Triton Kernel 的写法可以参考:官方 tutorial
add
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
import torch
import triton
import triton.language as tl
@triton.jit
def add_kernel(
a_ptr, # 输入向量 A 的指针
b_ptr, # 输入向量 B 的指针
output_ptr, # 输出向量的指针
N, # 向量长度
BLOCK_SIZE: tl.constexpr):
# 线程处理的索引
idx = tl.program_id(0) * BLOCK_SIZE + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE)
mask = idx < N
# 加载 A 和 B
a = tl.load(a_ptr + idx, mask=mask, other=0.0)
b = tl.load(b_ptr + idx, mask=mask, other=0.0)
# 执行加法
result = a + b
# 写入输出
tl.store(output_ptr + idx, result, mask=mask)
# 使用示例
def vector_add(a, b):
import torch
N = a.shape[0]
assert a.shape == b.shape, "A 和 B 必须具有相同的形状。"
output = torch.empty_like(a)
BLOCK_SIZE = 128
grid = ((N + BLOCK_SIZE - 1) // BLOCK_SIZE, )
add_kernel[
grid
](
a, b, output, N, BLOCK_SIZE
)
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
import torch
# 随机生成两个向量 A 和 B
N = 128
a = torch.randn(N, dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
b = torch.randn(N, dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
# 调用 vector_add 函数
output = vector_add(a, b)
laynernorm
最简单的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
import torch
import triton
import triton.language as tl
@triton.jit
def layernorm_kernel(
input_ptr, # 输入张量指针
output_ptr, # 输出张量指针
weight_ptr, # 缩放参数指针
bias_ptr, # 偏移参数指针
M, # 行数
N: tl.constexpr, # 列数
epsilon, # 防止除以 0 的
BLOCK_SIZE: tl.constexpr):
# 计算当前线程处理的行索引
row_idx = tl.program_id(0)
# 计算该行的起始地址
row_start = row_idx * N
# 加载该行的数据到共享内存
row = tl.load(input_ptr + row_start + tl.arange(0, N))
# Step 1: 计算均值
mean = tl.sum(row, axis=0) / N
# Step 2: 计算方差
var = tl.sum(tl.pow((row - mean), 2), axis=0) / N
# Step 3: 标准化
norm_row = (row - mean) / tl.sqrt(var + epsilon)
# Step 4: 应用权重
weight = tl.load(weight_ptr + tl.arange(0, N))
bias = tl.load(bias_ptr + tl.arange(0, N))
result = norm_row * weight + bias
# Step 5: 写入输出
tl.store(output_ptr + row_start + tl.arange(0, N), result)
# 使用示例
def layernorm(input, weight, bias, epsilon=1e-5):
import torch
M, N = input.shape
output = torch.empty_like(input)
# 确保 weight 和 bias 的形状一致
assert weight.shape[0] == bias.shape[0] == N
# 分配块大小
BLOCK_SIZE = 128 # 假设列数是 BLOCK_SIZE 的倍数
grid = (M,) # 每一行一个块
# 调用 Triton 内核
layernorm_kernel[
grid
](
input,
output,
weight,
bias,
M,
N,
epsilon,
BLOCK_SIZE
)
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 随机生成输入张量
M, N = 32, 128 # 假设有 32 行,每行 128 列
input = torch.randn(M, N, dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
weight = torch.randn(N, dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
bias = torch.randn(N, dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
# 调用 layernorm 函数
output = layernorm(input, weight, bias)
matmul
简单的 matmul
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
import torch
import triton
import triton.language as tl
@triton.jit
def matmul_kernel(
a_ptr, # 矩阵 A 的指针
b_ptr, # 矩阵 B 的指针
c_ptr, # 矩阵 C 的指针
M, # A 的行数
N, # B 的列数
K, # A 的列数 / B 的行数
BLOCK_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr, # 每个块的行数
BLOCK_SIZE_N: tl.constexpr, # 每个块的列数
BLOCK_SIZE_K: tl.constexpr # 中间维度的块大小
):
# 计算当前线程块的起始索引
pid_m = tl.program_id(0)
pid_n = tl.program_id(1)
