>()) {
Block &block1 = moduleOp.getRegion().front();
transform::SequenceOp lastSeq;
auto iter = block1.rbegin();
while (iter != block1.rend()) {
if (auto seq = dyn_cast_if_present<transform::SequenceOp>(*iter)) {
lastSeq = seq;
break;
}
++iter;
}
if (lastSeq) {
Block &block2 = lastSeq.getRegion().front();
iter = block2.rbegin();
transform::MatchOp lastMatch;
while (iter != block2.rend()) {
if (auto match = dyn_cast_if_present<transform::MatchOp>(*iter)) {
lastMatch = match;
break;
}
++iter;
}
if (lastMatch) {
rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(lastMatch);
return lastMatch.getResult();
}
}
}
return failure();
}
static Value getTargetHandle(PatternRewriter &rewriter, value &handle,
Operation *op) {
return rewriter.create<transform::MatchOp>(...)
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// rewrite methods
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
static void tileOpImpl(PatternRewriter &rewriter, Operation *op,
ArrayAttr tileSize) {
DBGS() << "Enter rewrite rule [tileOp], with target op: ";
LLVM_DEBUG(op->print(DBGS()));
auto handle = getLastMatchOpAndSetRewriter(rewriter, op); // 当前 transform sequence 中最后一个 matchOp
if (failed(handle)) return;
MLIRContext *context = op->getContext();
auto pdlOpType = pdl::OperationType::get(context);
Value target = getTargetHandle(rewriter, *handle, op); // 生成对target的match op
tileSize = tileSize.empty() ? nullptr : tileSize;
rewriter.create<transform::TileToForallOp>(
rewriter.getUnknownLoc(),
/*resultTypes=*/TypeRange({pdlOpType, pdlOpType}),
/*target=*/target,
/*tile_sizes=*/tileSize,);
}
constrain pattern impl
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
static LogicalResult tilingLoopSizeLimitImpl(PatternRewriter &rewriter,
Operation *root,
Attribute loopPosAttr,
Attribute lowNumAttr,
Attribute highNumAttr) {
DBGS() << "Enter constraint check: [tilingLoopSizeLimitImpl]\n";
LLVM_DEBUG(op->print(DBGS()))
auto loopPosIntAttr = loopPosAttr.dyn_cast_if_present<IntegerAttr>();
auto lowNumIntAttr = lowNumAttr.dyn_cast_if_present<IntegerAttr>();
auto highNumIntAttr = highNumAttr.dyn_cast_if_present<IntegerAttr>();
if (!loopPosIntAttr || !lowNumIntAttr || !highNumIntAttr)
return failure();
auto loopPos = loopPosIntAttr.getInt();
auto lowNum = lowNumIntAttr.getInt();
auto highNum = highNumIntAttr.getInt();
if (auto tilingInterface = llvm::dyn_cast_if_present<TilingInterface>(root)) {
auto ranges = tilingInterface.getIterationDomain(rewriter);
if (loopPos > ranges.size())
return failure();
if (ranges[loopPos].size.is<Attribute>()) {
auto loopLimit =
ranges[loopPos].size.get<Attribute>().cast<IntegerAttr>().getInt();
if (loopLimit >= lowNum && loopLimit <= highNum)
return success();
}
}
return failure();
}
pdll文件定义pattern
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// ==== Rewrite Rule ======================
Rewrite tileOp(op: Op, tileSize: Attr);
// ==== Constraint Rule ======================
Constraint tilingLoopSizeLimit(op:Op, loopPosAttr:Attr, lowNumAttr:Attr, highNumAttr:Attr);
// Constraint + Rewrite -> Patterns
// ==== Patterns ======================
Pattern TileParallelofConvOpUseRange with benefit(9) {
let root = op<linalg.conv_2d_nhwc_fhwc>; // payloadOp
canTileParallel(root); // Constraint1
tilingLoopSizeLimit(root, attr<"1">, attr<"513">, attr<"2000">); // Constraint2
rewrite root with {
tileOp(root, attr<"[1, 6, 1, 4, 1, 1, 1]">);
};
}
pass中parse pdll并解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
// 输入为.pdll文件的路径
// 参考:mlir/lib/Tools/mlir-pdll-lsp-server/PDLLServer.cpp
static inline OwningOpRef<ModuleOp>
parsePdllSourceFile(llvm::StringRef pdllSource, MLIRContext *context) {
std::string errorMessage;
auto memoryBuffer = mlir::openInputFile(pdllSource, &errorMessage);
if (!memoryBuffer)
return OwningOpRef<ModuleOp>();
llvm::SourceMgr sourceMgr;
sourceMgr.AddNewSourceBuffer(std::move(memoryBuffer), llvm::SMLoc());
ods::Context odsContext;
ast::Context astContext(odsContext);
FailureOr<ast::Module *> module = parsePDLLAST(astContext, sourceMgr);
if (failed(module))
return OwningOpRef<ModuleOp>();
return codegenPDLLToMLIR(context, astContext, sourceMgr, **module);
}
struct AutoScheduler : public AutoSchedulerPassBase<AutoScheduler> {
void getDependentDialects(DialectRegistry ®istry) const override {
registry.insert<::mlir::transform::TransformDialect>();
codegen::registerAllDialects(registry);
}
void runOnOperation() override {
...
OwningOpRef<ModuleOp> pdllModuleOp =
parsePdllSourceFile(StringRef(pdllSource), context);
if (!parsePdllSourceFile) {
return signalPassFailure();
}
RewritePatternSet patternSet(context);
PDLPatternModule patternModule(std::move(pdlModuleOp));
patternSet.add(std::move(patternModule));
// Register pattern rules.
registerRuleFunctions(patternSet);
// match and rewrite
...
}
}
匹配 pattern
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
// class element
using PatternStateMap = llvm::DenseMap<const Pattern *, Operation *>;
PatternApplicator matcher;
std::unique_ptr<PatternRewriter> rewriter;
LogicalResult XXXX::applyPatterns(
Operation *module, PatternStateMap &patternStateMap) {
auto callback = [&](Operation *op) {
auto onSuccess = [&](const Pattern &pattern) -> LogicalResult {
patternStateMap[&pattern] = op;
return success();
};
auto canApply = [&](const Pattern &pattern) -> bool {
return patternStateMap.find(&pattern) != patternStateMap.end();
};
if (succeeded(
matcher.matchAndRewrite(op, *rewriter, canApply, {}, onSuccess))) {
return WalkResult::interrupt();
}
return WalkResult::advance();
};
WalkResult walkRes = module->walk(callback);
// 一次只匹配一个 pattern
// apply 成功后 transform ir 就会写到 module 上
return walkRes.wasInterrupted();
}
static LogicalResult applyTransformOps(Operation *module) {
PassManager passManager(module->getContext(),
module->getName().getStringRef(),
OpPassManager::Nesting::Implicit);
passManager.addPass(createTransformDialectInterpreterPass());
passManager.addPass(createTransformDialectErasePass());
return passManager.run(module);
}
LogicalResult XXXX::runLoop(Module module) {
auto *context = module->getContext();
OpBuilder builder(context);
PatternStateMap patternStateMap;
OwningOpRef<ModuleOp> tmpModuleRef(cast<ModuleOp>(module->clone()));
while (true) {
if (failed(applyPatterns(tmpModuleRef->getOperation(), patternStateMap))) {
// No pattern to match.
break;
}
auto seqCount =
cloneAllTransformSequences(module, tmpModuleRef->getOperation());
if (failed(applyTransformOps(tmpModuleRef->getOperation()))) {
popBackTransformSequence(module, seqCount);
tmpModuleRef = ModuleOp(module->clone());
(void)applyTransformOps(tmpModuleRef->getOperation());
}
}
}
Pass
优雅Pass守则
In Short:
- 必须不依赖于当前target的相邻op状态,因为其相邻op可能在多线程的过程中被修改
- 根据当前target的ancestor/parent是可以的
- 不能修改超出当前target作用域的东西(可以理解为顶多只能修改当前target所附带region的部分)
- op上的attr的修改是安全的
- 不能维护全局信息,例如pass之间不能维护一个变量用来传递信息
- 使用attr是可以的
- analysis中也有提供
markAnalysesPreserved接口
详见:
1
mlir/docs/PassManagement.md
写一个 pass
1.Passes.td中定义pass的基本信息(描述、作用对象)
include/xxx/Transforms/Passes.td (xxxx一般为project名字,例如iree,一般也会定义相应的namespace mlir::iree)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
def passNamePass : Pass<"pass-flag">, "该pass的作用对象" > { // 作用域可以为 func::FuncOp 或 mlir::ModuleOp
let summary = "";
let description = [{
more detail
For example, consider the following input:
...