# 确定块的起始位置
block_m = pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M
block_n = pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N
# 初始化累积值
c = tl.zeros((BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N), dtype=tl.float32)
# 循环处理中间维度的块
for k in range(0, K, BLOCK_SIZE_K):
# 加载 A 和 B 的块
a = tl.load(
a_ptr + (block_m + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M))[:, None] * K + (k + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K)),
mask=(block_m + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M))[:, None] < M,
other=0.0
)
b = tl.load(
b_ptr + (k + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K))[:, None] * N + (block_n + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)),
mask=(k + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K))[:, None] < K,
other=0.0
)
# 计算局部矩阵乘法并累积
c += tl.dot(a, b)
# 将结果写回 C
tl.store(
c_ptr + (block_m + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M))[:, None] * N + (block_n + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)),
c,
mask=((block_m + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M))[:, None] < M) & ((block_n + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)) < N)
)
# 使用示例
def matmul(a, b):
import torch
M, K = a.shape
K_b, N = b.shape
assert K == K_b, "A 的列数必须等于 B 的行数。"
c = torch.empty((M, N), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
BLOCK_SIZE_M = 32
BLOCK_SIZE_N = 32
BLOCK_SIZE_K = 32
grid = ((M + BLOCK_SIZE_M - 1) // BLOCK_SIZE_M, (N + BLOCK_SIZE_N - 1) // BLOCK_SIZE_N, 1)
matmul_kernel[
grid
](
a, b, c, M, N, K, BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N, BLOCK_SIZE_K
)
return c
if __name__ == "__main__":
import torch
# 随机生成两个矩阵 A 和 B
M, K, N = 128, 128, 128
a = torch.randn((M, K), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
b = torch.randn((K, N), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
# 调用 matmul 函数
c = matmul(a, b)
tutorial_mm 源码说明
来自 03-mm
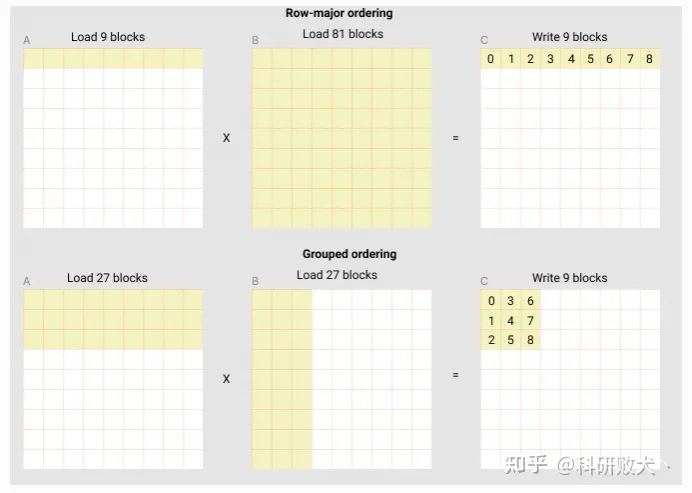
以 tutorials/03-matrix-multiplication.py 中矩阵乘优化为例。
下面的group-order的行为能获得更好的data-reuse
分析:A和B中的内容都是行优先存储,以计算九个数为例,那么原始的一次load需要9+9$\times$9=90次read和9次write。而group order中,一次load需要9$\times$3+3$\times$9=54次read和9次write
- num_pid_m 和 num_pid_n 就是为来获得矩阵长宽各可以分为多少个block(上图的黄色小块)
1
2
3
4
pid = tl.program_id(axis=0)
# number of program ids along the M / N axis
num_pid_m = tl.cdiv(M, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
num_pid_n = tl.cdiv(N, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
- num_pid_in_group 表示一个高是
GROUP_SIZE_M, 宽是num_pid_n的group中包含多少个黄色小块
1
2
# number of program in group
num_pid_in_group = GROUP_SIZE_M * num_pid_n
- group_id表示当前循环iter是在哪个group内
1
2
# id of the group which related to this program
group_id = pid // num_pid_in_group
- first_pid_m 表示当前所在的的group内的第一个黄色block是全局的第几个黄色block(从m的维度上看)
1
2
# row-id of the first program in the group
first_pid_m = group_id * GROUP_SIZE_M = (pid // (GROUP_SIZE_M * num_pid_n)) * GROUP_SIZE_M
- 重复计算下group_size_m,防止越界
1
group_size_m = min(num_pid_m - first_pid_m, GROUP_SIZE_M)
- 得到当前循环需要处理哪个块 [pid_m, pid_n]
pid_m ≤ first_pid_m + group_size_m
pid_n 是从左到右一列列来的,000111222
1
2
3
4
5