After running, we get the expected:
...
]};
let constructor = "mlir::xxxx::createPassNamePass()";
let options = [
Option<"OptionName", "option-tag", "option-input-type", /*default*/"default-option-input-value",
"Option description.">
];
let dependentDialects = [
// 例如:
"func::FuncDialect";
"linalg::LinalgDialect",
"tensor::TensorDialect",
];
2.Passes.h 中声明pass
include/xxx/Transforms/Passes.h
1
std::unique_ptr<Pass> createPassNamePass();
3.passName.cpp中定义pass的实现
lib/xxx/Transforms/PassName.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
//===- passNamePass.cpp -----------------------------------------*- cpp -*-===//
//
// description
//
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// 头文件,常见的如下
#inlcude "xxxx/xxx/Transforms/Passes.h"
#include "mlir/Dialect/xxx" // #include "mlir/Dialect/SCF/IR/SCF.h"
#include "mlir/IR/BuiltinAttribute.h"
#include "mlir/IR/BuiltinType.h"
#include "mlir/IR/Operation.h"
#include "mlir/IR/Region.h"
#include "mlir/IR/Type.h"
#include "mlir/Pass/Pass.h"
#include "mlir/Support/LLVM.h"
#define DEBUG_TYPE "pass-flag"
using namespace mlir;
using namespace mlir::xxxx;
namespace{
template<class OpTy>
class XXXXPattern : public OpRewritePattern<OpTy> {
using OpRewritePattern<OpTy>::OpRewritePattern;
LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(OpTy op,
PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override {
}
}
// 相关代码runOperation()写在匿名空间,匿名空间可以限制标识符的作用域,防止全局空间污染
struct PassNamePass : public PassNamePassBase<PassNamePass> {
// explicit PassNamePass() = default(option-input-type optionName) {
// this->optionName.setValue(optionName);
// }
explicit PassNamePass() = default;
void runOnOperation() override {
// 根据td中的作用域来返回,如果pass的td定义的作用域是mlir::ModuleOp,则这里返回moduleOp。
// 如果pass.td中没有设置,则返回输入ir的top-level op
auto targetOp = getOperation();
MLIRContext *ctx = targetOp->getContext();
...
// 也可以使用pattern
}
}
}; // end struct
} //namespace
// std::unique_ptr mlir::xxxx::createPassNamePass(option-input-type optionName)
std::unique_ptr mlir::xxxx::createPassNamePass(){
// return std::make_unique<PassNamePass>(optionName);
return std::make_unique<PassNamePass>();
}
4.passName.mlir中添加对该pass的单元测试
mlir/test/XXX/PassName.mlir
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// RUN: mlir-opt -allow-unregistered-dialect %s -pass-pipeline='builtin.module(func.func(passname))' | FileCheck %s
func.func @example() -> () {
...
return ...
}
// CHECK-LABEL: @example
// CHECK-NEXT:
// CHECK-NEXT
使用
mlir-tblgen主动生成pass.h.incmlir-tblgen -gen-op-defs Passes.td -o Passes.h.inc详细查看mlir-tblgen -h | grep gen
Pass infrastructure
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/Pass/Pass.h
mlir/lib/Pass/Pass.cpp
1.在pipeline中添加pass
- addPass
1
2
// unique_ptr 申明独占资源,防止pass之间抢占资源
void addPass(std::unique_ptr<Pass> pass);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
void mlir::bufferization::buildBufferDeallocationPipeline(
OpPassManager &pm, const BufferDeallocationPipelineOptions &options) {
pm.addPass(memref::createExpandReallocPass(/*emitDeallocs=*/false));
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(createOwnershipBasedBufferDeallocationPass(options));
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addPass(createBufferDeallocationSimplificationPass());
pm.addPass(createLowerDeallocationsPass());
pm.addPass(createCSEPass());
pm.addPass(createCanonicalizerPass());
}
- addNestPass: 制定pass的作用op,常见的有FuncOp、ModuleOp,这个一般在
pass.td中就定义该pass的作用域
1
2
3
4
5
6
void addNestedPass(std::unique_ptr<Pass> pass) {
nest<OpT>().addPass(std::move(pass));
}
OpPassManager &nest() {
return nest(OpT::getOperationName());
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
void mlir::tosa::addTosaToLinalgPasses(
OpPassManager &pm, const TosaToLinalgOptions &options) {
if (!options.disableTosaDecompositions)
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(tosa::createTosaOptionalDecompositions());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(tosa::createTosaInferShapesPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(tosa::createTosaMakeBroadcastablePass());
...
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(createCanonicalizerPass());
pm.addNestedPass<func::FuncOp>(tosa::createTosaToLinalg());
}
2.保留当前IR的分析信息
markAllAnalysesPreserved()
markAnalysesPreserved(id)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// If there was no change to the IR, we mark all analyses as preserved.
if (!changed)
return markAllAnalysesPreserved();
// We currently don't remove region operations, so mark dominance as
// preserved.
markAnalysesPreserved<DominanceInfo, PostDominanceInfo>();
Rank
“Rank” 表示数组的维度数量,而 “Dim” 表示数组在某个具体轴上的大小
- MemRefType 和 RankedTensorType 可以getRank():因为都是继承自ShapedType
补充点常用的ShapedType函数
- isDynamicDim(unsigned idx) ←→ getShape()[idx] == ShapedType::kDynamic
- hasStaticShape()
- int64_t getNumDynamicDims()
- getDimSize(unsigned idx)
Range
表示范围
| ValueRange | ValueRange(ArrayRef |
|---|---|
| TypeRange | TypeRange(ArrayRef |
| ValueTypeRange | 代表给定value的type |
| OperandRange | TypeRange(ArrayRef |
| ResultRange | TypeRange(ArrayRef |
| MutableOperandRange | 可以进行修改操作 append / assign / erase |
SymbolTable
1
2
3
mlir/include/mlir/IR/SymbolTable.h
mlir/lib/SymbolTable.cpp
mlir/docs/SymbolsAndSymbolTables.md
Symbol
Symbol 提供了一种非 SSA 机制(SSA机制采用值引用的方法)的引用方法,通过名称引用。SSA 类的值引用生命周期管理比较复杂。
换言之,可以把 Symbol 理解为一种带有名称的操作,例如 func 和 module 上挂的名字,而 SymbolTable 负责记录,其中的所有 Symbol 名称唯一。SymbolTable 能够通过作用域的隔离性,保证多线程环境下的安全性。作为 Symbol 的类必须实现 SymbolOpInterface。
常见的 symbol 有 funcOp、 memref.global
例如
func.callop 的SymbolTable中存在其使用的func.func对象名称(func.func的名字确实不能重复)。
使用 Symbol 的方式访问 global value or vairable,可以实现 multi-threaded compilation without this locking。
(1) SSA 访问
这样会导致 foo 就不能 IsolatedFromAbove,依赖于 %a,且可能影响 %a,所以为了线程安全性,就需要加锁。
1
2
3
4
%a = global xxx
foo {
use %a
}
(2) Symbol 访问
foo 内的操作以 Symbol 的形式使用了全局变量,不能对其进行修改。所以 foo 内依旧保持 IsolatedFromAbove。
1
2
3
4
global "a"
foo {
use "a"
}
嵌套访问的形式也很常见,Symbol 的形式访问并不会影响访问的内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
module @module_symbol {
// This `func.func` operation defines a symbol named `nested_symbol`.
func.func @nested_symbol()
}
// Our `foo.user` operation may refer to the nested symbol, by resolving through
// the parent.
"foo.user"() {uses = [@module_symbol::@nested_symbol]} : () -> ()
在 op 的 liveness 相关计算中常见到
1
mlir/lib/Analysis/DataFlow/DeadCodeAnalysis.cpp
SymbolTable用法
SymBolTable 继承自 TraitBase,用来给 region operation 提供 symbol table 信息的。即定义 SymbolTable 的 op 必须继承 OpTrait::SymbolTable。
一般 func 这里 op 都继承了 SymbolOpInterface。
SymbolDCE pass 应该在有 OpTrait::SymbolTable operation 的开始运行。
- 构建: SymbolTable(Operation *symbolTableOp)
- getSymbolAttrName { return “sym_name”; }
- lookup()
- getOp() : 获得该symbolTable对应的Operation
- SymbolTable::SymbolUse
- getUser() 返回该symbol ref的user operation
SymbolUserMap
表示 a map of symbols to users,前文提到 symbol 是“一种带有名称的操作”, SymbolUserMap 用来存储这种 symbol 的 users
例如消除没有 user 的 memref.global
1
2
3
4
5
6
SymbolTableCollection symbolTable;
SymbolUserMap symbolUsers(symbolTable, root);
root->walk([&](memref::GlobalOp global) {
if (symbolUsers.getUsers(global).empty() && global.isPrivate())
global->erase();
});
Region
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Region.h
mlir/include/mlir/Transforms/RegionUtils.h
region包含若干个block,一般linalgOp都包含一个region
接口
bool hasOneBlock() 常用来判断region内只有一个block,取Block的时候用
a.front()getUsedValuesDefinedAbove(MutableArrayRef
regions, SetVector &values) 收集在regions中使用,但不在region中的blockArg上定义的Value,将其放入values takeBody: 把另外一个region的block占为己有(相当于把另外一个region的block的所有权给拿走了)
newforallOp.getRegion().takeBody(forallOp.getRegion());
- findAncestorOpInRegion: 判断某个 op 是否在region 中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// 返回region包含的最上层op
Operation *Region::findAncestorOpInRegion(Operation &op) {
Operation *curOp = &op;
while (Region *opRegion = curOp->getParentRegion()) {
if (opRegion == this)
return curOp;
curOp = opRegion->getParentOp();
if (!curOp)
return nullptr;
}
return nullptr;
}
判断 userOp 在 ifOp 的哪个 region。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
if (ifOp->isProperAncestor(resUser)) {
if (ifOp.getThenRegion().findAncestorOpInRegion(*resUser) !=
nullptr) {
// The user is inside the ThenRegion of the scf.if.
...
} else {
// The user is inside the ElseRegion of the scf.if.
...
}
}
- getOps() : 获得region内的所有op,有相对次序
for (Operation &op : region.getOps())
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
for (Region *region : regions()) {
std::queue<Operation *>worklist; // 如果不在乎遍历顺序,或者可以按压入顺序来逆序遍历
for (Operation &op : region.getOps()) {
worklist.push(&op);
}
while (!worklist.empty()) {
Operation *op = worklist.front();
worklist.pop();
if (op->getParentRegion() != region)
// 防止某些op提前被修改
continue;
}
...
}
举例:合并多余的barrier op
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
static bool hasReadOrWriteEffect(Operation *op) {
WalkResult ret = op->walk([&](Operation *innerOp) ->WalkResult {
if (auto interface = dyn_cast<MemoryEffectOpInterface>(innerOp)) {
if (interface.hasEffect<MemoryEffects::Read>() ||
interface.hasEffect<MemoryEffects::Write>())
return WalkResult::interrupt();
}
return WalkResult::advance();
});
return ret == WalkResult::interrupt();
}
// 下面的op都是随意的给的
std::optional<Attribute> getExecutorAttr(Operation *op) {
std::optional<Attribute> executor;
bool hasExecutorAttr =
llvm::TypeSwitch<Operation *, bool>(op)
.Case<gpu::BarrierOp, gpu::MemsetOp,
gpu::PrintfOp> ([&](auto oriOp) {
executor = gpu;
return true;
}
.Case<gpu::WrapOp, gpu::AllocOp> ([&](auto oriOp) {
executor = cpu;
return true;
}
.Case<gpu::SubgroupMmaStoreMatrixOp> ([&](auto oriOp) {
executor = oriOp.getExecutorAttr();
return true;
}
.Default([&](Operation *other) {
return false;
});
if (!hasExecutorAttr) {
llvm::SmallDenseSet<Attribute> executorSets;
WalkResult ret = op->walk([&](Operation *innerOp) -> WalkResult {
if (innerOp == op || !hasReadOrWriteEffect(innerOp))
return WalkResult::advance();
auto currentExecutor = getExecutorAttr(innerOp);
if (currentExecutor.has_value()) {
executorSets.insert(currentExecutor.value());
return WalkResult::advance();
}
// 那么就无法判断executor,采取保守
return WalkResult::interrupt();
});
if (ret == WalkResult::advance() && executorSets.size() == 1)
return *executorSets.begin();
}
return executor;
}
bool checkBarriersCanBeCombined(Operation *front,
Operation *backOp, std::optional<Attribute> &recordExecutor) {
bool canBeCombined = true;
auto currentOp = frontOp->getNextNode();
// Combine consecutive barriers.
while (currentOp != backOp) {
// 当barrier之间全为无读写effect的op也可以合并
if (hasReadOrWriteEffect(currentOp)) {
auto currentExecutor = getExecutorAttr(currentOp);
if (!currentExecutor.has_value() ||
(recordExecutor.has_value() &&
(recordExecutor.value() != currentExecutor.value()))) {
canBeCombined = false;
break;
}
if (!recordExecutor.has_value()) {
recordExecutor = curretExecutor;
}
}
currentOp = currentOp->getNextNode();
}
}
static void foldBarrierInFunc(gpu::FuncOp func) {
auto barrierOpVec = llvm::to_vector(func.getOps<gpu::BarrierOp>());
size_t numOfBarrier = barrierOpVec.size();
if (numOfBarrier < 2)
return;
llvm::SmallDenseSet<Operation *> opsToCombine;
size_t idxOfFront = 0;
for (size_t idxOfBack = 1; idxOfBack < numOfBarrier; ++idxOfBack) {
gpu::BarrierOp frontOp = barrierOpVec[idxOfFront];
gpu::BarrierOp backOp = barrierOpVec[idxOfBack];
std::optional<Attribute> recordExecutor;
bool canBeCombined =
checkBarriersCanBeCombined(frontOp, backOp, recordExecutor);
if (recordExecutor.has_value() && canBeCombined = true) {
size_t idxOfNext = idxOfBack + 1;
if (idxOfNext < numOfBarrier) {
canBeCombined = checkBarriersCanBeCombined(backOp,
barrierOpVec[idxOfNext],
recordExecutor);
}
}
if (canBeCombined) {
opsToCombine.insert(backOp);
} else {
// Update the idx of frontOp.