# row-id of the p in the launch grid
pid_m = first_pid_m + pid % group_size_m # 行id
# col-id of the p in the launch grid
pid_n = (pid % num_pid_in_group) // group_size_m # 列id
# num_pid_in_group = GROUP_SIZE_M * num_pid_n
a_ptr 是A矩阵第一个元素的地址
offs_am 和 offs_bn 是 A 矩阵 9 个 block 中第一个 block 中, 每个元素在整个 A 矩阵中的坐标,即 m 维度的 index 和 k 维度的 index
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# `a_ptrs` is a block of [BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_K] pointers
# `b_ptrs` is a block of [BLOCK_SIZE_K, BLOCK_SIZE_N] pointers
offs_am = (pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)) % M
offs_bn = (pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)) % N
offs_k = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K)
a_ptrs = a_ptr + (offs_am[:, None] * stride_am + offs_k[None, :] * stride_ak)
b_ptrs = b_ptr + (offs_k[:, None] * stride_bk + offs_bn[None, :] * stride_bn)
1
2
3
4
5
offs_cm = pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
offs_cn = pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
c_ptrs = c+ptr + stride_cm * offset_cm[:, None] + stride_cn * offset_cn[None, :]
c_mask = (offset_cm[:, None] < M) & (offset_cn[None, :] < N)
tl.store(c_ptrs, mask=c_mask)
计算循环,mask保证load和store不越界
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
for k in range(0, tl.cdiv(K, BLOCK_SIZE_K)):
# Load the next block of A and B, generate a mask by checking the K dimension.
a = tl.load(a_ptrs, mask=offs_k[None, :] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K, other=0.0)
b = tl.load(b_ptrs, mask=offs_k[:, None] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K, other=0.0)
# We accumulate along the K dimension.
accumulator += tl.dot(a, b)
# 计算下K个BLOCK
a_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_ak
b_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_bk
mn 主序
输入 A, B,输出C,计算:$C = A \times B$
- A shape (M, K)
- B shape (K, N)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
@triton.jit
def matmul_kernel(
# Pointers to matrices
a_ptr, b_ptr, c_ptr,
# Matrix dimensions
M, N, K,
stride_am, stride_ak,
stride_bk, stride_bn,
stride_cm, stride_cn,
# Meta-parameters
BLOCK_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr, BLOCK_SIZE_N: tl.constexpr, BLOCK_SIZE_K: tl.constexpr,
GROUP_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr,
ACTIVATION: tl.constexpr
):
pid = tl.program_id(axis=0)
num_pid_m = tl.cdiv(M, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
num_pid_n = tl.cdiv(N, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
num_pid_in_group = GROUP_SIZE_M * num_pid_n
group_id = pid // num_pid_in_group
first_pid_m = group_id * GROUP_SIZE_M
group_size_m = min(num_pid_m - first_pid_m, GROUP_SIZE_M)
pid_m = first_pid_m + ((pid % num_pid_in_group) % group_size_m)
pid_n = (pid % num_pid_in_group) // group_size_m
offs_am = (pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)) % M
offs_bn = (pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)) % N
offs_k = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K)
a_ptrs = a_ptr + (offs_am[:, None] * stride_am + offs_k[None, :] * stride_ak)
b_ptrs = b_ptr + (offs_k[:, None] * stride_bk + offs_bn[None, :] * stride_bn)