idxOfFront = idxOfBack;
}
}
IRRewriter rewriter = IRRewriter(func->getContext());
for (auto barrierOp : opsToCombine) {
rewriter.eraseOp(barrierOp);
}
}
inline region
若需要创建新 resTys 的 op,还需要将原先的 region 给转移
- if op
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
bool hasElseRegion = !op.getElseRegion().empty();
auto ifOp = rewriter.create<scf::IfOp>(loc, newResultTypes,
op.getCondition(), hasElseRegion);
// Inline if region and legalize yield op.
rewriter.inlineRegionBefore(op.getThenRegion(),
&ifOp.getThenRegion().back());
rewriter.eraseBlock(&ifOp.getThenRegion().back());
Block *thenBlock = &(ifOp.getThenRegion().front());
// legalizeYieldOp 用于保证 res 合法
legalizeYieldOp(loc, rewriter, thenBlock);
if (hasElseRegion) {
rewriter.inlineRegionBefore(op.getElseRegion(),
&ifOp.getElseRegion().back());
rewriter.eraseBlock(&ifOp.getElseRegion().back());
Block *elseBlock = &(ifOp.getElseRegion().front());
legalizeYieldOp(loc, rewriter, elseBlock);
}
- for op
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
auto forOp = rewriter.create<scf::ForOp>(loc, lb, ub, st, newInits);
// Clone inner op in region.
Block *oldBlock = &(op.getRegion().front());
Block *newBlock = &(forOp.getRegion().front());
rewriter.setInsertionPointToStart(newBlock);
IRMapping mapping;
for (const auto &pair : llvm::zip(op.getRegion().getArguments(),
forOp.getRegion().getArguments())) {
Value oldBbArg = std::get<0>(pair);
// 由于 iter_args type 改变,所以 newRegion 的 bbarg type 也会改变,所以需要对应进行修改
Value newBbArg = legalizeVals(std::get<1>(pair));
mapping.map(oldBbArg, newBbArg);
}
if (op.getRegionIterArgs().empty()) {
// If there is iter_args, the builder of scf.for will usually implicitly
// add a scf.yield operation with no operands for you to ensure the
// validity of the IR. If we clone the terminator of the block at this
// time, there would be two yields in the block.
for (Operation &operation : oldBlock->without_terminator()) {
rewriter.clone(operation, mapping);
}
} else {
for (Operation &operation : *oldBlock) {
rewriter.clone(operation, mapping);
}
legalizeYieldOp(loc, rewriter, newBlock);
}
SideEffect
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/Interfaces/SideEffectInterfaces.h
mlir/lib/Interfaces/SideEffectInterfaces.cpp
sideeffect 是一种用于表示函数或操作可能引起的副作用的概念。副作用是指对程序状态的任何更改,这可能包括但不限于内存写入、I/O 操作、全局状态的更改等。
sideeffect 通常与函数签名或操作的属性一起使用,以指定可能的副作用。对优化很重要
读写 side-effect 在程序中可能会导致一些问题,例如:
- 并发问题: 多个线程同时访问和修改共享状态时可能导致竞态条件和数据竞争问题。
- 可变性引入的不确定性: 当代码的行为依赖于外部状态时,其行为可能不确定,因为外部状态可能会在代码执行过程中发生变化。
因此,在编写代码时,需要谨慎处理读写 side-effect,尽量减少对共享状态的依赖,使用不可变数据结构和函数式编程技术可以帮助减少 side-effect 带来的问题。
一些常见的 “no side-effect” 操作:
- 纯函数(Pure Functions): 纯函数是指没有副作用的函数,它的输出只取决于输入参数,不会影响程序的状态或外部环境。在纯函数中,不会对传入的参数进行修改,并且每次调用都会返回相同的结果。该op 可以被 CSE 和 DCE
- 访问不可变数据结构: 如果在代码中只读取不可变数据结构(如不可变数组、元组、字符串等),则这些操作通常不会引起副作用。因为不可变数据结构的内容在创建后是不可更改,因此不会影响其他部分或外部环境。
- 访问只读变量或常量: 如果在代码中只读取只读变量或常量,而不对其进行修改,则这些操作也不会引起副作用。只读变量或常量的值在初始化后是不可更改的。
- 纯函数式编程操作: 在纯函数式编程范式中,许多操作都是不可变的,因此它们通常不会引起副作用。这包括函数组合、映射、过滤等操作。
见 Interface 节中 MemoryEffectOpInterface 相关用法
TableGen
基础语法 见 LLVM TableGen 一文
可变/可选参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
def AddOp : ToyOp<"add", [Pure]> {
let summary = "add operation";
// Variadic描述可变参数
let arguments = (ins Variadic<AnyInteger>:$inputs);
let results = (outs AnyInteger:$result);
}
def ReturnOp : ToyOp<"return", [Terminator, ReturnLike]> {
let summary = "return operation"
// Optional描述可选参数,在对应的cpp中也用optional声明该变量
let arguments = (ins Optional<AnyInteger>:$data);
}
def HWRegOp : ToyOp<"reg"> {
let summary = "hardware register";
let arguments = (ins I1:$clock, AnyInteger:$input, Optional<I1>:$reset, UnitAttr:$is_public);
let results = (outs AnyInteger:$result);
// [{}] 来表示长文本
// (`a`, $a)表示分组,当^存在时,只有对应的 Optional 或 UnitAttr 存在的时候,才会输出这个分组。
let assemblyFormat = [{
(`public` $is_public^)? $input
`clock` $clock
(`reset` $reset^)?
attr-dict `:` functional-type($input, results)
}];
}
输出格式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
def AddOp : ToyOp<"add", [Pure]> {
let summary = "add operation";
let arguments = (ins Variadic<AnyInteger>:$inputs);
let results = (outs AnyInteger:$result);
// 原本 %0 = “toy.add”(%a, %b) : (i32, i32) -> (i32)
let assemblyFormat = "$inputs attr-dict `:` type($inputs) `->` type($result)";
// 现在下面的也可行 %0 = toy.add %a, %b : i32, i32 -> i32
}
OpVerifier
首先在td中声明 hasVerifier=true
1
2
3
4
5
6
def SubOp : ToyOp<"sub", [Pure]> {
let summary = "sub operation";
let arguments = (ins AnyInteger:$lhs, AnyInteger:$rhs);
let results = (outs AnyInteger:$result);
let hasVerifier = true;
}
然后在toy.cpp中写该op的verifier
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
using namespace mlir;
LogicalResult SubOp::verify() {
if (getLhs().getType() != getRhs().getType())
return this->emitError() << "Lhs Type " << getLhs().getType()
<< " not equal to rhs " << getRhs().getType();
return success();
}
builder
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
def SubOp : ToyOp<"sub", [Pure]> {
let summary = "sub operation";
let arguments = (ins AnyInteger:$lhs, AnyInteger:$rhs);
let results = (outs AnyInteger:$result);
let builders = [
OpBuilder<
(ins "mlir::Value":$lhs, "mlir::Value":$rhs),
"build($_builder, $_state, lhs.getType(), lhs, rhs);"
>
];
let hasVerifier = true;
}
例如: fuse-into-containing-op 的定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
def FuseIntoContainingOp :
Op<Transform_Dialect, "structured.fuse_into_containing_op",
[DeclareOpInterfaceMethods<TransformOpInterface,
["allowsRepeatedHandleOperands"]>,
DeclareOpInterfaceMethods<MemoryEffectsOpInterface>,
ReportTrackingListenerFailuresOpTrait]> {
let summary = "Fuse a producer into a containing operation.";
let description = [{
...