# -----------------------------------------------------------
# Iterate to compute a block of the C matrix.
# We accumulate into a `[BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N]` block
accumulator = tl.zeros((BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N), dtype=tl.float32)
for k in range(0, tl.cdiv(K, BLOCK_SIZE_K)):
a = tl.load(a_ptrs, mask=offs_k[None, :] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K, other=0.0)
b = tl.load(b_ptrs, mask=offs_k[:, None] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K, other=0.0)
# We accumulate along the K dimension.
accumulator = tl.dot(a, b, accumulator)
# Advance the ptrs to the next K block.
a_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_ak
b_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_bk
if ACTIVATION == "leaky_relu":
accumulator = leaky_relu(accumulator)
c = accumulator.to(tl.float32)
offs_cm = pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
offs_cn = pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
c_ptrs = c_ptr + stride_cm * offs_cm[:, None] + stride_cn * offs_cn[None, :]
c_mask = (offs_cm[:, None] < M) & (offs_cn[None, :] < N)
tl.store(c_ptrs, c, mask=c_mask)
def matmul(a, b, activation=""):
# Check constraints.
assert a.shape[1] == b.shape[0], "Incompatible dimensions"
assert a.is_contiguous(), "Matrix A must be contiguous"
M, K = a.shape
K, N = b.shape
# Allocates output.
c = torch.empty((M, N), device=a.device, dtype=torch.float32)
# 1D launch kernel where each block gets its own program.
grid = lambda META: (triton.cdiv(M, META['BLOCK_SIZE_M']) * triton.cdiv(N, META['BLOCK_SIZE_N']), )
matmul_kernel[grid](
a, b, c, #
M, N, K, #
a.stride(0), a.stride(1), #
b.stride(0), b.stride(1), #
c.stride(0), c.stride(1), #
ACTIVATION=activation #
)
return c
kk 主序
输入 A, B,输出C,计算:$C = A^{T} \times B^{T}$
- A shape (K, M)
- B shape (N, K)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
@triton.jit
def matmul_kernel(
# Pointers to matrices
a_ptr, b_ptr, c_ptr,
# Matrix dimensions
M, N, K,
stride_ak, stride_am,
stride_bn, stride_bk,
stride_cm, stride_cn,
# Meta-parameters
BLOCK_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr, BLOCK_SIZE_N: tl.constexpr, BLOCK_SIZE_K: tl.constexpr,
GROUP_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr,
ACTIVATION: tl.constexpr
):
pid = tl.program_id(axis=0)
num_pid_m = tl.cdiv(M, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
num_pid_n = tl.cdiv(N, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
num_pid_in_group = GROUP_SIZE_M * num_pid_n
group_id = pid // num_pid_in_group
first_pid_m = group_id * GROUP_SIZE_M
group_size_m = min(num_pid_m - first_pid_m, GROUP_SIZE_M)
pid_m = first_pid_m + ((pid % num_pid_in_group) % group_size_m)
pid_n = (pid % num_pid_in_group) // group_size_m
offs_am = (pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)) % M
offs_bn = (pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)) % N
offs_k = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K)
# 这里开始有区别
# a_ptrs = a_ptr + (offs_am[:, None] * stride_am + offs_k[None, :] * stride_ak) ->
a_ptrs = a_ptr + (offs_k[:, None] * stride_ak + offs_am[None, :] * stride_am)
# b_ptrs = b_ptr + (offs_k[:, None] * stride_bk + offs_bn[None, :] * stride_bn) ->
b_ptrs = b_ptr + (offs_bn[:, None] * stride_bn + offs_k[None, :] * stride_bk)
# -----------------------------------------------------------
accumulator = tl.zeros((BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N), dtype=tl.float32)
for k in range(0, tl.cdiv(K, BLOCK_SIZE_K)):
# mask也是不同的
a = tl.load(a_ptrs, mask=offs_k[:, None] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K, other=0.0)
b = tl.load(b_ptrs, mask=offs_k[None, :] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K, other=0.0)
# We accumulate along the K dimension.
accumulator = tl.dot(a.T, b.T, accumulator)