}];
let arguments = (ins TransformHandleTypeInterface:$producer_op,
TransformHandleTypeInterface:$containing_op);
let results = (outs TransformHandleTypeInterface:$fused_op,
TransformHandleTypeInterface:$new_containing_op);
let assemblyFormat = "$producer_op `into` $containing_op attr-dict "
" `:` functional-type(operands, results)";
let builders = [
OpBuilder<(ins "Value":$producerOp, "Value":$containingOp)>
];
}
FuseIntoContainingOp继承自Op,这是所有op的基类,实现了一些共有的方法1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
template <typename ConcreteType, template <typename T> class... Traits> class Op : public OpState, public Traits<ConcreteType>... { public: /// Inherit getOperation from `OpState`. using OpState::getOperation; using OpState::verify; using OpState::verifyRegions; ...
DeclareOpInterfaceMethods用来声明一个op继承了某个interface,并需要对其重写
使用 DeclareOpInterfaceMethods 声明的interface时需要被重写覆盖,而其他都是默认继承(采用默认实现)。
builders用来声明一个op的builder。这里只是声明好了接口,要在其对应的文件中写一下实现1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
void transform::FuseIntoContainingOp::build(OpBuilder &builder, OperationState &result, Value producerOp, Value containingOp) { result.addOperands({producerOp, containingOp}); auto resultType = transform::AnyOpType::get(builder.getContext()); result.addTypes({resultType, resultType}); }
TD中定义RewritePattern
上述TD都是用来定义op、dialect、pass的玩法,其实还可以用它来写一些RewritePattern,本质上也是match+rewrite,例如Triton官方的lib/Dialect/Triton/Transforms/Combine.td。
例如用 TD 写一些 arith op 的变换 pattern
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
include "mlir/IR/PatternBase.td"
include "mlir/Dialect/Arith/IR/ArithOps.td"
include "mlir/Dialect/Math/IR/MathOps.td"
// select(cmpi(uge or ugt, x, y), x, y) -> maxui(x, y)
def SelectOfCmpIToMaxUI0:
Pat<(SelectOp (Arith_CmpIOp $pred, $x, $y), $x, $y),
(Arith_MaxUIOp $x, $y),
[(Constraint<
CPred<"$0.getValue() == arith::CmpIPredicate::uge || "
"$0.getValue() == arith::CmpIPredicate::ugt">> $pred)]>;
// 把 uge or ugt 换成 sge or sgt,maxui 换乘 maxsi
// select(cmpi(ule or ult, y, x), x, y) -> maxui(x, y)
def SelectOfCmpIToMaxUI1:
Pat<(SelectOp (Arith_CmpIOp $pred, $y, $x), $x, $y),
(Arith_MaxUIOp $x, $y),
[(Constraint<
CPred<"$0.getValue() == arith::CmpIPredicate::ule || "
"$0.getValue() == arith::CmpIPredicate::ult">> $pred)]>;
// 把 ule or ult 换成 sle or slt,maxui 换乘 maxsi
tensor
mlir 的框架中主要有两种数据抽象, tensor 和 memref(aka. buffer),这两者分别对应着 ML 编译器中的高层抽象(torch.tensor)和传统低级编译器的低层抽象 memory buffer。tensor 和 memref 之间通过 bufferization 衔接。Linalg Dialect 中很多 op 的 operand 可以是 tensor 也可以是 memref。
- 相同点:都可以用来表示算子的operand
- 不同点:
- tensor 语义上只能被定值一次,即声明的那一次,和 SSA 的定义有点相似。(SSA IR 要求每个变量只能有一次值域,且使用前需要先定义)
- memref 是可变的,可以被多次 def,并且许多 memref 是可能存在 alias 关系,所以在 data flow analysis 中需要考虑 alias analysis。
- tensor 上的 rewrite 更简单,因为 tensor 操作都没有 side-effect,而 memref 操作大概率有。
- memref 中 ir 的顺序很重要,移动 ir 可能导致程序语义改变,所以 clone 行为要注意。而 tensor 中的 clone 行为一般没问题。
- memref 上的读写和依赖分析会更加复杂,因为有 alias 行为,所以需要找到所有的定值行为。
对于 ir-on-memref,我们不能轻易改变 ir 的相对位置,例如以下情况,我们不能将 %load 直接拷贝到 scf.forall 的body中,因为 %load 到 scf.forall 之间可能存在对 %alloc 的写 def %alloc。
1
2
3
4
%load = memref.load %alloc
// def %alloc
scf.forall
use %load
但是在 ir-on-tensor 中,这样的 clone 行为是可以的,因为 tensor 只会有一次定值(自其创建后),不会被改变。我们从下面的 ir 的 a、b、c 三个点去获得 extract 的值,都是相同的,都是源自于 %1 = tensor.empty 创建时获得的随机值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
%1 = tensor.empty
%extract = tensor.extract %1 // a 点
%fill = linalg.fill outs(%1)
%extract = tensor.extract %1 // b 点
%map = linalg.map outs(%1)
%extract = tensor.extract %1 // c 点
test
当我们增加一个新feature后,需要添加对应的测试文件。
以mlir/test/Dialect/Linalg/decompose-ops.mlir为例:
(0) 文件开头 // RUN: opt_name -pass-name -split-input-file %s | FileCheck %s
FileCheck 后可以所使用 check-prefix 来自定义 CHECK 的头
1
2
// RUN: mlir-opt -test-linalg-decompose-ops -cse -split-input-file %s | FileCheck %s
// RUN: mlir-opt -test-linalg-decompose-ops=remove-dead-args-and-results -cse -split-input-file %s | FileCheck %s --check-prefix=CANONICALIZECHECK
(1) CHECK : 最通用
1
2
// CHECK: %[[ALLOC0:.*]] = memref.alloc() : () -> memref<32xf32>
// 检查使用它时 %[[ALLOC0]]
(2) CHECK-LABEL : 一般后接func名
1
// CHECK-LABEL: func @simple_op(
(3)CHECK-SAME : 上一个CHECK的延伸,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// CHECK-LABEL: func.func @forward_no_view(
// CHECK-SAME: %[[ARG0:[a-zA-Z0-9_]+]]: memref<32xf32>
// CHECK-SAME: %[[ARG1:[a-zA-Z0-9_]+]]: i1
// CHECK: %[[GENERIC1:.+]]:3 = linalg.generic
// CHECK-SAME: [#[[MAP0]], #[[MAP1]], #[[MAP2]], #[[MAP3]], #[[MAP0]], #[[MAP3]]]
// CHECK-SAME: ["parallel", "parallel"]
// CHECK-SAME: ins(%[[ARG0]], %[[ARG1]], %[[ARG2]] :
// CHECK-SAME: outs(%[[INIT1]], %[[INIT2]], %[[INIT1]] :
(4) CHECK-NEXT : 检查紧挨上一个ir的ir
(5) CHECK-DAG : 不考虑检查的顺序,对于 arith.constant 这样的,最好这么用 CHECK-DAG 检查,因为 llvm 版本更新后 constant 生成的位置可能改变。
- 测试方法
1
build/bin/llvm-lit mlir/test/Dialect/Linalg/decompose-ops.mlir -a
综合例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// CHECK-LABEL: func.func @forward_no_view(
// CHECK-SAME: %[[ARG0:[a-zA-Z0-9_]+]]: memref<32xf32>
// CHECK-SAME: %[[ARG1:[a-zA-Z0-9_]+]]: i1
// CHECK: %[[ALLOC0:.*]] = memref.alloc() : () -> memref<32xf32>
// CHECK-NOT: memref.copy
// CHECK: cf.cond_br %[[ARG1]], ^bb1(%[[ALLOC0]], %[[ARG0]] : memref<32xf32>, memref<32xf32>), ^bb2(%[[ARG0]] : memref<32xf32>)
// CHECK: ^bb1(%[[VAL0:.*]]: memref<32xf32>, %[[VAL1:.*]]: memref<32xf32>):
// CHECK: %[[ALLOC1:.*]] = memref.alloc() : () -> memref<32xf32>
// CHECK: vector.xxx %[[ALLOC1]], %[[VAL1]], []) : (memref<32xf32>, memref<32xf32>) -> ()
// CHECK: cf.br ^bb2(%[[ALLOC1]] : memref<32xf32>)
(6) expected-error:用来检查代码中的检查行为是否生效
1
// expected-error @+1
Trait
1
mlir/include/mlir/IR/OpDefinition.h
OpTrait
用 mightHaveTrait 、 hasTrait 来判断
一般以 trait 的形式写在 op 定义的 td 中,当 op 不符时会报错。
1.SameTypeOperands : 所有operand type相同
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
class Arith_CompareOp<string mnemonic, list<Trait> traits = []> :
Arith_Op<mnemonic, traits # [Pure, SameTypeOperands, TypesMatchWith<
"result type has i1 element type and same shape as operands",
"lhs", "result", "::getI1SameShape($_self)">]> {
let results = (outs BoolLike:$result);
let assemblyFormat = "$predicate `,` $lhs `,` $rhs attr-dict `:` type($lhs)";
}
2.SameOperandsAndResultType:操作数和返回值有相同的类型,使用后 assemblyFormat 里就只需要写任何某一个操作数的类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
class Math_IntegerBinaryOp<string mnemonic, list<Trait> traits = []> :
Math_Op<mnemonic, traits # [SameOperandsAndResultType]> {
let arguments = (ins SignlessIntegerLike:$lhs, SignlessIntegerLike:$rhs);
let results = (outs SignlessIntegerLike:$result);
let assemblyFormat = "$lhs `,` $rhs attr-dict `:` type($result)";
}
3.InferTypeOpInterface :通过输入和 attr 的类型推断返回值类型,自己写推断函数
4.InferTypeOpAdaptor :与上一个相似,但封装了一个 Adaptor,写起来会更简单
5.ConstantLike : 代表该op是个constant op
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
def LLVM_ConstantOp
: LLVM_Op<"mlir.constant", [Pure, ConstantLike]>,
LLVM_Builder<[{$res = getLLVMConstant($_resultType, $value, $_location,
moduleTranslation);}]>
{
let summary = "Defines a constant of LLVM type.";
...
6.IsTerminator : 表示该op是一个block的最后一个操作(terminator operations)
一般pass处理op时都要避免处理带有该 trait 的op
1
2
3
if (op->hasTrait<OpTrait::IsTerminator>()) {
return;
}
- IsIsolatedFromAbove :表示该op不会读取或修改其父操作的任何值,有这个trait的op是不能被schedule的
找到op的符合条件的parentOp作为基点来计算liveness,带有该 trait 的op一般可以理解为是 isolateOp
1
2
3
Liveness liveness(op->getParentWithTrait<OpTrait::IsIsolatedFromAbove>());
Block *block = op->getBlock();
const LivenessBlockInfo *blockInfo = liveness.getLiveness(block);
trait vs OpInterface
trait 一般用来检查一个 op 是否实现了一个 trait,相当于concrete Op without virtual methods 的一个基类,一般就用在 op 的 verify。
OpInterface 都带有 trait,提供了多态,相当于 op with virtual methods 的一个基础类,例如 CopyOpInterface。
transform dialect
transform Interface
1
mlir/include/mlir/Dialect/Transform/Interfaces/TransformInterfaces.h
transform IR: 实现 transformOpInterface 和相关的数据结构的op
payload IR: transfromations apply的对象
transform IR 应用在 payload IR(operations) 对应的 values 上,这些value又称为 handle。这些tansform IR也能应用在 Attribute 上,例如对module内的op进行排序,以 op-indexing 来作为handle。
transform op在应用时,一般调用 apply方法,该方法需要传入三个元素
1
2
3
4
DiagnosedSilenceableFailure
transform::FuseIntoContainingOp::apply(transform::TransformRewriter &rewriter,
transform::TransformResults &results,
transform::TransformState &state) {
1.transform::TransformRewriter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
class TransformRewriter : public RewriterBase {
protected:
friend class TransformState;
public:
// notify给定的op已经被另一个op替换了,应该修改handle和payload(ops/val)之间的map
LogicalResult notifyPayloadOperationReplaced(Operation *op,
Operation *replacement);
2.transform::TransformResults
1
2
3
4
class TransformResults {
friend class TransformState;
public:
// 各种set方法...
常用 RaggedArray 数据结构, RaggedArray 表示2D数组,每行元素连续,每列元素并不固定
3.transform::TransformState
Operation *getTopLevel : topLevel包含all payload IR,一般来说是一个moduleOp。当transform ir应用在全局使用
- getPayloadOps : 返回给定operand的对应payloadOps。当transform ir应用在特定的handle使用
定义
1 2
auto getPayloadOps(Value value) const { ArrayRef<Operation *> view = getPayloadOpsView(value);
使用
1 2 3
auto targetOps = state.getPayloadOps(getTarget()) auto producerOps = state.getPayloadOps(getProducerOp()); auto containingOps = state.getPayloadOps(getContainingOp());
ArrayRef<Attribute> getParams(Value value): 返回传入transform ir中,给定operand对应的参数(都是以Attribute的形式传入的,例如tile_size)1 2 3 4
auto tileSizeIntAttr = tileSizeAttr.dyn_cast_or_null<IntegerAttr>(); if (!tileSizeIntAttr) return failure(); auto tileSize = tileSizeIntAttr.getInt();
linalg transformOp
1
mlir/lib/Dialect/Linalg/TransformOps/LinalgTransformOps.cpp
常见op(详细请学习https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/Dialects/Transform/)
- transform.structured.match
其他transform ir使用前一般都要先match。 ir中可能包含多个同名op,所以可以通过opIndexing来锁定handle。
- transform.structured.tile_reduction_using_for
对reduction轴的tile
继承了 TilingInterface 的op都可以进行tile,每个可以tile的维度属于parallel或reduction
transform.structured.tile_reduction_using_forall
transform.structured.tile_using_forall
个人理解:forall region内的计算可以并行,for region内的计算不能并行
- transform.structured.fuse_into_containg
要求producer op一定是 linalg::::GenericOp ,常见的linalgOp都可以表示为linalg.generic
Type
Value 必然包含 Type,Type 也可以作为 Attribute 附加在 Operation 上
常见类型
1.ShapedType
- ShapedType::kDynamic 用于判断某个数不是
? - isDynamicDim(i)
- getNumElements(ArrayRef
shape) 获得给定 shape 所表示的元素个数 - 当Type满足
!llvm::isa<BaseMemRefType, TensorType>(type)时,认为该type是个scalar
2.TensorType
- kind: RankedTensorType / UnrankedTensorType
- function:
- hasRank() -> bool
- getShape() -> ArrayRef
- getElementType() -> Type
- getElementTypeBitWidth()
- clone(ArrayRef
shape, Ttpe elemType) -> RankedTensorType
3.BaseMemRefType
- kind: MemRefType / UnrankedMemRefType
- function: 大部分和 TensorType 相同,继承自 ShapedType的
- clone(ArrayRef
shape, Ttpe elemType) -> MemRefType - getMemorySpace() -> Attribute
- getMemorySpaceAsInt -> unsigned
- clone(ArrayRef
3.MemRefType
- getLayout() -> MemRefLayoutAttrInterface
- isIdentity() : result type has no offset.
- 当MemRefType不带layout的时候返回true
- 判断之前先将
MemRefType规范化一下canonicalizeStridedLayout
- isIdentity() : result type has no offset.