# Advance the ptrs to the next K block.
a_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_ak
b_ptrs += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_bk
if ACTIVATION == "leaky_relu":
accumulator = leaky_relu(accumulator)
c = accumulator.to(tl.float16)
offs_cm = pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
offs_cn = pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
c_ptrs = c_ptr + stride_cm * offs_cm[:, None] + stride_cn * offs_cn[None, :]
c_mask = (offs_cm[:, None] < M) & (offs_cn[None, :] < N)
tl.store(c_ptrs, c, mask=c_mask)
def matmul(a, b, activation=""):
# Check constraints.
assert a.is_contiguous(), "Matrix A must be contiguous"
K, M = a.shape
N, K = b.shape
c = torch.empty((M, N), device=a.device, dtype=torch.float16)
grid = lambda META: (triton.cdiv(M, META['BLOCK_SIZE_M']) * triton.cdiv(N, META['BLOCK_SIZE_N']), )
matmul_kernel[grid](
a, b, c, #
M, N, K, #
a.stride(0), a.stride(1), #
b.stride(0), b.stride(1), #
c.stride(0), c.stride(1), #
ACTIVATION=activation #
)
return c
batch matmul
以下给的是MN主序的BMM,KK主序的很容易照着改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
@triton.autotune(
configs=get_autotune_config(),
key=['M', 'N', 'K'],
)
@triton.jit
def bmm_kernel(
# Pointers to matrices
A_ptr, B_ptr, C_ptr,
# Matrix dimensions
B, M, N, K,
stride_ab, stride_am, stride_ak,
stride_bb, stride_bk, stride_bn,
stride_cb, stride_cm, stride_cn,
# Meta-parameters
BLOCK_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr, BLOCK_SIZE_N: tl.constexpr, BLOCK_SIZE_K: tl.constexpr,
GROUP_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr,
ACTIVATION: tl.constexpr,
):
pid = tl.program_id(axis=0)
offs_b = tl.program_id(axis=1)
num_pid_m = tl.cdiv(M, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
num_pid_n = tl.cdiv(N, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
num_pid_in_group = GROUP_SIZE_M * num_pid_n
group_id = pid // num_pid_in_group
first_pid_m = group_id * GROUP_SIZE_M
group_size_m = min(num_pid_m - first_pid_m, GROUP_SIZE_M)
pid_m = first_pid_m + (pid % group_size_m)
pid_n = (pid % num_pid_in_group) // group_size_m
offs_m = (pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)) % M // 防止越界
offs_n = (pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)) % N
offs_k = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K)
A_ptr = A_ptr + (offs_b * stride_ab + offs_m[:, None] * stride_am + offs_k[None, :] * stride_ak)
B_ptr = B_ptr + (offs_b * stride_bb + offs_k[:, None] * stride_bk + offs_n[None, :] * stride_bn)
# -----------------------------------------------------------
# Iterate to compute a block of the C matrix.
# We accumulate into a `[BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N]` block
acc = tl.zeros((BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N), dtype=tl.float32)
for k in range(0, tl.cdiv(K, BLOCK_SIZE_K)):
a_mask = (offs_b < B) & (offs_k[None, :] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K)
b_mask = (offs_b < B) & (offs_k[:, None] < K - k * BLOCK_SIZE_K)
a = tl.load(A_ptr, mask=a_mask, other=0.0)
b = tl.load(B_ptr, mask=b_mask, other=0.0)
acc += tl.dot(a, b, out_dtype=tl.float32)
A_ptr += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_ak
B_ptr += BLOCK_SIZE_K * stride_bk
# Write back.
if ACTIVATION == "leaky_relu":
acc = leaky_relu(acc)
c = acc.to(tl.float16)
C_ptr = C_ptr + (offs_b * stride_cb + offs_m[:, None] * stride_cm + offs_n[None, :] * stride_cn)
c_mask = (offs_b < B) & (offs_m[:, None] < M) & (offs_n[None, :] < N)
tl.store(C_ptr, c, mask=c_mask)
@triton.jit
def leaky_relu(x):
return tl.where(x >= 0, x, 0.01 * x)
def bmm(a, b, activation=""):