获得dim
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SmallVector<Value, 4> dynamicOperands; for (int i = 0; i < memrefType.getRank(); ++i) { if (!memrefType.isDynamicDim(i)) continue; Value dim = rewriter.createOrFold<memref::DimOp>(loc, op.getInput(), i); dynamicOperands.push_back(dim); }
- getStridesAndOffset(MemRefType t, SmallVectorImpl
**&**strides, int64_t **&**offset) - 对于 identity layout,也能拿到 strides 和 offset
- canonicalizeStridedLayout(MemRefType t) -> MemRefType : 标准化t的layout格式,如果能canonicalize成静态的就没问题,否则返回MemRefType的layout将是affineMap的形式
例: bufferize时创建memref
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
auto bufferType = cast<MemRefType>(buffer.getType());
MemRefType resultType;
if (bufferType.getLayout().isIdentity()) {
// Standard layout: result type has no offset.
MemRefLayoutAttrInterface layout;
resultType = MemRefType::get({}, tensorResultType.getElementType(),
layout, bufferType.getMemorySpace());
} else {
// Source memref has a layout map: result type has the same offset as
// the source type.
SmallVector<int64_t> strides;
int64_t offset;
if (failed(getStridesAndOffset(bufferType, strides, offset)))
return failure();
resultType = MemRef::get(
{}, tensorResultType.getElementType,
StrideLayoutAttr::get(op->getContext(), offset, {}),
bufferType.getMemorySpace());
}
常用方法
src -> type (Value::getType())
- dyn_cast
() / dyn_cast - ShapedType
- getElementTypeBitWidth
- getRank
- getShape: 当该type为ranked返回 ArrayRef
,否则assert - isDynamicDim / getNumDynamicDims / getDynamicDimIndex
- getElementTypeOrSelf:获得当前 Type 的 elementType
- mlir/include/mlir/IR/TypeUtilities.h 中的一些函数
- verifyCompatibleShape(Type lhs, Type rhs) : 比较两个Type的shape是否一致,不关心elemType
tiling
1
mlir/lib/Dialect/Linalg/Transforms/Tiling.cpp
常见概念
- TilingInterface:对于有该interface的op可以cast成该interface
llvm::cast<TilingInterface>(op)- getLoopIteratorTypes:每个元素为utils::IteratorType,表示为utils::IteratorType::parallel或utils::IteratorType::reduction
- getIterationDomain:每个元素是一个Range,Range中有三个元素(offset,size,stride),都是 OpFoldResult
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
OpBuilder builder(op);
TilingInterface tilingOp = mlir::cast<TilingInterface>(op);
SmallVector<Range> loopRanges = tilingOp.getInterationDomain(builder);
int64_t setTileSize = xxx; // 认为设置一个期望的 tile_size
for (Range range : loopRanges) {
if (auto intAttr = mlir::dyn_cast<Attribute>(range.size)) {
tileSize = std::min(setTileSize, mlir::cast<IntegerAttr>(intAttr).getInt());
}
}
Value
value 只可能表现为 BlockArgument 和 OpResult 两种形式,所以从 value 找其对应 operation 的方法:
常用方法
- getDefiningOp: BlockArgument 返回 null
- getOwner()
- 对于 OpResult :返回拥有这个result的Operation。
getArgNumber - 对于 BlockArgument :返回拥有这个blockarg的Block。
getResultNumber
- 对于 OpResult :返回拥有这个result的Operation。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// Try to get a memory effect interface for the parent operation.
Operation *op;
if (BlockArgument arg = dyn_cast<BlockArgument>(value))
// getParentOp会返回包含该block的最近Operation
op = arg.getOwner()->getParentOp();
else
op = cast<OpResult>(value).getOwner();
MemoryEffectOpInterface interface = dyn_cast<MemoryEffectOpInterface>(op);
if (!interface)
return failure();
- getUses():返回 OpOperand 的迭代器,返回使用了这个value的OpOperand集合
OpOperand &operand : value.getUses()
- getUsers():返回 Operation 的迭代器 ,返回仅包括直接依赖于该value的其他operation
- user_iterator相当于对use_iterator使用getOwner()
- use.getOwner() —> Operation*
修改value
- replaceAllUseWith(Value newValue)
- replaceAllUsesExcept(Value newValue, Operation *exceptedUser)
相关类
- TypeValue
TypeValue 继承自 Value,有静态已知的 Type(使用 getType()) 获取,避免了普通 value getType() 后还要进行 case。
ValueBound
1
mlir/Interfaces/ValueBoundsOpInterface.h
常用来估算Value的某个index的LB和UB,每个Dialect需要自己实现这个Interface,会递归调用
Visitor
1
2
mlir/include/mlir/IR/Visitors.h
mlir/lib/IR/Visitors.cpp
用法
1
2
3
4
Operation a;
WalkResult ret = a.walk<WalkOrder::PreOrder>([&](Ty opOfTy) -> WalkResult {
...
});
Ty: 一般为Operation *,Block *,Region *,FuncOpInterface, 直接是opname (比如 memref.alloc)WalkResult: Interrupt, Advance, SkipWalkOrder: walk 的次序,PreOrder或PostOrder,默认PostOrder(region -> block -> op,即先内部最后op本身)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
ModuleOp m = getOperation();
// 本身 (moduleOp)先 dump,自外而内
m->walk<WalkOrder::PreOrder>([&](Operation *op) {
op->dump();
});
// nestedOp 先 dump,最后是本身 (moduleOp),自内而外
m->walk<WalkOrder::PostOrder>([&](Operation *op) {
op->dump();
});
// 默认 walkorder是PostOrder
m->walk([&](Operation *op) {
op->dump();
});
wasInterrupted(),wasSkipped()判断 walk 的结果(返回值)
clang code style
mlir的代码一般都得准守clang的format,简单的话可以使用 clang-format 工具
- 设置代码界限标识
一般clang format以80字符为换行界限,所以可以在vscode中设置显示提示竖线
- 在设置中搜索
editor.rulers - 在
setting.json中添加
1
2
3
4
5
"[cpp]": {
"editor.rulers": [
{ "column": 80, "color": "#ff0000" }
]
},
- 人为控制clang format开关
可以通过注释来实现
1
2
3
4
5
// clang-format off
patterns.add<
AffineVectorLoadLowering,
AffineVectorStoreLowering>(patterns.getContext());
// clang-format on
code tips
好用的pass
mlir-print-ir-after-all: 打印每次pass后的结果mlir-timing: 输出每个pass的耗时和百分比
coding优化
重开销类型返回 -> 引用传递
如果需要从函数中获得一个重开销数据结构的对象,那么函数使用引用传递,不要返回类型,会增加拷贝开销
1
2
3
4
5
SmallVector<Operation *> func(xxx);
- >
void func(xxx, SmallVector<Operation *> &res);
Operation* / Value 这类都是比较重开销的数据结构,但如果是 S mallVector
不会被修改的SmallVector -> ArrayRef
- 传递一个不会被修改的SmallVector对象可以使用ArrayRef作为形参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
// const llvm::SmallVector<Ty> & -> ArrayRef<Ty>
void func(const SmallVector<Operation *> &input);
->
void func(ArrayRef<Operation> input);
循环变量类型static_cast
for 循环中的循环变量类型使用 size_t,其常用来表示 一个数组的下标或对象的大小。在下面的代码中如果循环变量 i的类型使用 int64_t则会出现warning。
1
for (size_t i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i)
- 如果有需要使用
i和int64_t类型比较的时,就用static_cast<int64_t>(i) - 也可以一开始就将循环变量定义为
int64_t(推荐)
1
for (int64_t i = 0; i < static_cast<int64_t>(a.size()); ++i)
- 迭代变量i推荐使用
++i
i++可能会产生一个临时变量来保留前值,而++i并不会有这样的开销。虽然现代编译器一般能消除此类影响。
循环中的vec查找行为 -> set
如果需要在循环中查找,建议使用 DenseSet, DenseMap 类数据结构, contains, find, count等操作开销都小(也可以llvm::sort后查找)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
for(int64_t i = 0; i < static_cast<int_64>(a.size()); ++i) {
if (llvm::find(visitedIndexesVec, i) != visitedIndexesVec.end()) {
...