# Check constraints.
assert a.shape[0] == b.shape[0], "Incompatible dimensions"
assert a.shape[2] == b.shape[1], "Incompatible dimensions"
assert a.is_contiguous(), "Matrix A must be contiguous"
B, M, K = a.shape
B, K, N = b.shape
c = torch.empty((B, M, N), device=a.device, dtype=torch.float16)
# 2D launch kernel
grid = lambda META: (triton.cdiv(M, META['BLOCK_SIZE_M']) * triton.cdiv(N, META['BLOCK_SIZE_N']), B,)
bmm_kernel[grid](
a, b, c, #
B, M, N, K, #
a.stride(0), a.stride(1), a.stride(2), #
b.stride(0), b.stride(1), b.stride(2), #
c.stride(0), c.stride(1), c.stride(2), #
ACTIVATION=activation #
)
return c
attention
scaled_dot_product_attention_kernel
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
import torch
import triton
import triton.language as tl
@triton.jit
def scaled_dot_product_attention_kernel(
q_ptr, # Query 矩阵指针
k_ptr, # Key 矩阵指针
v_ptr, # Value 矩阵指针
o_ptr, # 输出矩阵指针
M, # Query 的行数
N, # Key 的列数 / Value 的列数
K, # Query 的列数 / Key 的行数
SCALE, # 缩放因子
BLOCK_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr, # 每个块的行数
BLOCK_SIZE_N: tl.constexpr, # 每个块的列数
BLOCK_SIZE_K: tl.constexpr # 中间维度的块大小
):
# 当前块的起始索引
pid_m = tl.program_id(0)
pid_n = tl.program_id(1)
# 块的起始位置
block_m = pid_m * BLOCK_SIZE_M
block_n = pid_n * BLOCK_SIZE_N
# 初始化累积值
output = tl.zeros((BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N), dtype=tl.float32)
# 循环处理中间维度的块
for k in range(0, K, BLOCK_SIZE_K):
# 加载 Query 和 Key 的块
q = tl.load(
q_ptr + (block_m + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M))[:, None] * K + (k + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K)),
mask=(block_m + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M))[:, None] < M,
other=0.0
)
k_block = tl.load(
k_ptr + (k + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K))[:, None] * N + (block_n + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)),
mask=(k + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K))[:, None] < K,
other=0.0
)
# 计算缩放点积并应用 softmax(近似处理,仅按列归一化)
logits = tl.dot(q, k_block) * SCALE
max_logits = tl.max(logits, axis=1)
logits_exp = tl.exp(logits - max_logits[:, None])
softmax = logits_exp / tl.sum(logits_exp, axis=1)[:, None]
# 加载 Value 的块并计算加权求和
v = tl.load(
v_ptr + (k + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K))[:, None] * N + (block_n + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)),
mask=(k + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_K))[:, None] < K,
other=0.0
)
output += tl.dot(softmax, v)
# 写回结果
tl.store(
o_ptr + (block_m + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M))[:, None] * N + (block_n + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)),
output,
mask=((block_m + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M))[:, None] < M) & ((block_n + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)) < N)
)
# 使用示例
def scaled_dot_product_attention(q, k, v, scale):
import torch
M, K = q.shape
K_k, N = k.shape
K_v, N_v = v.shape
assert K == K_k == K_v, "Q, K, V 的列数必须一致。"
assert N == N_v, "K 和 V 的列数必须一致。"
o = torch.empty((M, N), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
BLOCK_SIZE_M = 32
BLOCK_SIZE_N = 32
BLOCK_SIZE_K = 32
grid = ((M + BLOCK_SIZE_M - 1) // BLOCK_SIZE_M, (N + BLOCK_SIZE_N - 1) // BLOCK_SIZE_N)
scaled_dot_product_attention_kernel[