// 使用DenseSet 数据结构
for(int64_t i = 0; i < static_cast<int_64>(a.size()); ++i) {
if (visitedIndexesSet.contains(i)) {
...
// sort后顺序访问,llvm::stable_sort是稳定排序的版本
llvm::sort(visitedIndexesVec);
for(int64_t i = 0, index = 0; i < static_cast<int_64>(a.size()); ++i) {
if (index < static_cast<int64_t>(visitIndexesVec.size()) &&
visitedIndexesVec(index) == i) {
index++;
}
常用reserve来为SmallVector预分配size
防止每次压入后动态扩张size带来的开销
如果预先不确定需要用多大,也可以先分配4
1
SmallVector<Operation *, 4>
常用code
重排序 applyPermutationToVector
1
2
3
4
5
#include "mlir/Dialect/Utils/IndexingUtils.h"
auto srcShape = srcType.getShape();
SmallVector<int64_t> newShapes(srcShape.begin(), srcShape.end());
// New dimension information after translation.
applyPermutationToVector(newShapes, permutation); // permutation是shape的新序列
lambda函数编程习惯
1
2
3
4
5
6
// [] : 捕获列表,可以是值捕获、引用捕获或者不捕获任何变量
[capture clause](parameters) -> return_type {
// Lambda函数体
// 可以访问外部变量,参数等
return expression; // 可选
};
用 [&] 可以捕获外面的值,如果lambda函数内使用外面的值较少,可以直接加在 [] 内
最好指定输出格式
1
2
3
auto getReassociations = [&](const DenseSet<int64_t>& dimIndexSet) -> SmallVector<ReassociationIndices> {
// `const SmallVector<int64_t>&` -> `ArrayRef<int64_t>`
auto getNewPermutation = [](const SmallVector<int64_t>& relativeOrder) -> SmallVector<int64_t> {
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
llvm::for_each(relativeOrder, [](int64_t i) {llvm::outs() << i << " ";});
llvm::all_of(llvm::zip(array, array.slice(1)), [](const auto& pair) {
return std::get<0>(pair) <= std::get<1>(pair);
});
llvm::find_if(shapeIndexs, [&](int64_t shapeIndex) {
return !oneSizeDimIndexsSet.count(shapeIndex);
});
创建一个包含dynamic shape的tensor.empty
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
SmallVector<OpFoldResult> newShapes;
for (const auto &shape : llvm::enumerate(collapseResShape)) {
if (ShapedType::isDynamic(shape.value())) {
newShapes.emplace_back(rewriter.createOrFold<tensor::DimOp>(
loc, collapseRes, shape.index()));
continue;
}
newShapes.emplace_back(rewriter.getIndexAttr(shape.value()));
}
rewriter.create<tensor::EmptyOp>(loc, newShapes, srcType.getElementType());
判断输入是否为升序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
auto isIncremental = [](llvm::ArrayRef<int64_t> array) {
if (array.size() <= 1) {
return true;
}
return llvm::all_of(llvm::zip(array, array.slice(1)),
[](const auto &pair) {
return std::get<0>(pair) <= std::get<1>(pair);
});
};
输出SmallVector a的元素相对大小次序
输入一个SmallVector
输入 a = {3, 6, 4, 0} 则输出 b={1, 3, 2, 0}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
auto getNewOrder = [](const SmallVector<int64_t> &relativeOrder)
-> SmallVector<int64_t> {
SmallVector<int64_t> sortOrder = relativeOrder;
llvm::sort(sortOrder);
SmallVector<int64_t> res;
llvm::transform(relativeOrder, std::back_inserter(res),
[&](int64_t num) {
return llvm::find(sortOrder, num) - sortOrder.begin();
});
return res;
};
定义一个driver来递归地处理func中符合条件的op
例:收集一起wrap(或其他special)的op
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
namespace {
class WrapDriver {
public:
void processor(Operation *op);
private:
/// The map between candidateOp and its result indexes that returned from
/// scf.forall.
llvm::DenseMap<Operation*, llvm::DenseSet<unsigned>> opsWrapInfo;
/// Operations can be wrapped using one loop.
llvm::SmallVector<Operation *> opsToWrapTogather;
/// Record the visited ops.
llvm::DenseSet<Operation*> visited;
/// The result number of scf.forall.
unsigned replacementCount;
bool checkOpIfNeedWrap(Operation* op);
LogicalResult processOnOp(Operation* op);
void createWrapToWrap();
};
} // namespace
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Check if the op is a candidate.
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
bool WrapDriver::checkOpIfNeedWrap(Operation* op) {
// Check if the op is a candidate to be wrapped.
// 1. op needs to be a top level op.
op.getParentOp() == rootOp(func::FuncOp)
// 2. operands must has tensor semantic
op.getNumresults() != 0
llvm::all_of(op->getOperandTypes(), [&](Type operandtype){
return operandtype.isIntOrIndexOrFloat() ||
llvm::isa<RankedTensorType>(operandtype);
});
// The result value can only be scalar or ranked tensor with static shape.
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Process on the candidate op.
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
/// Use opsToWrapTogather and replacementCount to create a loop to wrap ops.
void WrapDriver::createWrapToWrap() {
// ...
}
void WrapDriver::processOnOp(Operation* op) {
if (visited.contains(op)) {
// The op has been visited.
return;
}
// Mark the op has been visited.
visited.insert(op);
for (auto operand : op->getOperands()) {
if (auto *operandOp = operand.getDefiningOp()) {
if (checkOpIfNeedWrap(operandOp)) {
if (failed(processOnOp(operandOp))) {
visited.earse(op);
return failure();
}
continue;
}
// 则需遍历candidate的输入operand,如果operand的defineOp不存在 或 存在且在scf.forall之前,
//则该op加入opsToWrapTogather是合法。反之(存在且在之后)将后续op的visited都清除。
if (!opsToWrapTogather.empty() && opsToWrapTogather.front()->isBeforeInRegion(operandOp)) {
visited.earse(op);
return failure();
}
}
}
opsWrapInfo.try_emplace(op);
opsToWrapTogather.push_back(op);
llvm::DenseSet<unsigned> replacementIndexes;
for (const auto &[idx, resVal] : llvm::enumerate(op->getResults())) {
for (auto *candidateOp : resVal.getUsers()) {
if (!checkOpIfNeedWrap(candidateOp) ||
failed(processOnOp(candidateOp))) {
replacementIndexes.insert(idx);
}
}
}
opsWrapInfo[op] = replacementIndexes;
replacementNum += replacementIndexes.size();
return success();
}
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
// Collect the candidate op from input.
//===----------------------------------------------------------------------===//
void WrapDriver::processor(func::FuncOp funcOp) {
llvm::SmallVector<Operation*> worklist;
funcOp->walk([&](Operation* workOp){
if (checkOpIfNeedWrap(workOp)) {
worklist.push_back(workOp);
}
});
for (auto *candidateOp : worklist) {
if (visited.contains(candidateOp))
continue;
opsToWrapTogather.clear();
replacementCount = 0;
if (failed(processOnOp(candidateOp)))
continue;
createWrapToWrap();
}
}
namespace {
void runOnOperation() override {
WrapDriver driver;
driver.processor(getOperation());
}
} // namespace