grid
](
q, k, v, o, M, N, K, scale, BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N, BLOCK_SIZE_K
)
return o
if __name__ == "__main__":
import torch
# 随机生成 Query, Key, Value 矩阵
M, K, N = 128, 64, 128
q = torch.randn((M, K), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
k = torch.randn((K, N), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
v = torch.randn((K, N), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
# 缩放因子
scale = 1.0 / (K ** 0.5)
# 调用 scaled_dot_product_attention 函数
o = scaled_dot_product_attention(q, k, v, scale)
# # 打印结果
# print("Q:\n", q)
# print("K:\n", k)
# print("V:\n", v)
# print("Output:\n", o)
DL Network
resnet
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
import torch
import triton
import triton.language as tl
@triton.jit
def resnet_block_kernel(
x_ptr, # 输入张量指针
w1_ptr, # 第一个卷积核权重指针
w2_ptr, # 第二个卷积核权重指针
out_ptr, # 输出张量指针
M, N, K: tl.constexpr, # 输入和输出的尺寸参数
BLOCK_SIZE_M: tl.constexpr, # 行分块大小
BLOCK_SIZE_N: tl.constexpr # 列分块大小
):
# 当前线程块的起始索引
row_offsets = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_M)
col_offsets = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE_N)
row_idx = tl.program_id(0) * BLOCK_SIZE_M + row_offsets
col_idx = tl.program_id(1) * BLOCK_SIZE_N + col_offsets
mask_row = row_idx < M
mask_col = col_idx < N
# 每个线程块加载一部分输入数据
x = tl.load(x_ptr + row_idx[:, None] * K + tl.arange(0, K), mask=mask_row[:, None], other=0.0)
# 第一次卷积
w1 = tl.load(w1_ptr + col_idx[None, :] * K + tl.arange(0, K)[:, None], mask=mask_col[None, :], other=0.0)
h1 = tl.dot(x, w1)
# ReLU 激活
h1_relu = tl.where(h1 > 0, h1, 0.0)
# 第二次卷积
w2 = tl.load(w2_ptr + col_idx[None, :] * K + tl.arange(0, K)[:, None], mask=mask_col[None, :], other=0.0)
h2 = tl.dot(h1_relu, w2)
# 残差连接
x_residual = tl.load(x_ptr + row_idx[:, None] * K + col_idx[None, :], mask=(mask_row[:, None] & mask_col[None, :]), other=0.0)
out = h2 + x_residual
# 写回输出
tl.store(out_ptr + row_idx[:, None] * N + col_idx[None, :], out, mask=(mask_row[:, None] & mask_col[None, :]))
# 使用示例
def resnet_block(x, w1, w2):
import torch
M, K = x.shape
K_w1, N = w1.shape
K_w2, N_w2 = w2.shape
assert K == K_w1 == K_w2, "输入与权重维度不匹配"
assert N == N_w2, "两次卷积输出维度必须一致"
output = torch.empty((M, N), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
BLOCK_SIZE_M = 32
BLOCK_SIZE_N = 64
grid = ((M + BLOCK_SIZE_M - 1) // BLOCK_SIZE_M, (N + BLOCK_SIZE_N - 1) // BLOCK_SIZE_N)
resnet_block_kernel[
grid
](
x, w1, w2, output, M, N, K, BLOCK_SIZE_M, BLOCK_SIZE_N
)
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
import torch
# 初始化输入和权重
M, K, N = 128, 64, 128 # 输入大小: MxK, 权重大小: KxN
x = torch.randn((M, K), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
w1 = torch.randn((K, N), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
w2 = torch.randn((K, N), dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
# 调用 ResNet 块函数
output = resnet_block(x, w1, w2)
# # 打印结果
# print("Input:\n", x)
# print("Weight1:\n", w1)
# print("Weight2:\n", w2)
# print("Output:\n", output)
# attn(Q, K, V) = softmax(Q, K) * V
# scalar = 1 / tl.sqrt(K)
# logical = dot(Q, K)
# max_logical = tl.max(logical, axis = 1)
# logical_exp = tl.exp(logical - max_logicals[:, None])
#softmax = logical_exp / tl.sum(logical_exp, axis=1)[:, None]
# out += tl.dot(softmax, v)